
Hydrogen bonding is maximum in:
(A) Diethyl ether
(B) Triethylamine
(C) Ethanol
(D) None of these
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: Hydrogen bond is a kind of dipole-dipole interaction in which hydrogen is attached to an electronegative atom. Hydrogen bonds can vary in different systems and also depend upon the electronegative atom to which hydrogen atom is attached. Higher the electronegativity of the atom the hydrogen is attached to, higher is the hydrogen bonding.
Complete step by step solution:
Now let’s learn the hydrogen bonding in more detail. The hydrogen bonding refers to the formation of hydrogen bonds which are a special class of attractive intermolecular forces that arises due to the dipole-dipole interaction between a hydrogen atom that is bonded to a highly electronegative atom and another highly electronegative atom while lies in the vicinity of the hydrogen atom.
The greater electronegativity difference between the hydrogen and the hydrogen bond acceptor, stronger will be the hydrogen bond.
Normal hydrogen bond strength ranges from 4 to 60 kilojoules per mole although certain highly acidic compounds such as hydrogen fluoride have hydrogen bond energies up to 120 kilojoules per mol.
Let’s check hydrogen bonding in each option for determining in which maximum hydrogen bonding is present.
In diethyl ether, Hydrogen bonding does not occur. Although it contains an oxygen atom that is a hydrogen bond acceptor while the oxygen atom is not bonded to any hydrogen atom. The structure of the diethyl ether is given below.
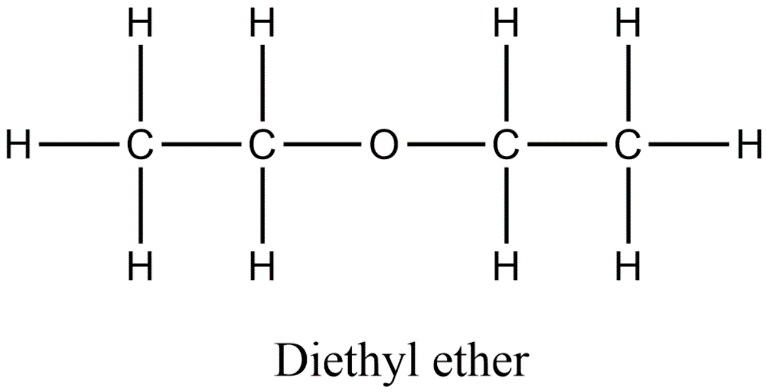
Thus, option a) is incorrect.
Now in option b) triethylamine does not have hydrogen bonding because there is no hydrogen which is attached to electronegative nitrogen. There are three ethyl groups which are attached to the Nitrogen. The structure is given below.
