
When the imidazole ring of Histidine is protonated, the tendency of nitrogen to be protonated (proton migrates from-COOH) is in the order?
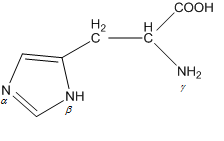
A. $\beta > \gamma > \alpha $
B. $\gamma > \beta > \alpha $
C. $\gamma > \alpha > \beta $
D. $\beta > \alpha > \gamma $

Answer
571.8k+ views
Hint: We know that protonation is the process of transfer of transfer of proton $\left( {{{\rm{H}}^{\rm{ + }}}} \right)$ from one atom to another. Here, we have to check the order in which three nitrogen atoms are protonated.
Complete step by step answer:
Here, $\gamma $ nitrogen is nearby to the COOH. And we know that protonation takes place first in the nearby atom from which hydrogen atoms get protonated. So, protonation occurs first in $\gamma $ nitrogen.
In $\beta $ nitrogen, the protonation results in counter resonance as from both sides double bonds try to break due to which resonance is nullified.
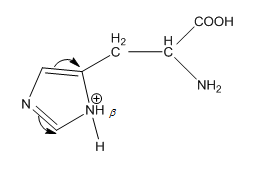
In $\alpha $ nitrogen, the lone pair of N is in resonance.
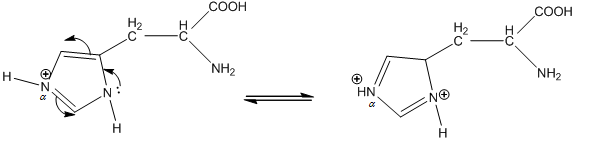
We know that the resonance makes a compound stable.Therefore, protonation occurs before $\alpha $ nitrogen than $\beta $ nitrogen.
So, the order of protonation is $\gamma > \alpha > \beta $.
So, the correct answer is Option C.
Additional Information:
Protonation is a known fundamental chemical reaction. It is a step of many catalytic and stoichiometric processes. If a molecule or ion can undergo more than one protonation it is termed as polybasic acid. Deprotonation is the reverse of protonation reaction. In deprotonation reaction, a proton is removed from a compound. This reaction occurs in most acid-base reactions. Substances that can protonate another substance are termed as Bronsted Lowry acid.
Note: Always remember that resonance stabilizes a compound. Resonance is the phenomenon as a result of which a molecule can be expressed in different forms, none of which can explain all the properties of the molecule. The actual structure of the molecule is termed a resonance hybrid.
Complete step by step answer:
Here, $\gamma $ nitrogen is nearby to the COOH. And we know that protonation takes place first in the nearby atom from which hydrogen atoms get protonated. So, protonation occurs first in $\gamma $ nitrogen.
In $\beta $ nitrogen, the protonation results in counter resonance as from both sides double bonds try to break due to which resonance is nullified.

In $\alpha $ nitrogen, the lone pair of N is in resonance.

We know that the resonance makes a compound stable.Therefore, protonation occurs before $\alpha $ nitrogen than $\beta $ nitrogen.
So, the order of protonation is $\gamma > \alpha > \beta $.
So, the correct answer is Option C.
Additional Information:
Protonation is a known fundamental chemical reaction. It is a step of many catalytic and stoichiometric processes. If a molecule or ion can undergo more than one protonation it is termed as polybasic acid. Deprotonation is the reverse of protonation reaction. In deprotonation reaction, a proton is removed from a compound. This reaction occurs in most acid-base reactions. Substances that can protonate another substance are termed as Bronsted Lowry acid.
Note: Always remember that resonance stabilizes a compound. Resonance is the phenomenon as a result of which a molecule can be expressed in different forms, none of which can explain all the properties of the molecule. The actual structure of the molecule is termed a resonance hybrid.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




