
How would you characterize a blastula?
Answer
558.6k+ views
Hint: The zygote is formed when the male gamete (sperm) and female gamete (egg) fuse during sexual reproduction. Later, the single-celled zygote begins to divide into a solid ball of cells.
Complete answer:
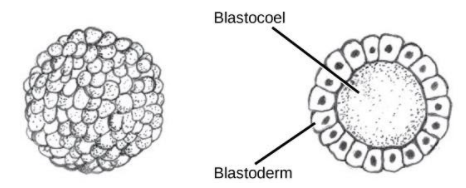
The development of organisms begins from a single-celled zygote, which undergoes rapid cell division to form the blastula. The rapid divisions of cells are termed as the cleavage. The cleavage produces more than 100 cells. The embryo is then called a blastula. The blastula is usually a spherical layer of cells surrounding the blastocoel which is a fluid-filled cavity. At this stage, the blastocyst is formed, which has an inner cell mass that is distinct from the surrounding blastula. Each cell within the blastula is known as a blastomere.
Cleavage can take place in two ways depending on the amount of yolk in the eggs. They are holoblastic (total) cleavage and meroblastic (partial) cleavage. Humans undergo holoblastic cleavage, whereas birds undergo meroblastic cleavage.
In mammals, the blastocyst is formed from the blastula during the development stage. The cells in the blastula are arranged in two layers forming the inner cell mass and an outer layer. The inner cell mass is known as the embryoblast, whereas the outer layer is called the trophoblast. Embryoblast cells finally go on to form the embryo. During the development stage, the inner cell mass consists of embryonic stem cells that will differentiate into the different cell types needed by the organism. The trophoblast will nourish the embryo and contribute to the placenta.
Note: The study of the blastula and of cell specification has many implications in stem cell research and assisted reproductive technology. By manipulating the cell signals during the blastula stage of development, various tissues can be formed which can be instrumental in regenerative medicine for disease and injury cases. In vitro fertilisation involves implantation of a blastula into a mother's uterus. Blastula cell implantation could serve to eliminate infertility.
Complete answer:
The development of organisms begins from a single-celled zygote, which undergoes rapid cell division to form the blastula. The rapid divisions of cells are termed as the cleavage. The cleavage produces more than 100 cells. The embryo is then called a blastula. The blastula is usually a spherical layer of cells surrounding the blastocoel which is a fluid-filled cavity. At this stage, the blastocyst is formed, which has an inner cell mass that is distinct from the surrounding blastula. Each cell within the blastula is known as a blastomere.
Cleavage can take place in two ways depending on the amount of yolk in the eggs. They are holoblastic (total) cleavage and meroblastic (partial) cleavage. Humans undergo holoblastic cleavage, whereas birds undergo meroblastic cleavage.
In mammals, the blastocyst is formed from the blastula during the development stage. The cells in the blastula are arranged in two layers forming the inner cell mass and an outer layer. The inner cell mass is known as the embryoblast, whereas the outer layer is called the trophoblast. Embryoblast cells finally go on to form the embryo. During the development stage, the inner cell mass consists of embryonic stem cells that will differentiate into the different cell types needed by the organism. The trophoblast will nourish the embryo and contribute to the placenta.

Note: The study of the blastula and of cell specification has many implications in stem cell research and assisted reproductive technology. By manipulating the cell signals during the blastula stage of development, various tissues can be formed which can be instrumental in regenerative medicine for disease and injury cases. In vitro fertilisation involves implantation of a blastula into a mother's uterus. Blastula cell implantation could serve to eliminate infertility.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




