
What is hysteresis? Define the terms 'coercivity' and 'retentivity' of a ferromagnetic material.
Answer
596.7k+ views
Hint: – In order to get this problem correct you need to draw the figure and show retentivity and coercivity. Hysteresis is the phenomena that happens when the magnetic induction lags behind the magnetizing field.
Step By Step Answer:
Magnetic field is a vector field that defines the magnetic effect of other moving loads or magnetized materials on the electrical charge. A charge that travels through a magnetic field encounters a force perpendicular to its own velocity and to the magnetic field.
The magnetic hysteresis, better known as the hysteresis loop, describes the magnetizing force (H) versus the magnetic flux density ( B) of the ferromagnetic material. The curvature of the hysteresis is characteristic of the form of material being observed and may differ in size and shape (i.e. narrow or wide). The loop can be produced using a Hall Effect sensor to calculate the amount of magnetic field at various points-when in the presence of a magnetic field, when it is separated from the magnetic field, and when a force is applied to bring the magnetic flux down to zero.These loops are essential for the storage capacity of audio recording devices or for the magnetic storage of data on computer disks.
Hysteresis -
The condition in which the magnetic induction 'B' lags behind the magnetizing field H is called hysteresis.
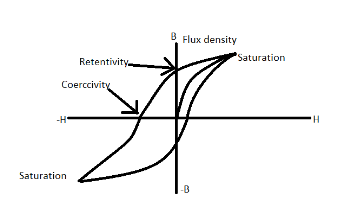
This happens when an external magnetic field is applied to a ferromagnet such as iron and the atomic dipoles are aligned with it. And when the field is removed, part of the alignment will be retained: the material has been magnetized. When magnetized, the magnet will remain magnetized indefinitely.
(i)Retentivity -
The tendency of the magnetic material to maintain magnetism, even in the absence of a magnetizing field, is known as retentivity or remanence.
(ii)Coercivity -
The magnetizing field 'H' required to demagnetize the magnetic material is known as its coerciveness.
Note – Hysteresis, coercivity and retentivity all three are dependent on the type of material we are using and the conductivity of the magnetic field in that particular material. One of the best ways to remember coercivity and retentivity is to remember the diagram above drawn. It will help you to remember this concept for a longer time.
Step By Step Answer:
Magnetic field is a vector field that defines the magnetic effect of other moving loads or magnetized materials on the electrical charge. A charge that travels through a magnetic field encounters a force perpendicular to its own velocity and to the magnetic field.
The magnetic hysteresis, better known as the hysteresis loop, describes the magnetizing force (H) versus the magnetic flux density ( B) of the ferromagnetic material. The curvature of the hysteresis is characteristic of the form of material being observed and may differ in size and shape (i.e. narrow or wide). The loop can be produced using a Hall Effect sensor to calculate the amount of magnetic field at various points-when in the presence of a magnetic field, when it is separated from the magnetic field, and when a force is applied to bring the magnetic flux down to zero.These loops are essential for the storage capacity of audio recording devices or for the magnetic storage of data on computer disks.
Hysteresis -
The condition in which the magnetic induction 'B' lags behind the magnetizing field H is called hysteresis.

This happens when an external magnetic field is applied to a ferromagnet such as iron and the atomic dipoles are aligned with it. And when the field is removed, part of the alignment will be retained: the material has been magnetized. When magnetized, the magnet will remain magnetized indefinitely.
(i)Retentivity -
The tendency of the magnetic material to maintain magnetism, even in the absence of a magnetizing field, is known as retentivity or remanence.
(ii)Coercivity -
The magnetizing field 'H' required to demagnetize the magnetic material is known as its coerciveness.
Note – Hysteresis, coercivity and retentivity all three are dependent on the type of material we are using and the conductivity of the magnetic field in that particular material. One of the best ways to remember coercivity and retentivity is to remember the diagram above drawn. It will help you to remember this concept for a longer time.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




