
Identify the intermediate formed in Grignard reagent reaction with ester?
A. Aldehyde
B. Ketone
C. Benzene
D. Propene
Answer
589.8k+ views
Hint: Grignard reagent is a chemical compound with general name as alkyl magnesium halide with alkyl chain possessing negative charge and magnesium due to electropositivity having $+2$ charge. Intermediate is a compound formed in-between the reaction. The intermediate of the reaction can be judged only by looking at its mechanism.
Complete answer:
Let us solve this question using the mechanism of ester with Grignard reagent:
Step (1)- The Grignard reagent acts as a nucleophile and attacks the carbonyl group present in esters. After, the attack oxygen atom present in the carbonyl group will have the negative charge and the alkyl group adds to the carbon atom of the carbonyl group.

Step (2)- The negative charge on the oxygen atom forms bond with carbon, leaving the $\text{RO}-$ group to separate from the compound as $\text{R}{{\text{O}}^{-}}$. Thus, forming a double bond with carbon atoms and obtaining ketone (a carbonyl group and other valencies satisfied by alkyl groups) as an intermediate.
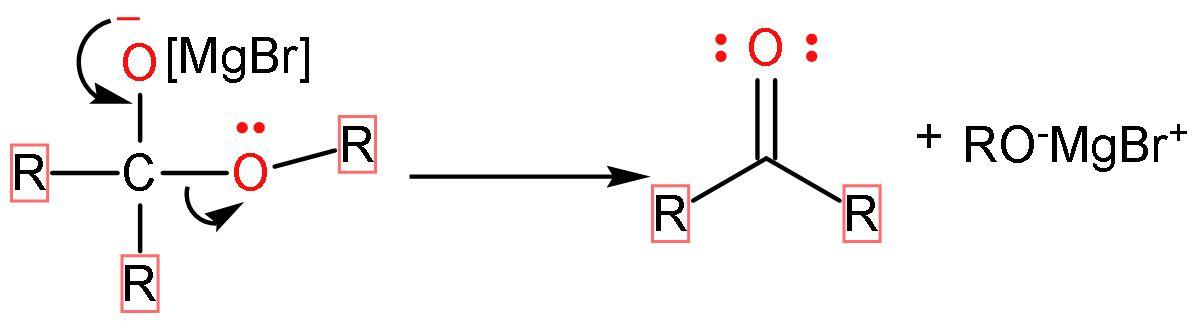
Step (3)- The ketone formed further undergoes nucleophilic addition or reaction with Grignard reagent because it has a carbonyl group present in it. The process restarts with addition of Grignard reagent and forming negative charge on oxygen atom of carbonyl group.
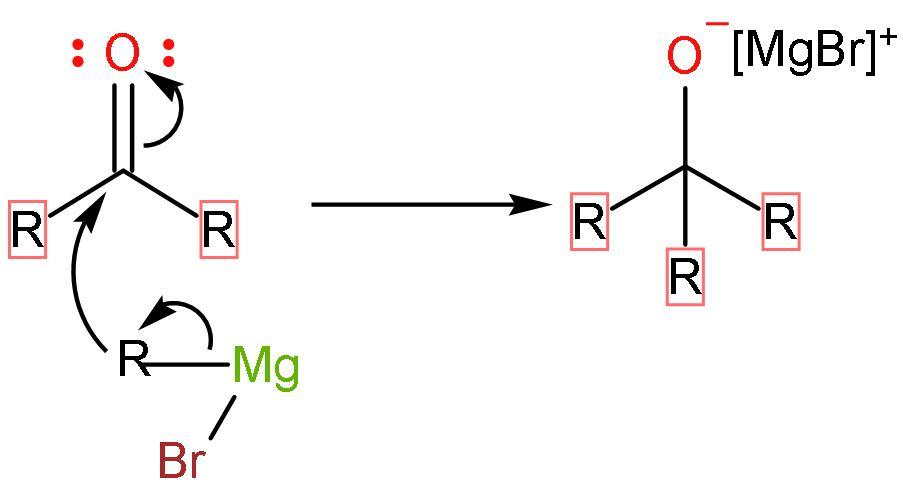
Step (4)- The last step includes the protonation of water or hydrolysis of the compound to finally form alcohol as its product.
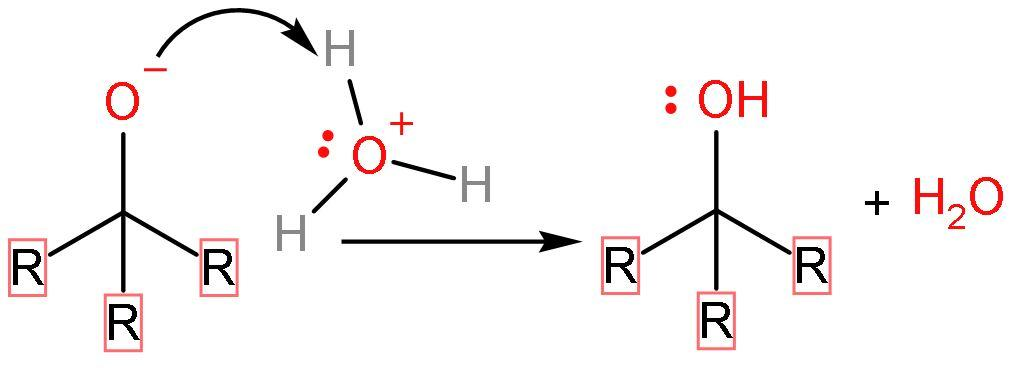
Ketone is the intermediate formed in Grignard reagent reaction with ester.
The correct option is option ‘b’.
Note:
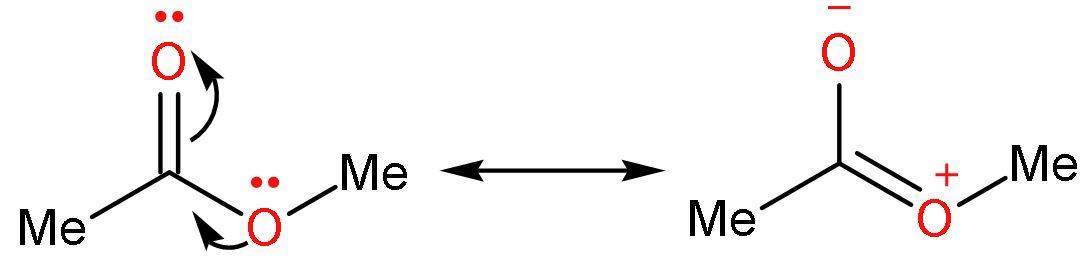
