
(i) Write the structural difference between starch and cellulose.
(ii) What type of linkage is present in nucleic acids?
(iii) Give one example each for fibrous protein and globular protein?
Answer
576.6k+ views
Hint: Both starch and cellulose are made up of glucose units. Cellulose is linear whereas starch is branched. Components of nucleic acids are sugar, bases, and phosphate groups. The phosphate group joins the two nucleotides. Fibrous and globular are types of proteins based on the structures of polypeptides chains in protein. Fibrous is a simple protein whereas globular is a complex protein.
Complete step by step solution:
(i) The structural difference between starch and cellulose are as follows:
Starch is found in both linear and branched chain form. Amylose is linear chains of $\alpha $-D-glucose molecules linked together by $\alpha - 1,4$glycosidic bonds and amylopectin is branched chain $\alpha $-D-glucose molecules linked together by $\alpha - 1,6$ glycosidic bond.
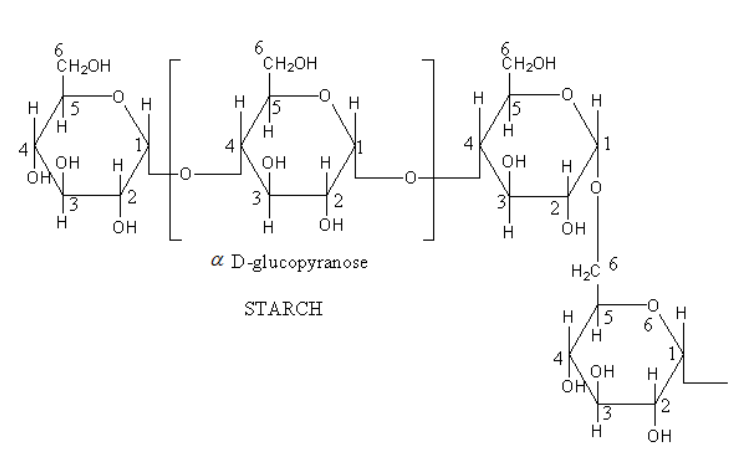
Cellulose is linear chains of $\beta $-D-glucose molecules linked together by $\beta - 1,4$ glycosidic bonds. Cellulose has $\beta - 1,4$ linkage between glucose units.
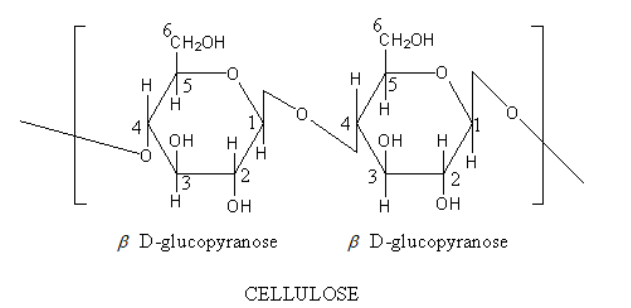
Therefore, starch is a branched molecule whereas the cellulose is a linear molecule. The starch has $\alpha - 1,4$ and $\alpha - 1,6$ glycosidic bonds whereas the cellulose has only $\beta - 1,4$ glycosidic bonds.
(ii) Phosphodiester linkage is commonly found in nucleic acid (DNA and RNA) and plays a critical role in their structure and function. Phosphodiester linkage is formed when a phosphoric acid molecule $\left( {{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{P}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}} \right)$ attached with sugar reacts with hydroxyl group$\left( {{\text{ - OH}}} \right)$ present at carbon$ - 3$ of another sugar thus forms an ester bond and removes water molecule.
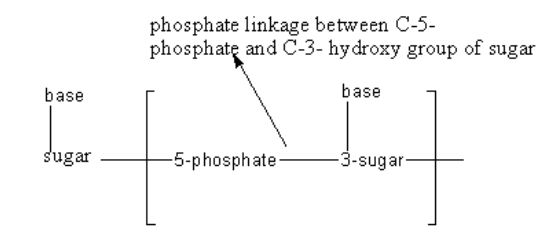
Therefore, phosphodiester linkage is present in nucleic acids.
(iii) Fibrous proteins have only primary structure means simple long polypeptide chains whereas globular proteins have complex structures means polypeptides chains are further coiled and form globule-like structures. Some examples of fibrous proteins are keratins (present in hairs), collagens, myosin and elastin. Globular proteins are albumin and haemoglobin.
Note: The major type of biomolecules are carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids and proteins. Starch and cellulose both are polysaccharides made up of glucose. Polysaccharides are carbohydrates having a large number of monosaccharides joined by glycosidic bonds. The name of the linkage gives an idea about the bonding such as phosphate linkage means the bond will involve a phosphate group. Glycosidic linkage means the bonding will involve the carbohydrates. In fibrous protein, the long polypeptides chains are bonded by hydrogen and disulphide bonds.
Complete step by step solution:
(i) The structural difference between starch and cellulose are as follows:
Starch is found in both linear and branched chain form. Amylose is linear chains of $\alpha $-D-glucose molecules linked together by $\alpha - 1,4$glycosidic bonds and amylopectin is branched chain $\alpha $-D-glucose molecules linked together by $\alpha - 1,6$ glycosidic bond.

Cellulose is linear chains of $\beta $-D-glucose molecules linked together by $\beta - 1,4$ glycosidic bonds. Cellulose has $\beta - 1,4$ linkage between glucose units.

Therefore, starch is a branched molecule whereas the cellulose is a linear molecule. The starch has $\alpha - 1,4$ and $\alpha - 1,6$ glycosidic bonds whereas the cellulose has only $\beta - 1,4$ glycosidic bonds.
(ii) Phosphodiester linkage is commonly found in nucleic acid (DNA and RNA) and plays a critical role in their structure and function. Phosphodiester linkage is formed when a phosphoric acid molecule $\left( {{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{P}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}} \right)$ attached with sugar reacts with hydroxyl group$\left( {{\text{ - OH}}} \right)$ present at carbon$ - 3$ of another sugar thus forms an ester bond and removes water molecule.

Therefore, phosphodiester linkage is present in nucleic acids.
(iii) Fibrous proteins have only primary structure means simple long polypeptide chains whereas globular proteins have complex structures means polypeptides chains are further coiled and form globule-like structures. Some examples of fibrous proteins are keratins (present in hairs), collagens, myosin and elastin. Globular proteins are albumin and haemoglobin.
Note: The major type of biomolecules are carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids and proteins. Starch and cellulose both are polysaccharides made up of glucose. Polysaccharides are carbohydrates having a large number of monosaccharides joined by glycosidic bonds. The name of the linkage gives an idea about the bonding such as phosphate linkage means the bond will involve a phosphate group. Glycosidic linkage means the bonding will involve the carbohydrates. In fibrous protein, the long polypeptides chains are bonded by hydrogen and disulphide bonds.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