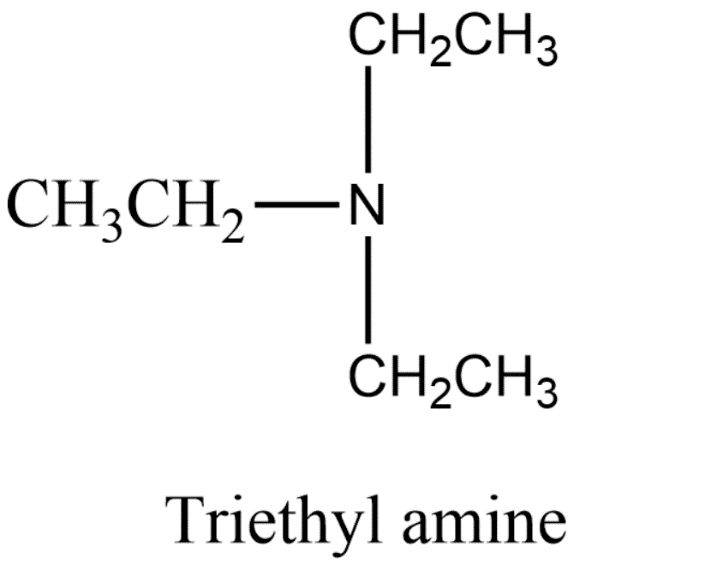
So, option b) is incorrect.
Lastly, in option C ethanol, it has strong hydrogen bonding due to the presence of a strongly polar bond in the –OH group. Ethanol contains a hydrogen atom and it is bonded to a highly electronegative oxygen atom. The structure is given below.
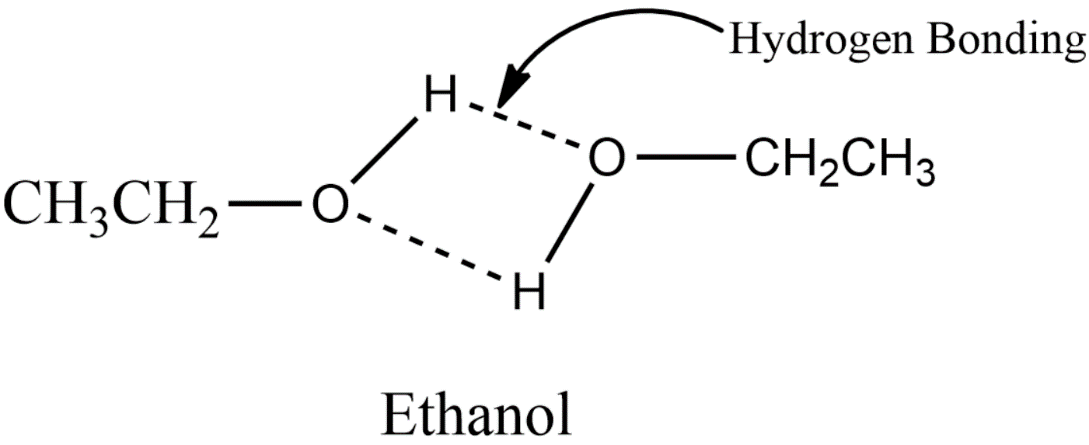
Therefore among all options only ethanol has hydrogen bonding and thus option c) is the correct one.
Note: Always remember that there are two types of hydrogen bondings present. One is the intermolecular hydrogen bonding, the other is the intramolecular hydrogen bonding. Intermolecular hydrogen bonding is seen in most of the compounds where the hydrogen bond is formed between two different molecules of the same compound. For example, the intermolecular hydrogen bonding in para nitrophenol is shown below.
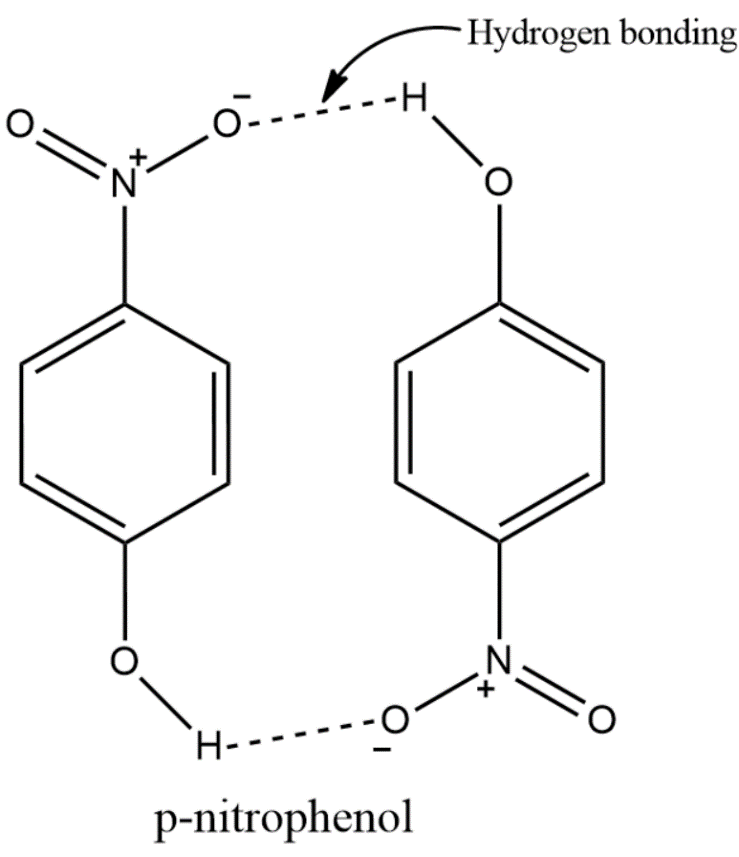
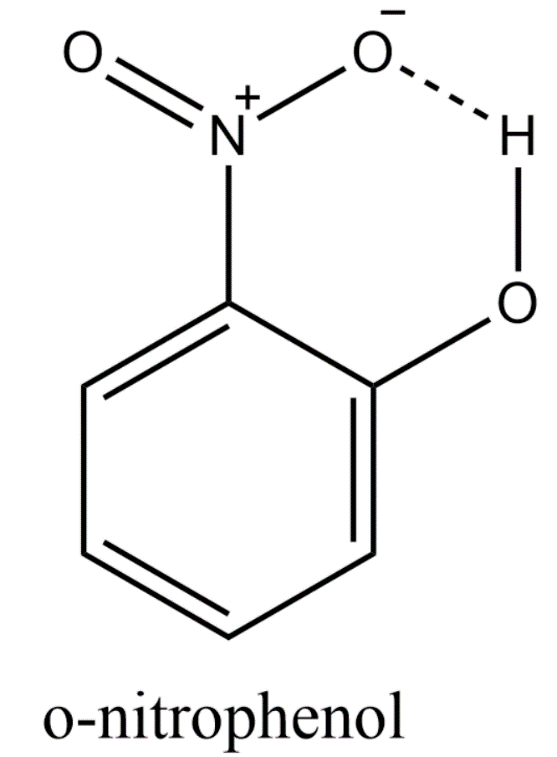
Intramolecular hydrogen bonding is seen in some of the compounds where the hydrogen bond is formed inside the same molecule of the same compound. For example, the intramolecular hydrogen bonding in ortho nitrophenol is shown below.
Complete step by step solution:
Now let’s learn the hydrogen bonding in more detail. The hydrogen bonding refers to the formation of hydrogen bonds which are a special class of attractive intermolecular forces that arises due to the dipole-dipole interaction between a hydrogen atom that is bonded to a highly electronegative atom and another highly electronegative atom while lies in the vicinity of the hydrogen atom.
The greater electronegativity difference between the hydrogen and the hydrogen bond acceptor, stronger will be the hydrogen bond.
