
If the L.S.A. of a cube is 64 ${\text{c}}{{\text{m}}^2}$ what will be the side of the cube.
Answer
612.3k+ views
HINT- Proceed the solution of this question on equalising the given lateral surface area of the cube with the formula of L.S.A. of a cube which states below.
Lateral surface area [L.S.A.] of cube =$4{l^2}$
Complete step-by-step answer:
In question it is given the L.S.A. of a cube is 64 ${\text{c}}{{\text{m}}^2}$ and we know that
Lateral surface area of a Cube is the sum of surface areas of all the sides except the top and bottom face of the solid is defined as the lateral surface area of a solid.
As we know that length, breadth and height of a cube are the same so consider a Cube of length, breadth and height to be l meters.
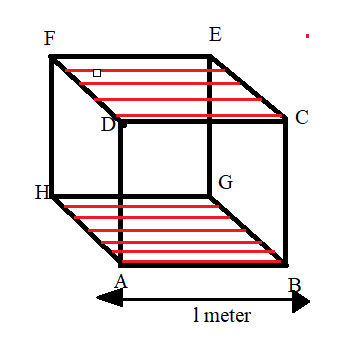
Lateral surface area of the cube = Area of face ABCD + Area of face BCGE + Area of face EFGH + Area of face ADFH [ leaving upper and lower face as shown by red colour in figure]
And formula of Lateral surface area [L.S.A.] of cube =$4{l^2}$
And in question it is given L.S.A. of a cube is 64 $cm^2$
So on equalising
$ \Rightarrow 4{l^2} = 64$
$ \Rightarrow {l^2} = \dfrac{{64}}{4}$
$ \Rightarrow {l^2} = 16$
On taking square root on both side
$ \Rightarrow \sqrt {{l^2}} = \sqrt {16} $
$ \Rightarrow l = 4$
Therefore, l = 4 cm
Thus, the side of the cube is 4 cm.
Note- In this particular question, we should have a clear understanding of lateral surface area i.e. surface area of a solid without its base areas.
We can also derive its formula with the formula of L.S.A. of a cuboid which is equal to
⇒2(b × h) + 2(l × h)
And as we know that Length, breadth and height of a cube are same so let it be equal to l meter
So put l=b=h= l in above formula
⇒2(l × l) + 2(l× l)
⇒$2{l^2} + 2{l^2} = 4{l^2}$
Hence LSA of Cube $ = 4{l^2}$
Lateral surface area [L.S.A.] of cube =$4{l^2}$
Complete step-by-step answer:
In question it is given the L.S.A. of a cube is 64 ${\text{c}}{{\text{m}}^2}$ and we know that
Lateral surface area of a Cube is the sum of surface areas of all the sides except the top and bottom face of the solid is defined as the lateral surface area of a solid.
As we know that length, breadth and height of a cube are the same so consider a Cube of length, breadth and height to be l meters.

Lateral surface area of the cube = Area of face ABCD + Area of face BCGE + Area of face EFGH + Area of face ADFH [ leaving upper and lower face as shown by red colour in figure]
And formula of Lateral surface area [L.S.A.] of cube =$4{l^2}$
And in question it is given L.S.A. of a cube is 64 $cm^2$
So on equalising
$ \Rightarrow 4{l^2} = 64$
$ \Rightarrow {l^2} = \dfrac{{64}}{4}$
$ \Rightarrow {l^2} = 16$
On taking square root on both side
$ \Rightarrow \sqrt {{l^2}} = \sqrt {16} $
$ \Rightarrow l = 4$
Therefore, l = 4 cm
Thus, the side of the cube is 4 cm.
Note- In this particular question, we should have a clear understanding of lateral surface area i.e. surface area of a solid without its base areas.
We can also derive its formula with the formula of L.S.A. of a cuboid which is equal to
⇒2(b × h) + 2(l × h)
And as we know that Length, breadth and height of a cube are same so let it be equal to l meter
So put l=b=h= l in above formula
⇒2(l × l) + 2(l× l)
⇒$2{l^2} + 2{l^2} = 4{l^2}$
Hence LSA of Cube $ = 4{l^2}$
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




