
If volume of a regular tetrahedron of edge length k is V and shortest distance between any pair of opposite edges of same regular tetrahedron is d, then find the value of $ \dfrac{{{d}^{3}}}{V} $
(a) $ \dfrac{\sqrt{6}}{5} $
(b) $ \dfrac{9\sqrt{3}}{4} $
(c) 3
(d) $ \dfrac{9\sqrt{6}}{4} $
Answer
530.1k+ views
Hint: First of all draw the tetrahedron. We know that when the edge length of the tetrahedron is k then the volume of the tetrahedron is equal to $ \dfrac{{{k}^{3}}}{6\sqrt{2}} $ . The shortest distance between the two opposite edges of the tetrahedron is d. Now, we will calculate the shortest distance between the opposite edges of tetrahedron from the figure then you will find the shortest distance as $ k\sqrt{2} $ . We know the value of V and d in terms of k. We have to find the value of $ \dfrac{{{d}^{3}}}{V} $ for that first of all take the cube of the d then substitute the values of V and $ {{d}^{3}} $ in $ \dfrac{{{d}^{3}}}{V} $ .
Complete step-by-step answer:
It is given that the volume of a tetrahedron with edge length k is V and the shortest distance between two opposite edges of the tetrahedron is d.
To get a better visualization of the problem, we have drawn a regular tetrahedron inside the cube in the below figure,
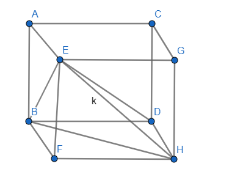
In the above figure, as you can see, EBHD is the regular tetrahedron with edge length as k that we have shown above by marking EH as k.
The shortest distance between the two opposite edges is d. Let us take edge ED and EH so the shortest distance between them is DH which is the side of the cube. Let us assume the side of the cube as “u”.
We are going to write the side of the cube in terms of k. Take the right angled triangle EFH in which EF is equal to FH which is “u”. As you can see from the above figure that EH is the hypotenuse of the $ \Delta EFH $ so applying Pythagoras theorem in this triangle we get,
$ \begin{align}
& {{\left( EF \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( FH \right)}^{2}}={{\left( EH \right)}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{u}^{2}}+{{u}^{2}}={{k}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow 2{{u}^{2}}={{k}^{2}} \\
\end{align} $
Taking square root on both the sides we get,
$ \begin{align}
& \sqrt{2}u=k \\
& \Rightarrow u=\dfrac{k}{\sqrt{2}} \\
\end{align} $
From the above, the shortest distance between the two opposite edges of the tetrahedron is $ \dfrac{k}{\sqrt{2}} $ .
It is given that the shortest distance between two opposite sides of the tetrahedron is d so:
$ d=\dfrac{k}{\sqrt{2}} $
We have to find the value of $ \dfrac{{{d}^{3}}}{V} $ so we need to take a cube on both sides of the above equation.
$ {{d}^{3}}=\dfrac{{{k}^{3}}}{2\sqrt{2}} $
We know that, the volume of the tetrahedron with edge length k is given by:
$ V=\dfrac{{{k}^{3}}}{6\sqrt{2}} $
Now, substituting the value of V and $ {{d}^{3}} $ in $ \dfrac{{{d}^{3}}}{V} $ we get,
$ \begin{align}
& \dfrac{{{d}^{3}}}{V}=\dfrac{\dfrac{{{k}^{3}}}{2\sqrt{2}}}{\dfrac{{{k}^{3}}}{6\sqrt{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{d}^{3}}}{V}=3 \\
\end{align} $
From the above, we have got the value of $ \dfrac{{{d}^{3}}}{V} $ as 3.
Hence, the correct option is (c).
Note: You might have been thinking why we have taken the shortest distance as DH (or side of the cube) not BH.
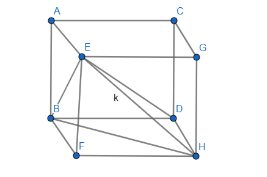
In the above figure, BH is also the distance between the edges then why we have not taken that distance because BH is the face diagonal of the cube which is $ \sqrt{2} $ times the side of the cube. We need to find the shortest distance as BH is the distance greater than DH. So, the shortest distance between BH and DH is DH and we have rejected the distance BH.
Complete step-by-step answer:
It is given that the volume of a tetrahedron with edge length k is V and the shortest distance between two opposite edges of the tetrahedron is d.
To get a better visualization of the problem, we have drawn a regular tetrahedron inside the cube in the below figure,

In the above figure, as you can see, EBHD is the regular tetrahedron with edge length as k that we have shown above by marking EH as k.
The shortest distance between the two opposite edges is d. Let us take edge ED and EH so the shortest distance between them is DH which is the side of the cube. Let us assume the side of the cube as “u”.
We are going to write the side of the cube in terms of k. Take the right angled triangle EFH in which EF is equal to FH which is “u”. As you can see from the above figure that EH is the hypotenuse of the $ \Delta EFH $ so applying Pythagoras theorem in this triangle we get,
$ \begin{align}
& {{\left( EF \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( FH \right)}^{2}}={{\left( EH \right)}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{u}^{2}}+{{u}^{2}}={{k}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow 2{{u}^{2}}={{k}^{2}} \\
\end{align} $
Taking square root on both the sides we get,
$ \begin{align}
& \sqrt{2}u=k \\
& \Rightarrow u=\dfrac{k}{\sqrt{2}} \\
\end{align} $
From the above, the shortest distance between the two opposite edges of the tetrahedron is $ \dfrac{k}{\sqrt{2}} $ .
It is given that the shortest distance between two opposite sides of the tetrahedron is d so:
$ d=\dfrac{k}{\sqrt{2}} $
We have to find the value of $ \dfrac{{{d}^{3}}}{V} $ so we need to take a cube on both sides of the above equation.
$ {{d}^{3}}=\dfrac{{{k}^{3}}}{2\sqrt{2}} $
We know that, the volume of the tetrahedron with edge length k is given by:
$ V=\dfrac{{{k}^{3}}}{6\sqrt{2}} $
Now, substituting the value of V and $ {{d}^{3}} $ in $ \dfrac{{{d}^{3}}}{V} $ we get,
$ \begin{align}
& \dfrac{{{d}^{3}}}{V}=\dfrac{\dfrac{{{k}^{3}}}{2\sqrt{2}}}{\dfrac{{{k}^{3}}}{6\sqrt{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{d}^{3}}}{V}=3 \\
\end{align} $
From the above, we have got the value of $ \dfrac{{{d}^{3}}}{V} $ as 3.
Hence, the correct option is (c).
Note: You might have been thinking why we have taken the shortest distance as DH (or side of the cube) not BH.

In the above figure, BH is also the distance between the edges then why we have not taken that distance because BH is the face diagonal of the cube which is $ \sqrt{2} $ times the side of the cube. We need to find the shortest distance as BH is the distance greater than DH. So, the shortest distance between BH and DH is DH and we have rejected the distance BH.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




