
Identify the diagram A and B.
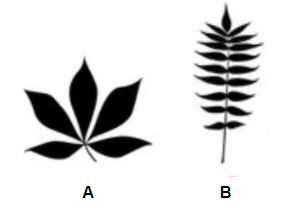
A) A= Palmate compound leaf ,B= Whorled phyllotaxy
B) A=Pinnate compound leaf ,B= Whorled phyllotaxy
C) A= Whorled phyllotaxy, B= Palmately compound leaf
D) None of these

Answer
566.7k+ views
Hint: Leaves are classified into different categories based on how their lamina is divided. Lamina is also termed as the blade of the leaf.
Complete answer:
Let us first analyze the structure of the leaves given in the figure to identify them
Figure A: The leaflets of this leaf are radiating outwards from the point where the petiole of the leaf ends. Also, all the leaflets are originating from a single common point. The leaflets are clustered together forming a palm like structure and a joint is found between the leaflet and the point of its attachment. These characteristic features resemble that of a palmate compound leaf.
Figure B: In this figure more than two or three leaves are present at a single node.It shows whorled phyllotaxy leaf arrangement. These kinds of leaves are found in Alstonia plants. Other examples of whorled phyllotaxy include aspergula and nerium.
Option A: This option matches the above description and identification of the leaf in the figures. Therefore, this is the correct option.
Option B and C: These options do not match the above identification of figure A and B. Therefore, this is the incorrect option.
Option D: Since one of the above mentioned options is correct.Therefore, this is the incorrect option.
Thus, the correct answer is option (A) A= Palmate compound leaf, B= Whorled phyllotaxy.
Note:Pinnate compound leaves occur in two rows and no joint is found in them unlike palmate compound leaves. In alternate phyllotaxy, a single leaf is present at each node.
Complete answer:
Let us first analyze the structure of the leaves given in the figure to identify them
Figure A: The leaflets of this leaf are radiating outwards from the point where the petiole of the leaf ends. Also, all the leaflets are originating from a single common point. The leaflets are clustered together forming a palm like structure and a joint is found between the leaflet and the point of its attachment. These characteristic features resemble that of a palmate compound leaf.
Figure B: In this figure more than two or three leaves are present at a single node.It shows whorled phyllotaxy leaf arrangement. These kinds of leaves are found in Alstonia plants. Other examples of whorled phyllotaxy include aspergula and nerium.
Option A: This option matches the above description and identification of the leaf in the figures. Therefore, this is the correct option.
Option B and C: These options do not match the above identification of figure A and B. Therefore, this is the incorrect option.
Option D: Since one of the above mentioned options is correct.Therefore, this is the incorrect option.
Thus, the correct answer is option (A) A= Palmate compound leaf, B= Whorled phyllotaxy.
Note:Pinnate compound leaves occur in two rows and no joint is found in them unlike palmate compound leaves. In alternate phyllotaxy, a single leaf is present at each node.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




