
Identify the parts labeled as a, b, c, d, and e of renal corpuscle.
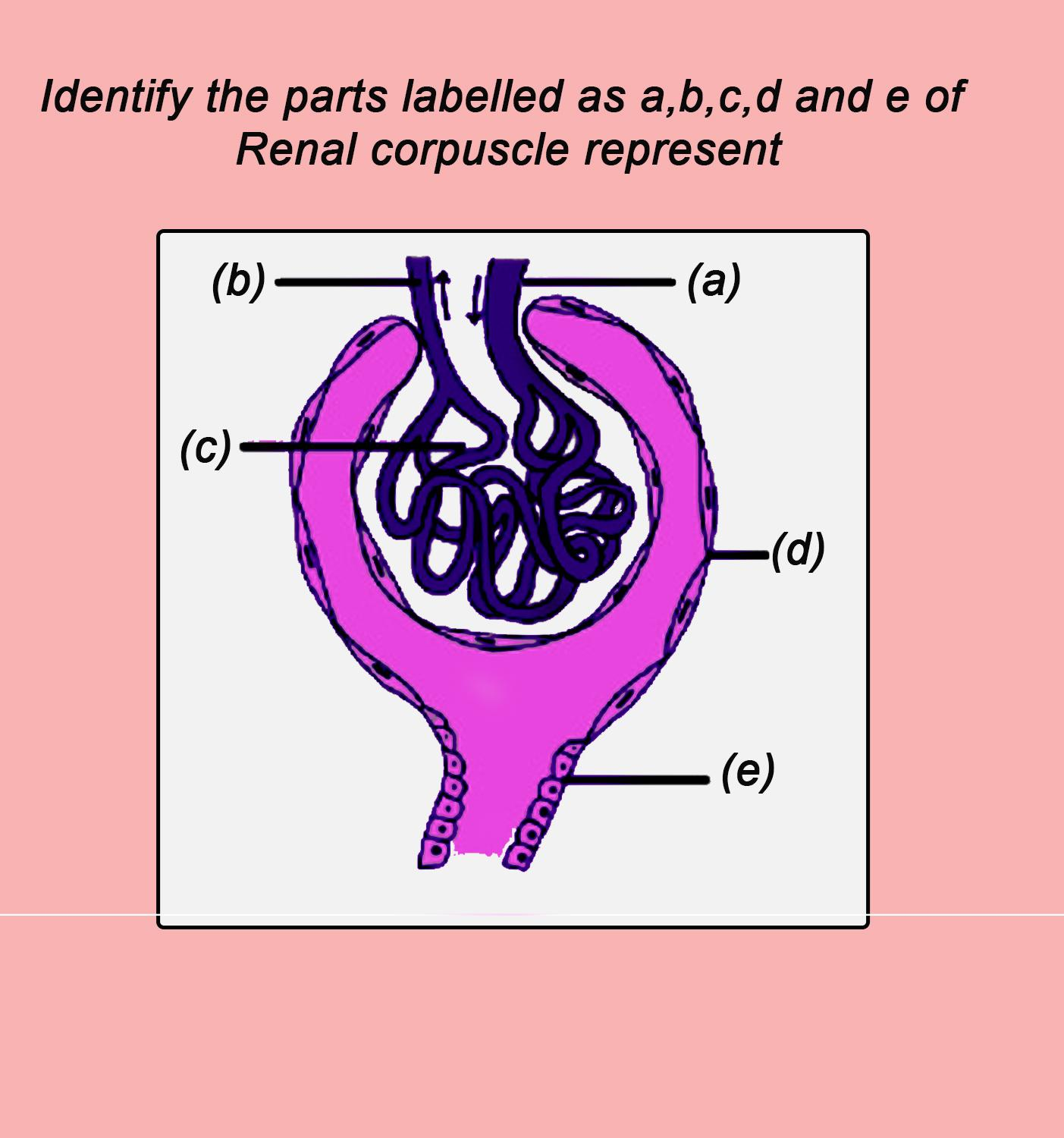
(A). a. Afferent arteriole, b. Efferent arteriole, c. The glomerulus, d. Bowman’s capsule, e. Proximal convoluted tubule
(B). a. Efferent arteriole, b. Afferent arteriole, c. The glomerulus, d. Bowman’s capsule, e. Proximal convoluted tubule
(C). a. Afferent arteriole, b. Efferent arteriole, c. The glomerulus, d. Bowman’s capsule, e. Distal convoluted tubule
(D). a. Afferent arteriole, b. Efferent arteriole, c. Bowman’s capsule, d. The glomerulus, e. Proximal convoluted tubule
(E). a. Afferent arteriole, b. Efferent arteriole, c. Bowman’s capsule, d. The glomerulus, e. Collecting tubule

Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint: It is the blood-filtering component of the nephron of the kidney. It is also known as a Malpighian corpuscle. It has a little tuft of vessels containing two cell types. Endothelial cells, which have enormous fenestrae, aren't covered by diaphragms. Mesangial cells are adjusted smooth muscle cells that lie between the vessels.
