
If the band-gap between valence band and conduction band in a material is 5.0 eV then the material is a/an-
A). Semiconductor
B). Good conductor
C). Superconductor
D). Insulator
Answer
596.4k+ views
Hint: In a medium where electrons cannot exist, is defined as the band gap is an energy range. The energy of this band gap is the energy difference between the valence and the conduction band. The calculation is usually performed in electron volts (eV).
Complete step-by-step solution -
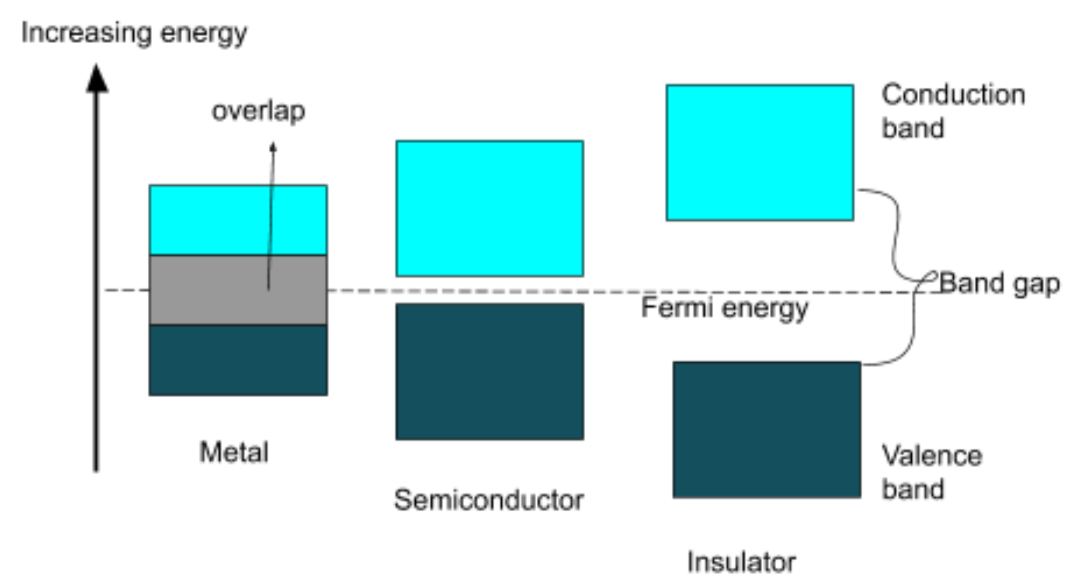
A semiconductor is a material with an intermediate but non-zero band gap which acts as an insulator at zero absolute but enables electrons to thermally excite at temperatures below their melting point in their conducting bands. By comparison, an insulator is a substance with a wide variety. Drivers will overlap the valence and driving bands such that the band difference cannot be identified.
An insulator is an essential element that is separated between the valence and the conductive band or a broad energy distinction. This major gap in energy allows it impossible for electrons to travel to the conductive band to migrate and generate an electric current. Insulators should be called the reverse of conductors; strong insulators have high resistivity and inhibit the movement of electricity.
The band difference is Zero in a conductor. The semiconductor band difference is about 1eV
For instance: The gap is 1.11eV for silicon.
Insulators usually do not permit electrons to pass from valence band to conduction band and typically have incredibly wide band gaps. The insulator 's band difference of 5eV
For instance: Diamond has the 5.5eV band gap
The substance given in the question will also be an insulator with a band gap of 5.0eV.
Hence, it is clear that option D is the correct option.
Note: The valence band comprises the largest electrons of energy in a substance. The conduction band is considered to be the lowest place where electrons will reside. The valence and conduction band overlap in metals and conductors and there is no belt difference. Small band differences are found in semiconductors and broadband differences in insulators.
Complete step-by-step solution -

A semiconductor is a material with an intermediate but non-zero band gap which acts as an insulator at zero absolute but enables electrons to thermally excite at temperatures below their melting point in their conducting bands. By comparison, an insulator is a substance with a wide variety. Drivers will overlap the valence and driving bands such that the band difference cannot be identified.
An insulator is an essential element that is separated between the valence and the conductive band or a broad energy distinction. This major gap in energy allows it impossible for electrons to travel to the conductive band to migrate and generate an electric current. Insulators should be called the reverse of conductors; strong insulators have high resistivity and inhibit the movement of electricity.
The band difference is Zero in a conductor. The semiconductor band difference is about 1eV
For instance: The gap is 1.11eV for silicon.
Insulators usually do not permit electrons to pass from valence band to conduction band and typically have incredibly wide band gaps. The insulator 's band difference of 5eV
For instance: Diamond has the 5.5eV band gap
The substance given in the question will also be an insulator with a band gap of 5.0eV.
Hence, it is clear that option D is the correct option.
Note: The valence band comprises the largest electrons of energy in a substance. The conduction band is considered to be the lowest place where electrons will reside. The valence and conduction band overlap in metals and conductors and there is no belt difference. Small band differences are found in semiconductors and broadband differences in insulators.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