Normal hydrogen bond strength ranges from 4 to 60 kilojoules per mole although certain highly acidic compounds such as hydrogen fluoride have hydrogen bond energies up to 120 kilojoules per mol.
Let’s check hydrogen bonding in each option for determining in which maximum hydrogen bonding is present.
In diethyl ether, Hydrogen bonding does not occur. Although it contains an oxygen atom that is a hydrogen bond acceptor while the oxygen atom is not bonded to any hydrogen atom. The structure of the diethyl ether is given below.

Thus, option a) is incorrect.
Now in option b) triethylamine does not have hydrogen bonding because there is no hydrogen which is attached to electronegative nitrogen. There are three ethyl groups which are attached to the Nitrogen. The structure is given below.

So, option b) is incorrect.
Lastly, in option C ethanol, it has strong hydrogen bonding due to the presence of a strongly polar bond in the –OH group. Ethanol contains a hydrogen atom and it is bonded to a highly electronegative oxygen atom. The structure is given below.

Therefore among all options only ethanol has hydrogen bonding and thus option c) is the correct one.
Note: Always remember that there are two types of hydrogen bondings present. One is the intermolecular hydrogen bonding, the other is the intramolecular hydrogen bonding. Intermolecular hydrogen bonding is seen in most of the compounds where the hydrogen bond is formed between two different molecules of the same compound. For example, the intermolecular hydrogen bonding in para nitrophenol is shown below.

Intramolecular hydrogen bonding is seen in some of the compounds where the hydrogen bond is formed inside the same molecule of the same compound. For example, the intramolecular hydrogen bonding in ortho nitrophenol is shown below.

Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




