
If ${K_i}$ and ${K_p}$ are the effective spring constant in series and parallel combination of springs as shown in figure, find \[\dfrac{{{K_i}}}{{{K_p}}}\].
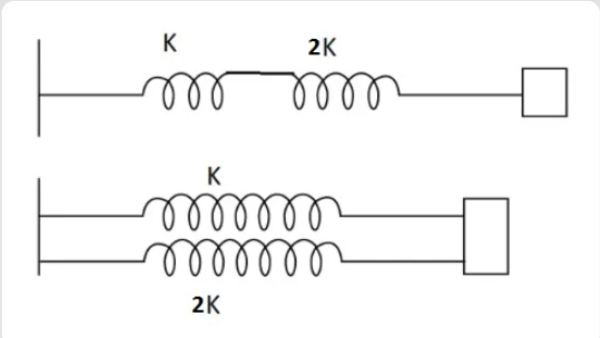
A. 9/2
B. 3/7
C. 2/9
D. 7/3
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: Try to recall the concept of dividing current in branches having resistance \[{R_1}\] and \[{R_2}\] which are firstly connected in series and secondly in parallel. From that concept we will get the idea of adding spring constants, either springs are connected in series or connected in parallel. And then simply take the ratio of and we will get the answer.
Complete step by step answer:
First we will see the concept of adding spring constants when they are connected in
1. Series
2. Parallel
Case:1 When Springs are connected in series.
When two spring are connected in series having spring constants \[{K_1}\] and \[{K_2}\] as shown in below figure
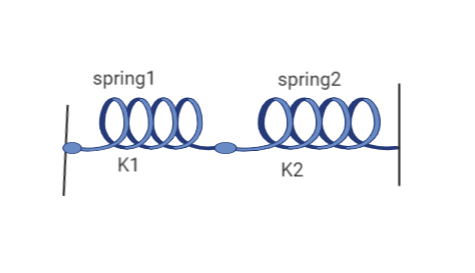
Then the resulting Spring constant ${K_r}$ is given by the formula:
\[\dfrac{1}{{{K_{}}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{K_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{K_2}}}\]
Now from the question
\[{K_1} = K\]
\[{K_2} = 2K\]
Putting values in formula
\[\dfrac{1}{{{K_r}}} = \dfrac{1}{K} + \dfrac{1}{{2K}}\]
\[\dfrac{1}{{{K_r}}} = \dfrac{{2K + K}}{{2{K^2}}}\]
\[\dfrac{1}{{{K_r}}} = \dfrac{3}{{2K}}\]
\[{K_r} = \dfrac{{2K}}{3}\]
Case 2: When springs are connected in parallel
When two spring are connected in parallel having spring constants \[{K_1}\] and \[{K_2}\] as shown in below figure
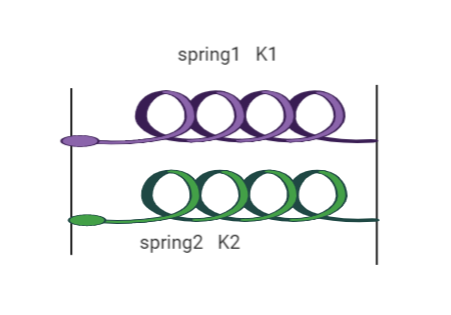
Then the resulting Spring constant \[{K_p}\] is given by the formula:
\[{K_p} = {K_1} + {K_2}\]
Given values of \[{K_1}\] and \[{K_2}\]from question:
\[{K_1} = K\]
\[{K_2} = 2K\]
Putting values in above equation:
\[{K_p} = K + 2K\]
\[{K_p} = 3K\]
Now we have both spring constant
\[\dfrac{{{K_i}}}{{{K_p}}} = \dfrac{{{K_r}}}{{{K_p}}} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{{2K}}{3}}}{{3K}}\]
\[\dfrac{{{K_i}}}{{{K_p}}} = \dfrac{2}{9}\]
Hence, option C is correct.
Note: This concept can be used to combine two springs and replace it with a new one. Not only we are bound to combine two springs we can also combine many strings. If the spring constant of a spring is high then it is difficult to stretch it more while spring having less or low spring constant can be elongated much more than the previous one.
Complete step by step answer:
First we will see the concept of adding spring constants when they are connected in
1. Series
2. Parallel
Case:1 When Springs are connected in series.
When two spring are connected in series having spring constants \[{K_1}\] and \[{K_2}\] as shown in below figure

Then the resulting Spring constant ${K_r}$ is given by the formula:
\[\dfrac{1}{{{K_{}}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{K_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{K_2}}}\]
Now from the question
\[{K_1} = K\]
\[{K_2} = 2K\]
Putting values in formula
\[\dfrac{1}{{{K_r}}} = \dfrac{1}{K} + \dfrac{1}{{2K}}\]
\[\dfrac{1}{{{K_r}}} = \dfrac{{2K + K}}{{2{K^2}}}\]
\[\dfrac{1}{{{K_r}}} = \dfrac{3}{{2K}}\]
\[{K_r} = \dfrac{{2K}}{3}\]
Case 2: When springs are connected in parallel
When two spring are connected in parallel having spring constants \[{K_1}\] and \[{K_2}\] as shown in below figure

Then the resulting Spring constant \[{K_p}\] is given by the formula:
\[{K_p} = {K_1} + {K_2}\]
Given values of \[{K_1}\] and \[{K_2}\]from question:
\[{K_1} = K\]
\[{K_2} = 2K\]
Putting values in above equation:
\[{K_p} = K + 2K\]
\[{K_p} = 3K\]
Now we have both spring constant
\[\dfrac{{{K_i}}}{{{K_p}}} = \dfrac{{{K_r}}}{{{K_p}}} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{{2K}}{3}}}{{3K}}\]
\[\dfrac{{{K_i}}}{{{K_p}}} = \dfrac{2}{9}\]
Hence, option C is correct.
Note: This concept can be used to combine two springs and replace it with a new one. Not only we are bound to combine two springs we can also combine many strings. If the spring constant of a spring is high then it is difficult to stretch it more while spring having less or low spring constant can be elongated much more than the previous one.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




