
Hybridization of central atom in $N{F_3}$ is:
$A.$ $s{p^3}$
$B.$ $sp$
$C.$ $s{p^2}$
$D.$ $ds{p^2}$
Answer
548.7k+ views
Hint: Before solving the question we need to have some idea about hybridization. Hybridization is defined as the intermixing of two atomic orbits having the similar energy to produce a new different orbital, a new orbital which is produced known as hybrid orbitals. This process is called hybridization.
Complete step by step answer:
In Nitrogen trifluoride $\left( {N{F_3}} \right)$ the central metal atom is nitrogen atom which is attached to three fluorine atoms. Nitrogen has five valence electrons in its valence shell; to complete its octet it requires three more electrons. So it forms three sigma bonds with fluorine atoms.
The hybridization of nitrogen atoms in $N{F_3}$ molecules can be determined by valence shell electron pair repulsion theory $\left( {VSEPR} \right)$ . The Lewis structure of $N{F_3}$ molecules shows that the nitrogen atom uses only its three electrons to complete the octet. It has five valence electrons in which three are used in the formation of \[3\sigma \] with fluorine atom and remaining two electrons on nitrogen atom, they remain of nitrogen atom as non- bonding electron is now an lone pair.
Hence, in the $N{F_3}$ molecule there are three bond pairs and one lone pair. Sum of bond pairs and lone pairs is four. Nitrogen atoms are $N{F_3}$ molecules and are supposed to be \[s{p^3}\] hybridization.
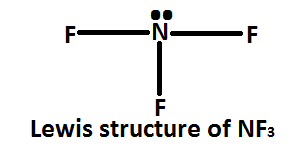
As we discussed above, the hybridisation of nitrogen atoms in $N{F_3}$ molecules. So, the correct option is $\left( A \right)$ .
Note:
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory $\left( {VSEPR} \right)$ .This is a very useful theory to predict the geometry or shape of a number of polyatomic molecules or ions on a non-transition element. This theory says that shapes of a species and hybridization of a molecule depend on the number of and nature of electron pairs surrounding the central atom of a species.
Complete step by step answer:
In Nitrogen trifluoride $\left( {N{F_3}} \right)$ the central metal atom is nitrogen atom which is attached to three fluorine atoms. Nitrogen has five valence electrons in its valence shell; to complete its octet it requires three more electrons. So it forms three sigma bonds with fluorine atoms.
The hybridization of nitrogen atoms in $N{F_3}$ molecules can be determined by valence shell electron pair repulsion theory $\left( {VSEPR} \right)$ . The Lewis structure of $N{F_3}$ molecules shows that the nitrogen atom uses only its three electrons to complete the octet. It has five valence electrons in which three are used in the formation of \[3\sigma \] with fluorine atom and remaining two electrons on nitrogen atom, they remain of nitrogen atom as non- bonding electron is now an lone pair.
Hence, in the $N{F_3}$ molecule there are three bond pairs and one lone pair. Sum of bond pairs and lone pairs is four. Nitrogen atoms are $N{F_3}$ molecules and are supposed to be \[s{p^3}\] hybridization.

As we discussed above, the hybridisation of nitrogen atoms in $N{F_3}$ molecules. So, the correct option is $\left( A \right)$ .
Note:
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory $\left( {VSEPR} \right)$ .This is a very useful theory to predict the geometry or shape of a number of polyatomic molecules or ions on a non-transition element. This theory says that shapes of a species and hybridization of a molecule depend on the number of and nature of electron pairs surrounding the central atom of a species.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




