
If A (-5, 7), B (-4, -5), C (-1, -6) and D (4, 5) are vertices quadrilateral, find the area of the quadrilateral ABCD.
Answer
618.9k+ views
Hint: In this question four vertices of a quadrilateral are given to us and we need to find its area. A quadrilateral can be converted into two triangles, then area of triangle with known vertices can be obtained using the direct formula $\dfrac{1}{2}\left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{{x_1}}&{{y_1}}&1 \\
{{x_2}}&{{y_2}}&1 \\
{{x_3}}&{{y_3}}&1
\end{array}} \right|$where $({x_1},{y_1}),({x_2},{y_2}){\text{ and (}}{{\text{x}}_3},{y_3})$are the coordinates of vertices.
Complete step-by-step answer:
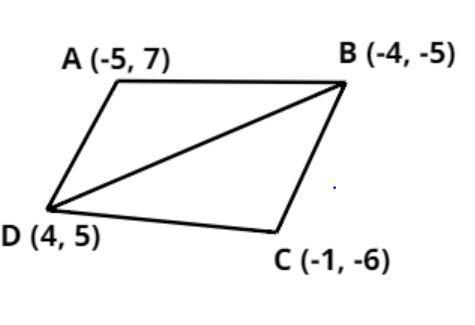
The quadrilateral ABCD is shown above where we join the coordinates B and D.
So the quadrilateral is converted into two triangles.
So the area (A) of the quadrilateral is the sum of the area (A1) of triangle ABD and the area (A2) of triangle BCD.
$ \Rightarrow A = {A_1} + {A_2}$
So first find out the area of triangle ABD
As we know if all the vertices of the triangle is given than the area of triangle is given as $\dfrac{1}{2}\left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{{x_1}}&{{y_1}}&1 \\
{{x_2}}&{{y_2}}&1 \\
{{x_3}}&{{y_3}}&1
\end{array}} \right|$.
So let $A = \left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right) \equiv \left( { - 5,7} \right)$, $B = \left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right) \equiv \left( { - 4, - 5} \right)$, $C = \left( {{x_3},{y_3}} \right) \equiv \left( { - 1, - 6} \right)$, $D = \left( {{x_4},{y_4}} \right) \equiv \left( {4,5} \right)$
So the area of the triangle ABD is
$ \Rightarrow {A_1} = \dfrac{1}{2}\left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{{x_1}}&{{y_1}}&1 \\
{{x_2}}&{{y_2}}&1 \\
{{x_4}}&{{y_4}}&1
\end{array}} \right| = \dfrac{1}{2}\left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{ - 5}&7&1 \\
{ - 4}&{ - 5}&1 \\
4&5&1
\end{array}} \right|$
Now expand the determinant we have,
$ \Rightarrow {A_1} = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ { - 5\left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{ - 5}&1 \\
5&1
\end{array}} \right| - 7\left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{ - 4}&1 \\
4&1
\end{array}} \right| + 1\left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{ - 4}&{ - 5} \\
4&5
\end{array}} \right|} \right]$
$ \Rightarrow {A_1} = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ { - 5\left( { - 5 - 5} \right) - 7\left( { - 4 - 4} \right) + 1\left( { - 20 + 20} \right)} \right]$
So on simplifying we get
$ \Rightarrow {A_1} = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {50 + 56} \right] = \dfrac{{106}}{2} = 53$ Square units.
Now calculate the area of the triangle BCD is
$ \Rightarrow {A_2} = \dfrac{1}{2}\left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{{x_2}}&{{y_2}}&1 \\
{{x_3}}&{{y_3}}&1 \\
{{x_4}}&{{y_4}}&1
\end{array}} \right| = \dfrac{1}{2}\left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{ - 4}&{ - 5}&1 \\
{ - 1}&{ - 6}&1 \\
4&5&1
\end{array}} \right|$
Now expand the determinant we have,
$ \Rightarrow {A_1} = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ { - 4\left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{ - 6}&1 \\
5&1
\end{array}} \right| - \left( { - 5} \right)\left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{ - 1}&1 \\
4&1
\end{array}} \right| + 1\left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{ - 1}&{ - 6} \\
4&5
\end{array}} \right|} \right]$
$ \Rightarrow {A_1} = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ { - 4\left( { - 6 - 5} \right) + 5\left( { - 1 - 4} \right) + 1\left( { - 5 + 24} \right)} \right]$
So on simplifying we get
$ \Rightarrow {A_1} = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {44 - 25 + 19} \right] = \dfrac{{38}}{2} = 19$ Square units.
