
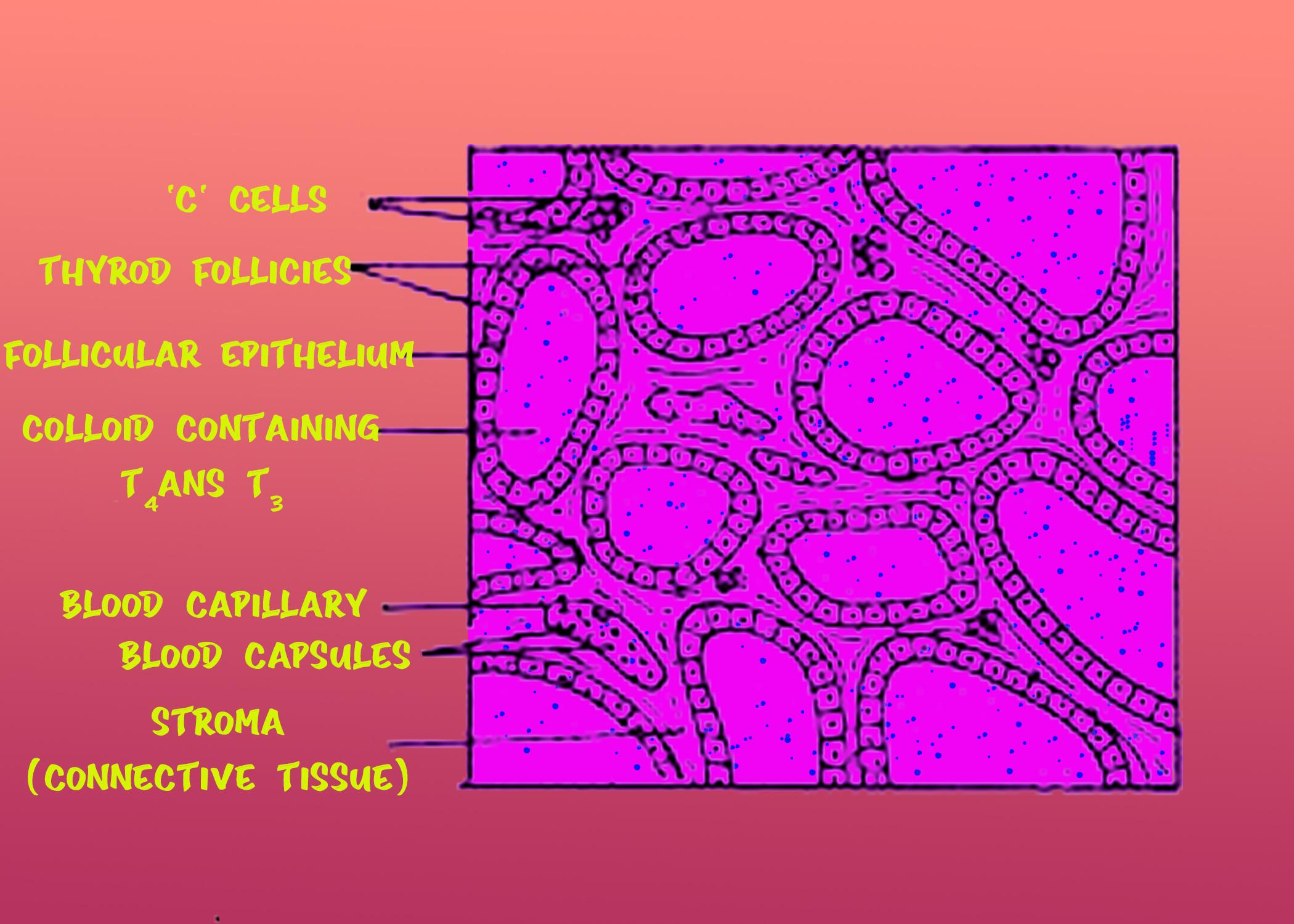
I) sketch and label the T.S of the thyroid gland.
II) With the help of a neat and labeled diagram describes the anatomy of the human eye (explain the mechanism of vision).
Answer
570k+ views
Hint: The human eye is a sensory organ that responds to light and enables vision. In the retina, rod and cone cells allow the conscious perception of light and vision, including color differentiation and depth perception.
