
How do you identify aldehydes in skeletal structure?

Answer
528.3k+ views
Hint: We know that an aldehyde is an organic compound which has a $ CHO $ functional group. To draw all the structures, we can start by drawing a linear chain with the substituents and then drawing branched carbon chains at non-equivalent carbon atoms.
Complete step by step solution:
We know that aldehydes are organic compounds and they contain a $ CHO $ functional group. It consists of a carbonyl center, which means a carbon will be double bonded to an oxygen atom and the same carbon Centre is attached to the alkyl group or other hydrogen atoms.
For a given compound we can have four possible isomers. Therefore, there will be four possible structures of aldehyde. We will start by arranging all the carbons linearly and putting the aldehyde group at the end of the chain, which will give us the structure.
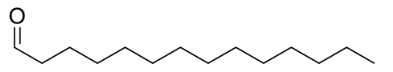
A bond-line structure hides all Hydrogen atoms directly attached to carbon atoms. Each carbon atom must have four bonds, so any missing ones are $ C-H $ bonds. In your structure, the carbon on the far right has only one bond, so there must be three $ C-H $ bonds. That carbon is a methyl group.
All the carbons at the angles of the zigzag line show two bonds. They must also have two $ C-H $ bonds, so they are a $ C{{H}_{2}} $ group. Now, we examine the $ =O $ group. It is not attached to a $ C-H $ , but to a $ C. $
The group is a C=O carbonyl group. It does not become an aldehyde or ketone until you identify the groups attached to it In the first structure, the carbonyl carbon has three bonds. The fourth bond must be a $ C-H $ bond, as in the middle structure, so the compound must be an aldehyde. A ketone must have a $ C-C~ $ on both sides of the carbonyl carbon, as in the third structure.
Note:
Remember that we can also draw ketones from the same formula which has a $ CO $ functional group fixed therefore, we fixed the position of the aldehyde first and then rearranged the other groups or else it would have been very confusing. The structures obtained here are isomers as they have the same chemical formula.
Complete step by step solution:
We know that aldehydes are organic compounds and they contain a $ CHO $ functional group. It consists of a carbonyl center, which means a carbon will be double bonded to an oxygen atom and the same carbon Centre is attached to the alkyl group or other hydrogen atoms.
For a given compound we can have four possible isomers. Therefore, there will be four possible structures of aldehyde. We will start by arranging all the carbons linearly and putting the aldehyde group at the end of the chain, which will give us the structure.
A bond-line structure hides all Hydrogen atoms directly attached to carbon atoms. Each carbon atom must have four bonds, so any missing ones are $ C-H $ bonds. In your structure, the carbon on the far right has only one bond, so there must be three $ C-H $ bonds. That carbon is a methyl group.
All the carbons at the angles of the zigzag line show two bonds. They must also have two $ C-H $ bonds, so they are a $ C{{H}_{2}} $ group. Now, we examine the $ =O $ group. It is not attached to a $ C-H $ , but to a $ C. $
The group is a C=O carbonyl group. It does not become an aldehyde or ketone until you identify the groups attached to it In the first structure, the carbonyl carbon has three bonds. The fourth bond must be a $ C-H $ bond, as in the middle structure, so the compound must be an aldehyde. A ketone must have a $ C-C~ $ on both sides of the carbonyl carbon, as in the third structure.
Note:
Remember that we can also draw ketones from the same formula which has a $ CO $ functional group fixed therefore, we fixed the position of the aldehyde first and then rearranged the other groups or else it would have been very confusing. The structures obtained here are isomers as they have the same chemical formula.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




