
How to identify epimers and anomers in carbohydrates (sugar)?
Answer
509.4k+ views
Hint: Isomerism is an important phenomenon for compounds. The phenomena in which different compounds having the same chemical formula but different structures are known as isomerism and the compounds exhibiting isomerism are known as isomers.
Complete answer:
Isomerism is of different types. Broadly they are divided into structural isomers and stereoisomers. Structural isomers are further divided into chain isomers, position isomers and functional isomers. Whereas stereoisomers are of two types namely enantiomers and diastereomers.
Enantiomers are non-superimposable chiral centers mirror type whereas diastereomers are non-superimposable chiral centers but are not mirror image to each other.
Epimers and Anomers are both diastereomers, but epimer is a stereoisomer that differs in configuration at any single stereogenic center, while anomers is actually an epimer that differs in configuration at the acetal/hemiacetal carbon.
Epimer at stereogenic centre, two isomers present in the molecules differ, while the rest remains identical. All other stereogenic centers in the molecules are the same in each.
Anomer is an epimer differing from each other in the configuration \[C - 1\] if they are aldoses or in configuration at \[C - 2\] if they are ketoses. The epimer carbon in anomers is known as anomeric carbon or anomeric center.
Epimers differ in the configuration of a single carbon atom. Examples are \[D - galactose\] and \[D - mannose\] which are epimers of \[D - glucose\]. \[D - galactose\] differ only at \[C - 4\] from D-glucose, whereas \[D - mannose\] differ only at the \[C - 2\] configuration.
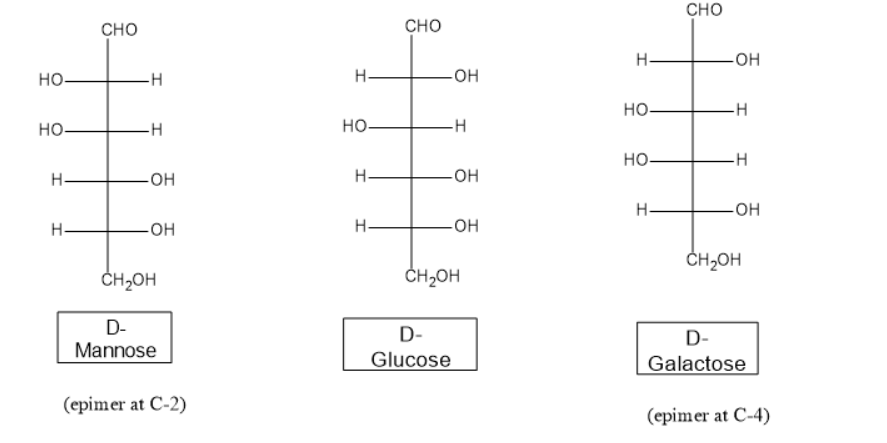
Anomers differ in a configuration only at the anomeric carbon.
For example, \[\alpha - D - glucose\] and \[\beta - D - glucose\] are anomers. The \[\alpha \] form has anomeric \[OH\] at \[C - 1\] on the opposite side of the ring from \[C{H_2}OH\] group at \[C - 5\] whereas the \[\beta \] form has anomeric \[OH\] group at \[C{H_2}OH\]
Note:
Anomers are cyclic monosaccharides or glycosides that are epimers, differing from each other in the configuration of C-1 if they are aldoses or in the configuration at C-2 if they are ketoses. The epimeric carbon in anomers is known as anomeric carbon or anomeric center.
Complete answer:
Isomerism is of different types. Broadly they are divided into structural isomers and stereoisomers. Structural isomers are further divided into chain isomers, position isomers and functional isomers. Whereas stereoisomers are of two types namely enantiomers and diastereomers.
Enantiomers are non-superimposable chiral centers mirror type whereas diastereomers are non-superimposable chiral centers but are not mirror image to each other.
Epimers and Anomers are both diastereomers, but epimer is a stereoisomer that differs in configuration at any single stereogenic center, while anomers is actually an epimer that differs in configuration at the acetal/hemiacetal carbon.
Epimer at stereogenic centre, two isomers present in the molecules differ, while the rest remains identical. All other stereogenic centers in the molecules are the same in each.
Anomer is an epimer differing from each other in the configuration \[C - 1\] if they are aldoses or in configuration at \[C - 2\] if they are ketoses. The epimer carbon in anomers is known as anomeric carbon or anomeric center.
Epimers differ in the configuration of a single carbon atom. Examples are \[D - galactose\] and \[D - mannose\] which are epimers of \[D - glucose\]. \[D - galactose\] differ only at \[C - 4\] from D-glucose, whereas \[D - mannose\] differ only at the \[C - 2\] configuration.

Anomers differ in a configuration only at the anomeric carbon.
For example, \[\alpha - D - glucose\] and \[\beta - D - glucose\] are anomers. The \[\alpha \] form has anomeric \[OH\] at \[C - 1\] on the opposite side of the ring from \[C{H_2}OH\] group at \[C - 5\] whereas the \[\beta \] form has anomeric \[OH\] group at \[C{H_2}OH\]
Note:
Anomers are cyclic monosaccharides or glycosides that are epimers, differing from each other in the configuration of C-1 if they are aldoses or in the configuration at C-2 if they are ketoses. The epimeric carbon in anomers is known as anomeric carbon or anomeric center.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




