
Identify the type of modified root and select the correct statement regarding it.
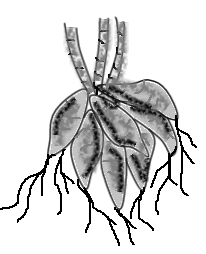
A. It is the tuberous root of Dahlia that stores insulin as a reserve food
B. It is a modified taproot that occurs in Dahlia
C. It is a modified adventitious root that shows reserve food material
D. These roots are modified to provide mechanical support to the plant

Answer
561.3k+ views
Hint: Roots are the water and nutrient absorbing structures that provide anchorage to the plant. The given diagram of the root shows a swollen root structure that is specialized to act as a storage site for the plant. Various root modifications are done for adaptation purposes.
Complete answer: Roots are underground thread-like structures of a plant that have specialized cells for the absorption of water and nutrients from the soil. These nutrients and water are supplied to the plant for growth and development. Roots also function to provide anchorage to the plant. In some plants, roots modify to adapt to a given environment. For example, the roots in desert plants are very deep anchored. This is because the water level is very deep in desert areas. Some roots swell and are modified to take up the function of food storage. Such modification is shown in the given figure. The shown figure depicts tap roots which are modified to become tuberous roots. These tuberous roots are of Dahlia. Dahlia is a genus of a bushy flowering plant. It is a herbaceous perennial plant that has characteristic tuberous roots that store insulin as reserve food. There are 42 species of Dahlia which are cultivated for their colourful and beautiful flowers. The insulin acquired from Dahlia tubers is called Dahlin.
Hence, option A is the right answer.
Note: The Dahlin extract is used as diabetic starch. Some special treatments are performed on tubers of Dahlia to obtain pure laevulose (simple sugar). This laevulose is useful for diabetic patients. The tubers are sliced and then treated with milk of lime. After this, they are steamed and juice is extracted by filtration. Hence, the tuberous roots of Dahlia have an important medical application.
Complete answer: Roots are underground thread-like structures of a plant that have specialized cells for the absorption of water and nutrients from the soil. These nutrients and water are supplied to the plant for growth and development. Roots also function to provide anchorage to the plant. In some plants, roots modify to adapt to a given environment. For example, the roots in desert plants are very deep anchored. This is because the water level is very deep in desert areas. Some roots swell and are modified to take up the function of food storage. Such modification is shown in the given figure. The shown figure depicts tap roots which are modified to become tuberous roots. These tuberous roots are of Dahlia. Dahlia is a genus of a bushy flowering plant. It is a herbaceous perennial plant that has characteristic tuberous roots that store insulin as reserve food. There are 42 species of Dahlia which are cultivated for their colourful and beautiful flowers. The insulin acquired from Dahlia tubers is called Dahlin.
Hence, option A is the right answer.
Note: The Dahlin extract is used as diabetic starch. Some special treatments are performed on tubers of Dahlia to obtain pure laevulose (simple sugar). This laevulose is useful for diabetic patients. The tubers are sliced and then treated with milk of lime. After this, they are steamed and juice is extracted by filtration. Hence, the tuberous roots of Dahlia have an important medical application.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




