
If ‘a’ the length of side of the cube, the distance between the body-centred atom and one corner atom in the cube will be:
[A] $\dfrac{4}{\sqrt{3}}a$
[B] $\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{4}a$
[C] $\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}a$
[D] $\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{3}}a$
Answer
579.9k+ views
Hint: A body centred atom lies in the body centre of the cube i.e. on the body diagonal. To find the correct answer firstly calculate the diagonal of the cube. Then from that value you can find the required distance by taking its half as the distance will be half the length of the body diagonal.
Complete answer:
We know that in a BCC lattice, one atom is placed in the centre of the cube and other atoms are placed at the corners. We know that there are 8 corners in a cube. Therefore, there are 8 atoms in a body centred cubic structure in the corners.
Now we have to find the distance between the body-centred atom and one corner atom. The body-centred atom lies in the middle of the body diagonal of the cube.
We know that the body diagonal of any polyhedron is a line connecting two vertices that do not lie on the same face.
Pictorially we can represent it as -
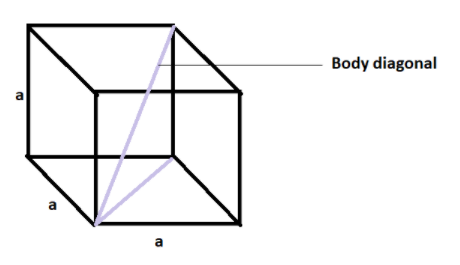
Where ‘a’ is the edge length which is equal for all the edges as it is a cube.
Now, we know that we can write the diagonal of a cuboid as $\sqrt{{{l}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}+{{h}^{2}}}$ , where l is the length of the cuboid, b is the breadth of the cuboid and h is the height of the cuboid.
In the given question we have a cube with edge length ‘a’ and for a cube, length, breadth and height all are will be equal to each other.
Therefore, we can write that the diagonal of the cube will be $\sqrt{3{{a}^{2}}}$ that is $\sqrt{3}a$ where ‘a’ is the edge length.
Therefore, if we half the distance of the diagonal, we can find out the distance between the corner atom and the body-centre atom that will be $\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}a$.
Therefore, the correct answer is option [C] $\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}a$.
Note:
We know that a lattice is a network which gives us the three dimensional arrangement of atoms. There are 14 different Bravais lattices that we study in case of solids. The body centred and the cubic close packed structures are also Bravais lattice. BCC is one of the primitive lattices and CCP is just like the face centred Bravais lattice.
Complete answer:
We know that in a BCC lattice, one atom is placed in the centre of the cube and other atoms are placed at the corners. We know that there are 8 corners in a cube. Therefore, there are 8 atoms in a body centred cubic structure in the corners.
Now we have to find the distance between the body-centred atom and one corner atom. The body-centred atom lies in the middle of the body diagonal of the cube.
We know that the body diagonal of any polyhedron is a line connecting two vertices that do not lie on the same face.
Pictorially we can represent it as -

Where ‘a’ is the edge length which is equal for all the edges as it is a cube.
Now, we know that we can write the diagonal of a cuboid as $\sqrt{{{l}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}+{{h}^{2}}}$ , where l is the length of the cuboid, b is the breadth of the cuboid and h is the height of the cuboid.
In the given question we have a cube with edge length ‘a’ and for a cube, length, breadth and height all are will be equal to each other.
Therefore, we can write that the diagonal of the cube will be $\sqrt{3{{a}^{2}}}$ that is $\sqrt{3}a$ where ‘a’ is the edge length.
Therefore, if we half the distance of the diagonal, we can find out the distance between the corner atom and the body-centre atom that will be $\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}a$.
Therefore, the correct answer is option [C] $\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}a$.
Note:
We know that a lattice is a network which gives us the three dimensional arrangement of atoms. There are 14 different Bravais lattices that we study in case of solids. The body centred and the cubic close packed structures are also Bravais lattice. BCC is one of the primitive lattices and CCP is just like the face centred Bravais lattice.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