Complete answer:
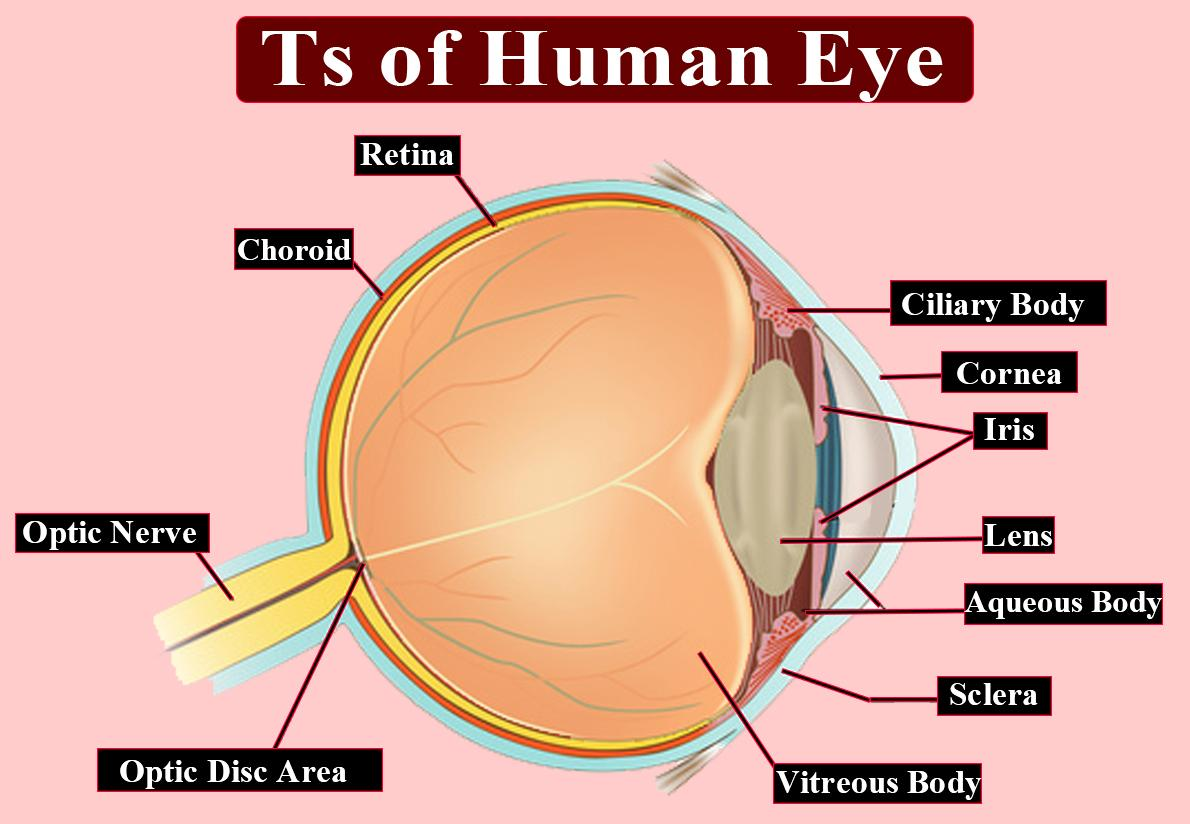
Eyes are the paired sense organs that are called orbits, found in the sockets of the skull. The second cranial nerve, called the optic nerve, supplies the eyes.
The eyeball wall is composed of the following three layers:
-External layer: It consists of a thick connective tissue called the sclera, which preserves and also protects the form of the eye. This layer's anterior section is called the cornea. The cornea absorbs oxygen from the air and helps to concentrate on light waves as they reach the eye.
-Middle layer: Choroid, which includes several blood vessels, is the middle layer and appears bluish in color. Over the posterior two-thirds of the eyeball, the choroid layer is thin and the anterior part becomes thick to form the ciliary body. The ciliary body goes forward and forms a structure called the iris that is pigmented and opaque.
-The ligaments attached to the ciliary body have a translucent crystalline lens held in place by the eyeball. The opening surrounded by the iris is called the pupil in front of the lens.
