
Hydrazobenzene on treatment with ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ forms:
A) Azobenzene
B) Azobenzene sulfonic acid
C) Benzidine
D) None of the above
Answer
563.1k+ views
Hint: To solve this we must know that hydrazobenzene is also known as diphenylhydrazine. The structure is two benzene rings to which $ - {\text{NH}}$ groups are attached. These two rings are then connected through the nitrogen-nitrogen $\left( {{\text{N}} - {\text{N}}} \right)$ bond. ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ which is known as sulphuric acid creates an acidic medium. A rearrangement reaction occurs.
Complete solution:
We know that hydrazobenzene as the name suggests hydrazo group is $ - {\text{NH}}$ group and benzene indicates that this hydrazo group is attached to the benzene ring.
Hydrazobenzene is two benzene rings to which $ - {\text{NH}}$ groups are attached. These two rings are then connected through the nitrogen-nitrogen $\left( {{\text{N}} - {\text{N}}} \right)$ bond.
The structure for hydrazobenzene is as follows:
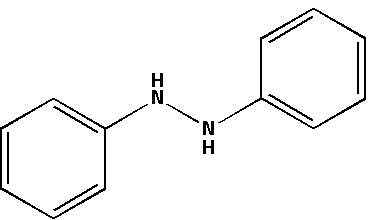
${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ which is known as sulphuric acid creates an acidic medium. Hydrazobenzene in an acidic medium accepts protons from the sulphuric acid. In an acidic medium, hydrazobenzene undergoes a rearrangement reaction.
The mechanism of the reaction when hydrazobenzene reacts with sulphuric acid i.e. ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ is as follows:
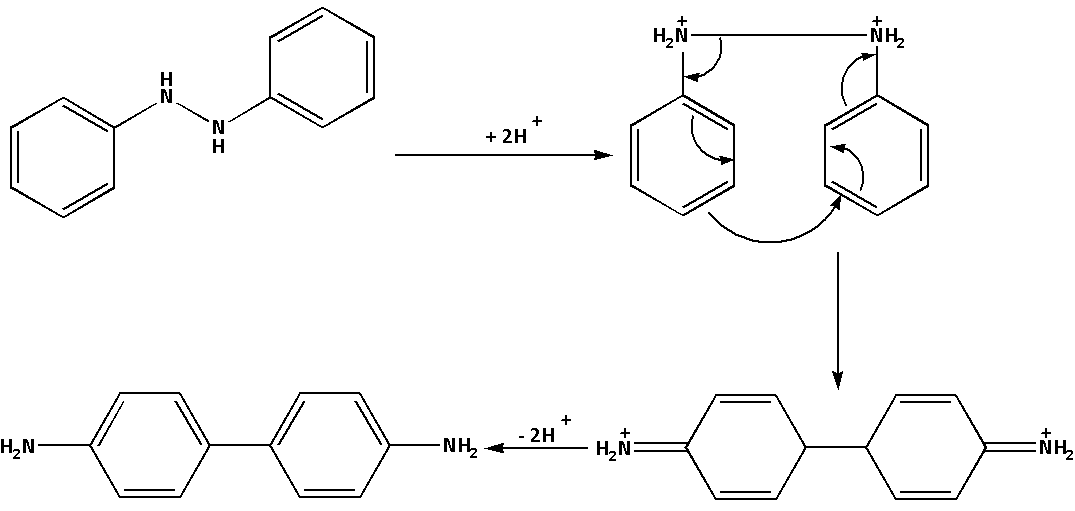
In the reaction, where hydrazobenzene reacts with sulphuric acid i.e. ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ a rearrangement reaction leads to the formation of benzidine. Thus, benzidine is a product of rearrangement of hydrazobenzene in an acidic medium.
Benzidine is not a naturally occurring substance and is synthesized mainly from hydrazobenzene on reacting it with sulphuric acid i.e. ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$.
Thus, hydrazobenzene on treatment with ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ forms benzidine.
Thus, the correct option is (C) benzidine.
Note: Benzidine is greyish-red, yellowish or white coloured powder. Benzidine can also be synthesized from nitrobenzene. Nitrobenzene is first converted to diphenylhydrazine or hydrazobenzene using iron powder as a reducing agent which then undergoes the same rearrangement reaction in acidic medium as shown above.
Complete solution:
We know that hydrazobenzene as the name suggests hydrazo group is $ - {\text{NH}}$ group and benzene indicates that this hydrazo group is attached to the benzene ring.
Hydrazobenzene is two benzene rings to which $ - {\text{NH}}$ groups are attached. These two rings are then connected through the nitrogen-nitrogen $\left( {{\text{N}} - {\text{N}}} \right)$ bond.
The structure for hydrazobenzene is as follows:

${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ which is known as sulphuric acid creates an acidic medium. Hydrazobenzene in an acidic medium accepts protons from the sulphuric acid. In an acidic medium, hydrazobenzene undergoes a rearrangement reaction.
The mechanism of the reaction when hydrazobenzene reacts with sulphuric acid i.e. ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ is as follows:

In the reaction, where hydrazobenzene reacts with sulphuric acid i.e. ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ a rearrangement reaction leads to the formation of benzidine. Thus, benzidine is a product of rearrangement of hydrazobenzene in an acidic medium.
Benzidine is not a naturally occurring substance and is synthesized mainly from hydrazobenzene on reacting it with sulphuric acid i.e. ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$.
Thus, hydrazobenzene on treatment with ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ forms benzidine.
Thus, the correct option is (C) benzidine.
Note: Benzidine is greyish-red, yellowish or white coloured powder. Benzidine can also be synthesized from nitrobenzene. Nitrobenzene is first converted to diphenylhydrazine or hydrazobenzene using iron powder as a reducing agent which then undergoes the same rearrangement reaction in acidic medium as shown above.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