Complete answer:
(a) Afferent arteriole is responsible for the blood entering into the Bowman's capsule.
(b) Efferent arteriole is responsible for the blood leaves the Bowman's capsule after ultrafiltration
(c) Glomerulus is responsible for the network of sieve-like capillaries where ultrafiltration takes place.
(d) Bowman's capsule is responsible for the collection of the glomerular filtrate.
(e) Proximal convoluted tubule is responsible for the filtrate passes through this technique, and water and salts are reabsorbed.
Additional Information: The renal corpuscle acts to filter blood. Fluid from the blood within the glomerulus is collected within the Bowman's capsule to make "glomerular filtrate", which is then further processed along the nephron to make urine. It does this via a filtration barrier. The malpighian body filtration obstruction comprises the fenestrated endothelium of glomerular vessels, the intertwined basal lamina of endothelial cells, and podocytes, and hence the filtration cuts of the podocytes.
This boundary allows the section of water, particles, and little atoms from the circulation system into Bowman's space (the space between the instinctive and parietal layers). Huge or potentially charged proteins are kept from passing into Bowman's space, hence holding these proteins inside the circulation. The basal lamina comprises three layers: lamina rara externa, lamina densa, and lamina rara interna. The lamina rara externa is adjoining the podocyte measures. The lamina densa is the central layer consisting of type IV collagen and laminin. This layer acts as a selective macromolecular filter, preventing the passage of huge protein molecules into Bowman's space. The lamina rara interna is neighboring endothelial cells. This layer contains heparan sulfate, a charged glycosaminoglycan that contributes to the electrostatic barrier of the glomerular filter.
So the correct answer is ‘a. Afferent arteriole, b. Efferent arteriole, c. The glomerulus, d. Bowman’s capsule, e. Proximal convoluted tubule’.
Note: The Bowman's capsule has an outer parietal layer composed of simple squamous epithelium. The visceral layer, made out of changed straightforward squamous epithelium, is lined by podocytes. Podocytes have foot measures, pedicels, that fold over glomerular vessels. These pedicels interdigitate with pedicels of neighboring podocytes framing filtration cuts.
Complete answer:
(a) Afferent arteriole is responsible for the blood entering into the Bowman's capsule.
(b) Efferent arteriole is responsible for the blood leaves the Bowman's capsule after ultrafiltration
(c) Glomerulus is responsible for the network of sieve-like capillaries where ultrafiltration takes place.
(d) Bowman's capsule is responsible for the collection of the glomerular filtrate.
(e) Proximal convoluted tubule is responsible for the filtrate passes through this technique, and water and salts are reabsorbed.
Additional Information: The renal corpuscle acts to filter blood. Fluid from the blood within the glomerulus is collected within the Bowman's capsule to make "glomerular filtrate", which is then further processed along the nephron to make urine. It does this via a filtration barrier. The malpighian body filtration obstruction comprises the fenestrated endothelium of glomerular vessels, the intertwined basal lamina of endothelial cells, and podocytes, and hence the filtration cuts of the podocytes.
This boundary allows the section of water, particles, and little atoms from the circulation system into Bowman's space (the space between the instinctive and parietal layers). Huge or potentially charged proteins are kept from passing into Bowman's space, hence holding these proteins inside the circulation. The basal lamina comprises three layers: lamina rara externa, lamina densa, and lamina rara interna. The lamina rara externa is adjoining the podocyte measures. The lamina densa is the central layer consisting of type IV collagen and laminin. This layer acts as a selective macromolecular filter, preventing the passage of huge protein molecules into Bowman's space. The lamina rara interna is neighboring endothelial cells. This layer contains heparan sulfate, a charged glycosaminoglycan that contributes to the electrostatic barrier of the glomerular filter.
So the correct answer is ‘a. Afferent arteriole, b. Efferent arteriole, c. The glomerulus, d. Bowman’s capsule, e. Proximal convoluted tubule’.
Note: The Bowman's capsule has an outer parietal layer composed of simple squamous epithelium. The visceral layer, made out of changed straightforward squamous epithelium, is lined by podocytes. Podocytes have foot measures, pedicels, that fold over glomerular vessels. These pedicels interdigitate with pedicels of neighboring podocytes framing filtration cuts.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




