
If two structures of same cross-sectional area, but different numerical apertures $N{A_1}$ and $N{A_2}$($N{A_2}$<$N{A_1}$) are joined longitudinally, the numerical aperture of the combined structure is
A. $\dfrac{{N{A_1}N{A_2}}}{{N{A_1} + N{A_2}}}$
B. $N{A_1} + N{A_2}$
C. $N{A_1}$
D. $N{A_2}$

Answer
571.5k+ views
Hint: This question is based on the total internal reflection phenomenon. There are two parts here which are called the core and the cladding. Core must be of higher refractive index than of the cladding so that total internal reflection occurs at the interface of the core and cladding.
Formula used:
$NA{\text{ }}\propto {\text{ }}{i_m}$
Complete step by step answer:
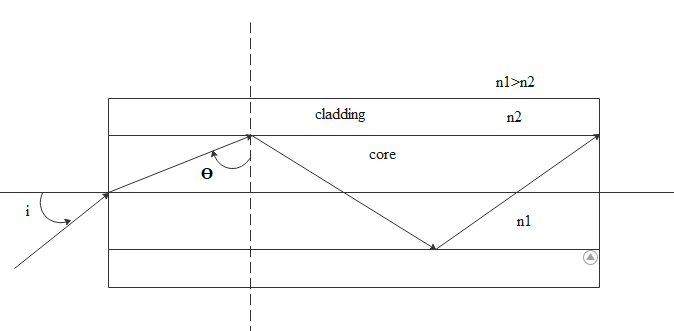
Whenever light travels from one medium to the other medium it bends. If the light travels from the denser medium to the rarer medium then there is a chance of total internal reflection(TIR). TIR is a phenomenon where the light ray travelling from denser to rarer medium hits the interface of the two mediums and will get reflected back to the denser medium itself. We consider the below diagram
The light tries to go from core to the cladding and reflects back which means it hit the interface with the critical angle. All the angles of incidence greater than the critical angle results in the TIR.
If the angle of incidence at the interface increases then angle p will decrease. If angle p decreases as angle ‘i’ is proportional to angle ‘p’ angle ‘i’ also decreases. There exists one value called ${i_m}$ from where TIR starts. For all the entering angles less than ${i_m}$ TIR will take place.
Numerical aperture is proportional to ${i_m}$. i.e $NA{\text{ }}\propto {\text{ }}{i_m}$
It is also given as $N{A_2}$<$N{A_1}$
Which means ${i_m}_2$<${i_m}_1$
So if $i$<${i_m}_2$ is satisfied, the $i$<${i_m}_1$ also will be satisfied.
Hence the numerical aperture of the combined structure must be $N{A_2}$
So option D will be the answer.
Note: This TIR methodology is vastly used in fiber communication. The optical fibers carry the information without any leakage by using this technology. The signals are travelled for the longer distances effectively through these optical fibers. The basic requirement is that the core refractive index must be greater than the cladding one.
Formula used:
$NA{\text{ }}\propto {\text{ }}{i_m}$
Complete step by step answer:
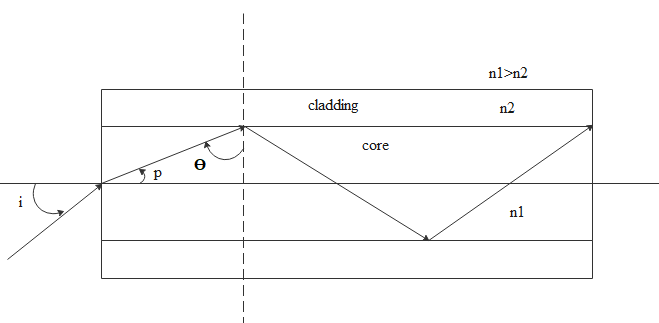
Whenever light travels from one medium to the other medium it bends. If the light travels from the denser medium to the rarer medium then there is a chance of total internal reflection(TIR). TIR is a phenomenon where the light ray travelling from denser to rarer medium hits the interface of the two mediums and will get reflected back to the denser medium itself. We consider the below diagram

The light tries to go from core to the cladding and reflects back which means it hit the interface with the critical angle. All the angles of incidence greater than the critical angle results in the TIR.
If the angle of incidence at the interface increases then angle p will decrease. If angle p decreases as angle ‘i’ is proportional to angle ‘p’ angle ‘i’ also decreases. There exists one value called ${i_m}$ from where TIR starts. For all the entering angles less than ${i_m}$ TIR will take place.
Numerical aperture is proportional to ${i_m}$. i.e $NA{\text{ }}\propto {\text{ }}{i_m}$
It is also given as $N{A_2}$<$N{A_1}$
Which means ${i_m}_2$<${i_m}_1$
So if $i$<${i_m}_2$ is satisfied, the $i$<${i_m}_1$ also will be satisfied.
Hence the numerical aperture of the combined structure must be $N{A_2}$
So option D will be the answer.
Note: This TIR methodology is vastly used in fiber communication. The optical fibers carry the information without any leakage by using this technology. The signals are travelled for the longer distances effectively through these optical fibers. The basic requirement is that the core refractive index must be greater than the cladding one.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




