
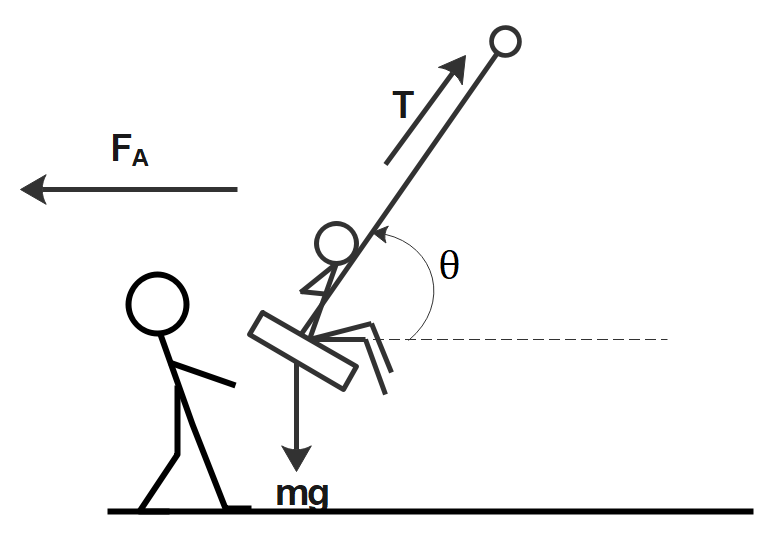
Imagine you are pulling horizontally on a child on swing as shown in the diagram. The child and the seat together weigh 100N. Take $\theta $ to be the angle the rope makes with the horizontal.
When $\theta = {30.0^o}$, what is the necessary ${F_A}$ you need to apply to keep the child still?
A. $50.0N$
B. $57.7N$
C. $86.6N$
D. $173N$

Answer
584.1k+ views
Hint: In the problem, they’ve given a child-swing system. They asked us to find the force that must act on the object to keep it in equilibrium. In order to find it, we need to know the tension in the string. From this, we can calculate the horizontal component of tension which will be the force needed to be applied.
Complete answer:
Let us draw a simple free body diagram of forces acting on the swing.
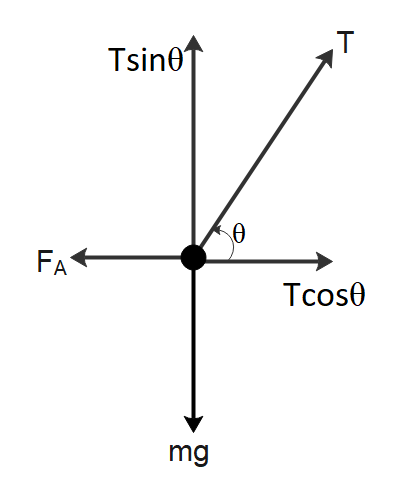
The weight mg of the swing and the child is acting downwards. The tension in the string is acting at an angle θ to the horizontal. Resolving the tension into components, we will have the vertical component balancing the weight of the swing-child system. Now, the force FA must be applied towards the left to balance the horizontal component of tension.
Considering the vertical forces acting on the system, we will have
$T\sin \theta = mg$
They’ve given the angle $\theta = {30.0^o}$ and the weight $mg = 100N$. Substituting the quantities in the formula we will have
$\eqalign{
& T\sin \theta = mg \cr
& \Rightarrow T\sin {30.0^o} = 100 \cr
& \Rightarrow T \times \dfrac{1}{2} = 100 \cr
& \Rightarrow T = 200N \cr} $
Now that we have the tension of the string, we can find the horizontal component and equate it to the force to be applied as follows
$\eqalign{
& T\cos \theta = {F_A} \cr
& \Rightarrow {F_A} = 100\cos {30.0^o} \cr
& \Rightarrow {F_A} = 100 \times \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2} = 86.6 \cr
& \therefore {F_A} = 86.6N \cr} $
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
Always draw a free body diagram, to analyze the forces acting on the system. It helps in knowing the cancellation or interaction of forces and the direction of acceleration of the body. Though in our problem there’s no acceleration, it helps find the equilibrium of forces. In a free body diagram (or F.B.D.) consider the object of interest as a point object and draw the forces acting on it.
Complete answer:
Let us draw a simple free body diagram of forces acting on the swing.

The weight mg of the swing and the child is acting downwards. The tension in the string is acting at an angle θ to the horizontal. Resolving the tension into components, we will have the vertical component balancing the weight of the swing-child system. Now, the force FA must be applied towards the left to balance the horizontal component of tension.
Considering the vertical forces acting on the system, we will have
$T\sin \theta = mg$
They’ve given the angle $\theta = {30.0^o}$ and the weight $mg = 100N$. Substituting the quantities in the formula we will have
$\eqalign{
& T\sin \theta = mg \cr
& \Rightarrow T\sin {30.0^o} = 100 \cr
& \Rightarrow T \times \dfrac{1}{2} = 100 \cr
& \Rightarrow T = 200N \cr} $
Now that we have the tension of the string, we can find the horizontal component and equate it to the force to be applied as follows
$\eqalign{
& T\cos \theta = {F_A} \cr
& \Rightarrow {F_A} = 100\cos {30.0^o} \cr
& \Rightarrow {F_A} = 100 \times \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2} = 86.6 \cr
& \therefore {F_A} = 86.6N \cr} $
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
Always draw a free body diagram, to analyze the forces acting on the system. It helps in knowing the cancellation or interaction of forces and the direction of acceleration of the body. Though in our problem there’s no acceleration, it helps find the equilibrium of forces. In a free body diagram (or F.B.D.) consider the object of interest as a point object and draw the forces acting on it.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




