
If a convergent beam of light passes through a diverging lens, the result
(This question has multiple correct answers.)
A. May be a convergent beam
B. May be divergent beam
C. May be parallel beam
D. Must be a parallel beam
Answer
587.7k+ views
Hint: If a beam of light is struck on a lens then the ability to diverge this beam of light by the lens will depend on the power of the lens and the degree of divergence of the power. We will analyse the possibility of each option here.
Complete step by step answer:
In the option (A) it is given that the beam of light may be a convergent beam after passing through a diverging lens. This is a correct answer because the ability to converge will depend upon the power and inability to diverge the incoming beam, hence the degree of divergence will be less for such lenses. Also, when the beam converges after the refraction there are more chances to form a real image and diverging lens i.e. concave lens is able to form real images.

In option (B) it is given that the beam after passing through a diverging lens may be a divergent beam, which is obvious. A diverging lens usually produces a diverging beam of the incoming beam after the process of refraction in normal conditions.
In option (C) it is given that the refracted beam of light may be a parallel beam of light, this may also be correct in some situations. As we know the rule of the refraction is that if a beam of light is going towards the focus of the concave lens (diverging lens) then after refraction it will go parallel to the axis.
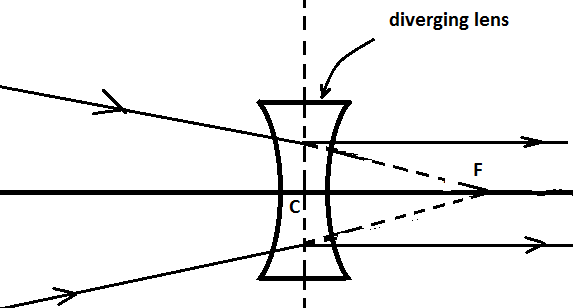
Option (D) is appropriate if all the above options are possible.
So, the options (A), (B), and (C) are correct.
Note:
Mathematically, the Power of a lens is the reciprocal of the focal length of that particular lens. So, we can write the following relation,
\[{\text{Power = }}\dfrac{1}{f}\], where $f = $focal length of the lens.
Power can also define as the ability to diverge or converge the incoming beam of light is known as power of the lens.
Complete step by step answer:
In the option (A) it is given that the beam of light may be a convergent beam after passing through a diverging lens. This is a correct answer because the ability to converge will depend upon the power and inability to diverge the incoming beam, hence the degree of divergence will be less for such lenses. Also, when the beam converges after the refraction there are more chances to form a real image and diverging lens i.e. concave lens is able to form real images.

In option (B) it is given that the beam after passing through a diverging lens may be a divergent beam, which is obvious. A diverging lens usually produces a diverging beam of the incoming beam after the process of refraction in normal conditions.
In option (C) it is given that the refracted beam of light may be a parallel beam of light, this may also be correct in some situations. As we know the rule of the refraction is that if a beam of light is going towards the focus of the concave lens (diverging lens) then after refraction it will go parallel to the axis.

Option (D) is appropriate if all the above options are possible.
So, the options (A), (B), and (C) are correct.
Note:
Mathematically, the Power of a lens is the reciprocal of the focal length of that particular lens. So, we can write the following relation,
\[{\text{Power = }}\dfrac{1}{f}\], where $f = $focal length of the lens.
Power can also define as the ability to diverge or converge the incoming beam of light is known as power of the lens.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