Ester is less prone to Grignard reagent in comparison to aldehydes and ketones because the electrophilicity of carbon atoms of carbonyl group is decreased by the self-resonance or intramolecular resonance of esters. The lone pair of oxygen undergoes resonance with the double bond between carbon and oxygen atoms.
Complete answer:
Let us solve this question using the mechanism of ester with Grignard reagent:
Step (1)- The Grignard reagent acts as a nucleophile and attacks the carbonyl group present in esters. After, the attack oxygen atom present in the carbonyl group will have the negative charge and the alkyl group adds to the carbon atom of the carbonyl group.

Step (2)- The negative charge on the oxygen atom forms bond with carbon, leaving the $\text{RO}-$ group to separate from the compound as $\text{R}{{\text{O}}^{-}}$. Thus, forming a double bond with carbon atoms and obtaining ketone (a carbonyl group and other valencies satisfied by alkyl groups) as an intermediate.

Step (3)- The ketone formed further undergoes nucleophilic addition or reaction with Grignard reagent because it has a carbonyl group present in it. The process restarts with addition of Grignard reagent and forming negative charge on oxygen atom of carbonyl group.

Step (4)- The last step includes the protonation of water or hydrolysis of the compound to finally form alcohol as its product.

Ketone is the intermediate formed in Grignard reagent reaction with ester.
The correct option is option ‘b’.
Note:
Ester is less prone to Grignard reagent in comparison to aldehydes and ketones because the electrophilicity of carbon atoms of carbonyl group is decreased by the self-resonance or intramolecular resonance of esters. The lone pair of oxygen undergoes resonance with the double bond between carbon and oxygen atoms.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




