
Identify the compound that exhibits tautomerism:
(A)- 2-Butene
(B)- Lactic acid
(C)- 2-Pentanone
(D)- Phenol
Answer
566.7k+ views
Hint: The phenomenon where a single chemical compound tends to exist in two or more interconvertible structures that are different from each other in terms of the relative position of one atomic nucleus, generally the hydrogen is known as Tautomerism.
Complete step by step solution:
-The structural isomers (constitutional isomers) of a compound which differs only in the position of protons and electrons and can readily interconvert are called Tautomers.
-The phenomenon of tautomerism happens in the presence of a catalyst. The catalyst may be of two types- Acid catalyst; Base catalyst.
-In acid catalyst first causes protonation to occur and the formed cation will be delocalized followed by the deprotonation of in the adjacent position of the carbon.
-In base catalyst, deprotonation is the first step and instead of delocalization of cation, anion delocalization occurs followed by the protonation at different positions of the anion.
-Following are the structural requirements for tautomerism to occur-
(i) Compounds must contain polar molecule and weakly acidic functional groups.
(ii) Tautomerism is the change of position of an atom.
(iii) Tautomerism has no effects on bond length and other such features.
(iv) Generally, tautomerism occurs in planar or non-polar molecules.
-Let us consider a general example to understand tautomerism. Addition of water to alkyne in the presence of $HgS{{O}_{4}}$or ${{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$gives two forms of products, aldehyde or ketone which are both interconvertible.
$RC=CR\xrightarrow{HOH,{{H}^{+}},{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}}RCH=CR(OR)(aldehyde)\to RC{{H}_{2}}CR=O(ketone)$
-So, from the options given, only 2-Pentanone falls in the category as mentioned.
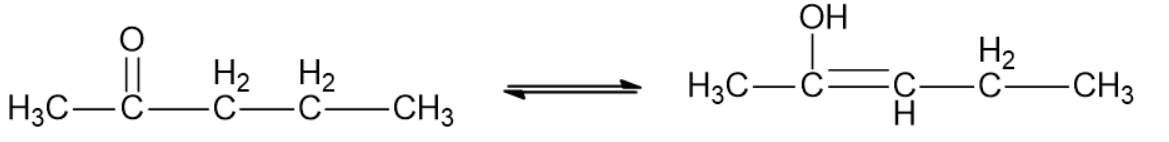
Therefore, the correct answer is option C.
Note: Let us now see the mechanism of tautomerization reactions. Tautomerization is a two-step process that occurs in an aqueous solution of acid. For tautomerization to occur, the molecule must have alpha hydrogen attached to an alpha carbon. The proton is added parallelly to the anti-bonding of the carbonyl group. The bond formed now will undergo hyperconjugation with the C-H bond, reducing the electron density at the alpha carbon and thus making alpha hydrogen more acidic than before. If the position of alpha hydrogen is not so, the process of tautomerization will become slow, for example in Adamantanone.
Complete step by step solution:
-The structural isomers (constitutional isomers) of a compound which differs only in the position of protons and electrons and can readily interconvert are called Tautomers.
-The phenomenon of tautomerism happens in the presence of a catalyst. The catalyst may be of two types- Acid catalyst; Base catalyst.
-In acid catalyst first causes protonation to occur and the formed cation will be delocalized followed by the deprotonation of in the adjacent position of the carbon.
-In base catalyst, deprotonation is the first step and instead of delocalization of cation, anion delocalization occurs followed by the protonation at different positions of the anion.
-Following are the structural requirements for tautomerism to occur-
(i) Compounds must contain polar molecule and weakly acidic functional groups.
(ii) Tautomerism is the change of position of an atom.
(iii) Tautomerism has no effects on bond length and other such features.
(iv) Generally, tautomerism occurs in planar or non-polar molecules.
-Let us consider a general example to understand tautomerism. Addition of water to alkyne in the presence of $HgS{{O}_{4}}$or ${{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$gives two forms of products, aldehyde or ketone which are both interconvertible.
$RC=CR\xrightarrow{HOH,{{H}^{+}},{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}}RCH=CR(OR)(aldehyde)\to RC{{H}_{2}}CR=O(ketone)$
-So, from the options given, only 2-Pentanone falls in the category as mentioned.

Therefore, the correct answer is option C.
Note: Let us now see the mechanism of tautomerization reactions. Tautomerization is a two-step process that occurs in an aqueous solution of acid. For tautomerization to occur, the molecule must have alpha hydrogen attached to an alpha carbon. The proton is added parallelly to the anti-bonding of the carbonyl group. The bond formed now will undergo hyperconjugation with the C-H bond, reducing the electron density at the alpha carbon and thus making alpha hydrogen more acidic than before. If the position of alpha hydrogen is not so, the process of tautomerization will become slow, for example in Adamantanone.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




