
Hydrogenation of alkyne may give:
A. alkane
B. alkene
C. both alkane and alkene
D. polymer
Answer
578.4k+ views
Hint: An alkyne is an organic compound that contains at least one triple bond. When a triple bond is hydrogenated, the bonds disappear as hydrogen occupies the electrons that are used in bonding. It also depends on the extent of hydrogenation.
Complete step by step solution:
In order to answer the question, let us first get to know what alkane, alkene and alkyne are. Alkane is an organic compound that consists only of single bonds throughout. Alkenes have at least one double bond and alkynes at least one triple bond( all the bonds are carbon-carbon). When an organic compound is hydrogenated, that means addition of hydrogen is taking place across the bonds, be it triple bond or double bond. So, as hydrogen gets added, the bonds reduce. So, a triple bond can be reduced to a single bond, as well as double bond, by the application of hydrogen.
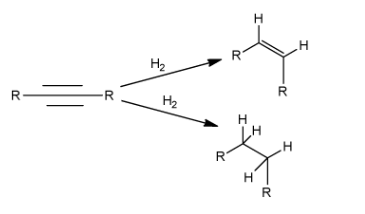
The hydrogenation depends on the choice of catalyst. If the major product of the alkyne is desired to be an alkene, then Lindlar’s catalyst is used. Lindlar’s catalyst consists of palladium which helps to reduce double bonds. For example, aromatic alkyne can be converted into an alkene, by using palladium and molecular hydrogen. But if we want to convert an alkyne directly to an alkane, then palladium, along with activated carbon catalyst, needs to be used. Following are the reactions:

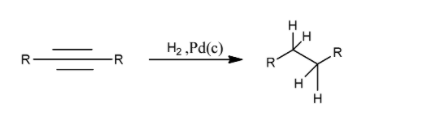
Hence, we can say that hydrogenation of an alkyne can give both alkanes, as well as alkynes as the desired product, based on the conditions.
So, we obtain the answer as option C.
Note: Lindars catalyst contains palladium, along with some impurities like sulphur too. So, these impurities stop the further hydrogenation of alkene to alkane. So, activated carbon catalyst is used to overcome it. Moreover, Lindlar’s catalyst always gives cis addition products, i.e hydrogens which get added are always on the same side.
Complete step by step solution:
In order to answer the question, let us first get to know what alkane, alkene and alkyne are. Alkane is an organic compound that consists only of single bonds throughout. Alkenes have at least one double bond and alkynes at least one triple bond( all the bonds are carbon-carbon). When an organic compound is hydrogenated, that means addition of hydrogen is taking place across the bonds, be it triple bond or double bond. So, as hydrogen gets added, the bonds reduce. So, a triple bond can be reduced to a single bond, as well as double bond, by the application of hydrogen.

The hydrogenation depends on the choice of catalyst. If the major product of the alkyne is desired to be an alkene, then Lindlar’s catalyst is used. Lindlar’s catalyst consists of palladium which helps to reduce double bonds. For example, aromatic alkyne can be converted into an alkene, by using palladium and molecular hydrogen. But if we want to convert an alkyne directly to an alkane, then palladium, along with activated carbon catalyst, needs to be used. Following are the reactions:


Hence, we can say that hydrogenation of an alkyne can give both alkanes, as well as alkynes as the desired product, based on the conditions.
So, we obtain the answer as option C.
Note: Lindars catalyst contains palladium, along with some impurities like sulphur too. So, these impurities stop the further hydrogenation of alkene to alkane. So, activated carbon catalyst is used to overcome it. Moreover, Lindlar’s catalyst always gives cis addition products, i.e hydrogens which get added are always on the same side.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