So the area (A) of the quadrilateral is
$ \Rightarrow A = {A_1} + {A_2} = 53 + 19 = 72$ Square units.
So this is the required area of the parallelogram.
Note: Whenever we face such types of problems the key concept is simply to have the gist of the direct formula to obtain the area of the triangle whose coordinates of vertices are known to us. Application of determinant expansion is a useful asset while solving problems of these kinds. This concept will help you get on the right track to reach the answer.
{{x_1}}&{{y_1}}&1 \\
{{x_2}}&{{y_2}}&1 \\
{{x_3}}&{{y_3}}&1
\end{array}} \right|$where $({x_1},{y_1}),({x_2},{y_2}){\text{ and (}}{{\text{x}}_3},{y_3})$are the coordinates of vertices.
Complete step-by-step answer:

The quadrilateral ABCD is shown above where we join the coordinates B and D.
So the quadrilateral is converted into two triangles.
So the area (A) of the quadrilateral is the sum of the area (A1) of triangle ABD and the area (A2) of triangle BCD.
$ \Rightarrow A = {A_1} + {A_2}$
So first find out the area of triangle ABD
As we know if all the vertices of the triangle is given than the area of triangle is given as $\dfrac{1}{2}\left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{{x_1}}&{{y_1}}&1 \\
{{x_2}}&{{y_2}}&1 \\
{{x_3}}&{{y_3}}&1
\end{array}} \right|$.
So let $A = \left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right) \equiv \left( { - 5,7} \right)$, $B = \left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right) \equiv \left( { - 4, - 5} \right)$, $C = \left( {{x_3},{y_3}} \right) \equiv \left( { - 1, - 6} \right)$, $D = \left( {{x_4},{y_4}} \right) \equiv \left( {4,5} \right)$
So the area of the triangle ABD is
$ \Rightarrow {A_1} = \dfrac{1}{2}\left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{{x_1}}&{{y_1}}&1 \\
{{x_2}}&{{y_2}}&1 \\
{{x_4}}&{{y_4}}&1
\end{array}} \right| = \dfrac{1}{2}\left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{ - 5}&7&1 \\
{ - 4}&{ - 5}&1 \\
4&5&1
\end{array}} \right|$
Now expand the determinant we have,
$ \Rightarrow {A_1} = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ { - 5\left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{ - 5}&1 \\
5&1
\end{array}} \right| - 7\left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{ - 4}&1 \\
4&1
\end{array}} \right| + 1\left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{ - 4}&{ - 5} \\
4&5
\end{array}} \right|} \right]$
$ \Rightarrow {A_1} = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ { - 5\left( { - 5 - 5} \right) - 7\left( { - 4 - 4} \right) + 1\left( { - 20 + 20} \right)} \right]$
So on simplifying we get
$ \Rightarrow {A_1} = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {50 + 56} \right] = \dfrac{{106}}{2} = 53$ Square units.
Now calculate the area of the triangle BCD is
$ \Rightarrow {A_2} = \dfrac{1}{2}\left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{{x_2}}&{{y_2}}&1 \\
{{x_3}}&{{y_3}}&1 \\
{{x_4}}&{{y_4}}&1
\end{array}} \right| = \dfrac{1}{2}\left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{ - 4}&{ - 5}&1 \\
{ - 1}&{ - 6}&1 \\
4&5&1
\end{array}} \right|$
Now expand the determinant we have,
$ \Rightarrow {A_1} = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ { - 4\left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{ - 6}&1 \\
5&1
\end{array}} \right| - \left( { - 5} \right)\left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{ - 1}&1 \\
4&1
\end{array}} \right| + 1\left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{ - 1}&{ - 6} \\
4&5
\end{array}} \right|} \right]$
$ \Rightarrow {A_1} = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ { - 4\left( { - 6 - 5} \right) + 5\left( { - 1 - 4} \right) + 1\left( { - 5 + 24} \right)} \right]$
So on simplifying we get
$ \Rightarrow {A_1} = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {44 - 25 + 19} \right] = \dfrac{{38}}{2} = 19$ Square units.
So the area (A) of the quadrilateral is
$ \Rightarrow A = {A_1} + {A_2} = 53 + 19 = 72$ Square units.
So this is the required area of the parallelogram.
Note: Whenever we face such types of problems the key concept is simply to have the gist of the direct formula to obtain the area of the triangle whose coordinates of vertices are known to us. Application of determinant expansion is a useful asset while solving problems of these kinds. This concept will help you get on the right track to reach the answer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