-Inside layer: The retina is embedded in this layer. Three layers of cells are in the retina — ganglion cells, bipolar cells, and photoreceptor cells. There are two kinds of photoreceptor cells, rods, and cones containing light-sensitive proteins called photopigments.
-The optic nerve leaves the eye and at a medial point to and just above the posterior eyeball pole, called the blind spot, retinal blood vessels join it because photoreceptor cells are absent here.
-At the posterior pole of the eye and laterally to the blind spot, a yellow-pigmented spot called macula lutea with a central pit called fovea is present. The visual resolution of the fovea is maximal.
-The space that contains a thin watery fluid between the cornea and the lens is called the aqueous chamber. The space between the lens and the retina is called a vitreous chamber filled with vitreous humor called transparent gel.
Vision Mechanism:
-Via the cornea, the eye obtains light rays and the lens produces impulses in the rods and cones. In the human eye, photosensitive compounds consist of opsin (a protein) and retinal (vitamin A aldehyde).
-Dissociation of the retina from opsin is caused by the light obtained and this results in a change in the opsin structure. Because of this, membrane permeability changes result in potential differences in the photoreceptor cells and this creates a signal through the bipolar cells that generate an action potential in the ganglion cells. The optic nerves transmit these impulses to the brain's visual cortex region, where neural impulses are analyzed and the image created on the retina is recognized.
Note: It's about 1 inch between your eyes and weighs about 0.25 ounces.
Approximately 10 million different colors will differentiate the human eye.
Throughout life, our eyes remain the same size, while the nose and ears never stop increasing.
The human eye blinks 4,200,000 times a year, on average.
Complete answer:


Eyes are the paired sense organs that are called orbits, found in the sockets of the skull. The second cranial nerve, called the optic nerve, supplies the eyes.
The eyeball wall is composed of the following three layers:
-External layer: It consists of a thick connective tissue called the sclera, which preserves and also protects the form of the eye. This layer's anterior section is called the cornea. The cornea absorbs oxygen from the air and helps to concentrate on light waves as they reach the eye.
-Middle layer: Choroid, which includes several blood vessels, is the middle layer and appears bluish in color. Over the posterior two-thirds of the eyeball, the choroid layer is thin and the anterior part becomes thick to form the ciliary body. The ciliary body goes forward and forms a structure called the iris that is pigmented and opaque.
-The ligaments attached to the ciliary body have a translucent crystalline lens held in place by the eyeball. The opening surrounded by the iris is called the pupil in front of the lens.
-Inside layer: The retina is embedded in this layer. Three layers of cells are in the retina — ganglion cells, bipolar cells, and photoreceptor cells. There are two kinds of photoreceptor cells, rods, and cones containing light-sensitive proteins called photopigments.
-The optic nerve leaves the eye and at a medial point to and just above the posterior eyeball pole, called the blind spot, retinal blood vessels join it because photoreceptor cells are absent here.
-At the posterior pole of the eye and laterally to the blind spot, a yellow-pigmented spot called macula lutea with a central pit called fovea is present. The visual resolution of the fovea is maximal.
-The space that contains a thin watery fluid between the cornea and the lens is called the aqueous chamber. The space between the lens and the retina is called a vitreous chamber filled with vitreous humor called transparent gel.
Vision Mechanism:
-Via the cornea, the eye obtains light rays and the lens produces impulses in the rods and cones. In the human eye, photosensitive compounds consist of opsin (a protein) and retinal (vitamin A aldehyde).
-Dissociation of the retina from opsin is caused by the light obtained and this results in a change in the opsin structure. Because of this, membrane permeability changes result in potential differences in the photoreceptor cells and this creates a signal through the bipolar cells that generate an action potential in the ganglion cells. The optic nerves transmit these impulses to the brain's visual cortex region, where neural impulses are analyzed and the image created on the retina is recognized.
Note: It's about 1 inch between your eyes and weighs about 0.25 ounces.
Approximately 10 million different colors will differentiate the human eye.
Throughout life, our eyes remain the same size, while the nose and ears never stop increasing.
The human eye blinks 4,200,000 times a year, on average.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




