
What is the hybridization of copper in tetraamine copper$\left( {II} \right)$ in water? Why it is not $s{p^3}$, and how do you prove this using group theory?
Answer
493.8k+ views
Hint: Group theory is basically used in describing molecular orbitals in a compound. Molecular orbitals have a tendency to combine with each other to form the entire compound. Group theory is helpful in determining the nature of orbitals used in molecular orbitals.
Complete answer:
According to the basic rules of valence bond theory, the central metal atom in its ion form provides empty orbitals for making coordination bonds with appropriate ligands.
In the case of tetraamine copper$\left( {II} \right)$, copper acts as a central atom which provides an empty orbital for making coordination bonds with amine ligands.
As we know, the atomic number of Copper is $29$ and electronic configuration is $\left[ {Ar} \right]3{d^{10}}4{s^1}$. Oxidation number of Copper in ${\left[ {Cu{{\left( {N{H_3}} \right)}_4}} \right]^{ + 2}}$ is $\left( { + 2} \right)$. Now the electronic configuration of Copper atoms will become $\left[ {Ar} \right]3{d^9}4{s^0}$.
Now copper atom can increase its valency by two ways: -
Either by promoting electrons from $3{d^9}$ to higher energy state but it may lead to formation of $C{u^{ + 3}}$ ions which is practically unstable in nature.
Another way to create an empty orbital is by involving its vacant $4d$ orbitals for formation of coordination bonds with amines.
DIAGRAM SHOWS THE FORMATION OF COORDINATION BOND
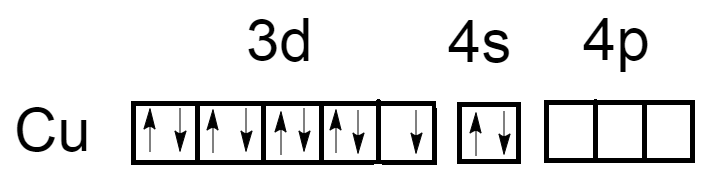
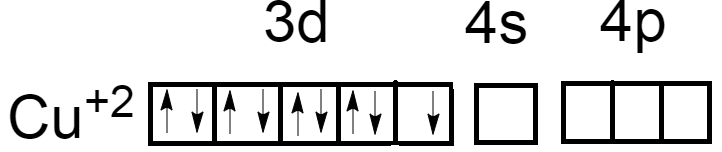
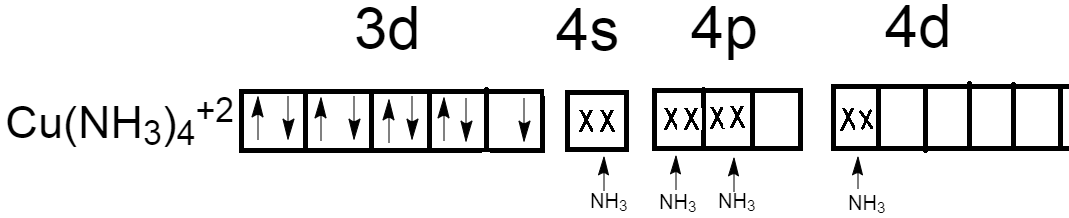
Therefore, copper atoms form coordination with four amines by involving one orbital of $4s$, two orbitals of $4p$ and remaining one orbital from vacant $4d$ orbital.
Therefore, hybridization of ${\left[ {Cu{{\left( {N{H_3}} \right)}_4}} \right]^{ + 2}}$ will become $s{p^2}d$ and have geometry square planar.
Note:
There are a number of drawbacks which are associated with valence bond theory like it relies on a number of assumptions, it fails to explain the magnetic behaviour of a compound, it fails to differentiate weak ligand from strong ligand.
Complete answer:
According to the basic rules of valence bond theory, the central metal atom in its ion form provides empty orbitals for making coordination bonds with appropriate ligands.
In the case of tetraamine copper$\left( {II} \right)$, copper acts as a central atom which provides an empty orbital for making coordination bonds with amine ligands.
As we know, the atomic number of Copper is $29$ and electronic configuration is $\left[ {Ar} \right]3{d^{10}}4{s^1}$. Oxidation number of Copper in ${\left[ {Cu{{\left( {N{H_3}} \right)}_4}} \right]^{ + 2}}$ is $\left( { + 2} \right)$. Now the electronic configuration of Copper atoms will become $\left[ {Ar} \right]3{d^9}4{s^0}$.
Now copper atom can increase its valency by two ways: -
Either by promoting electrons from $3{d^9}$ to higher energy state but it may lead to formation of $C{u^{ + 3}}$ ions which is practically unstable in nature.
Another way to create an empty orbital is by involving its vacant $4d$ orbitals for formation of coordination bonds with amines.
DIAGRAM SHOWS THE FORMATION OF COORDINATION BOND



Therefore, copper atoms form coordination with four amines by involving one orbital of $4s$, two orbitals of $4p$ and remaining one orbital from vacant $4d$ orbital.
Therefore, hybridization of ${\left[ {Cu{{\left( {N{H_3}} \right)}_4}} \right]^{ + 2}}$ will become $s{p^2}d$ and have geometry square planar.
Note:
There are a number of drawbacks which are associated with valence bond theory like it relies on a number of assumptions, it fails to explain the magnetic behaviour of a compound, it fails to differentiate weak ligand from strong ligand.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




