
In a convergent beam of light, all the light rays meet at a point.
A. True
B. False
Answer
584.7k+ views
Hint: Concave mirrors are known as converging mirrors because they collect all the light falling on them coming from infinity. At different points of the mirror, light gets reflected at different angles and tends to end up on the same point i.e., focus of the mirror.
Complete step by step answer:
Convergent beams of light ray change their direction and meet at a point known as focus.
For a concave mirror, rays of light travelling parallel before reflection meet at the focus and the ray through the focus reflects as parallel to the principal axis. Also, the ray through the center of curvature of the mirror reflects back through the same path. Beam of light meets on the same side of the source.
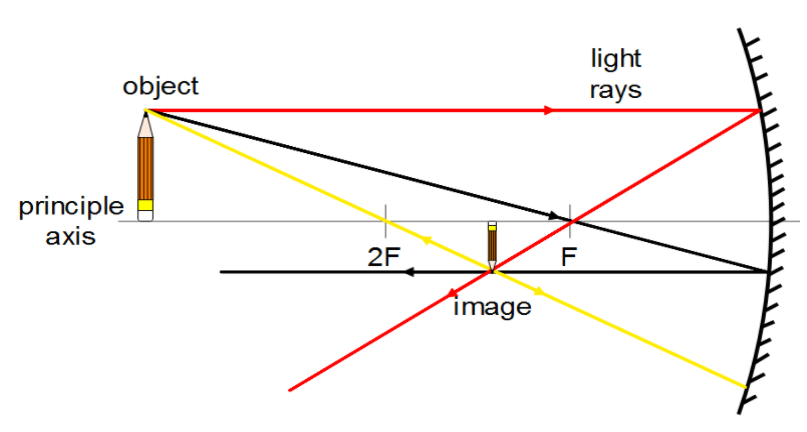
For a convex lens, the parallel rays of light to the principal axis refract to meet at the focus and the ray through the pole goes through the lens without any deviation. Beam of light meets at the opposite side of the source.
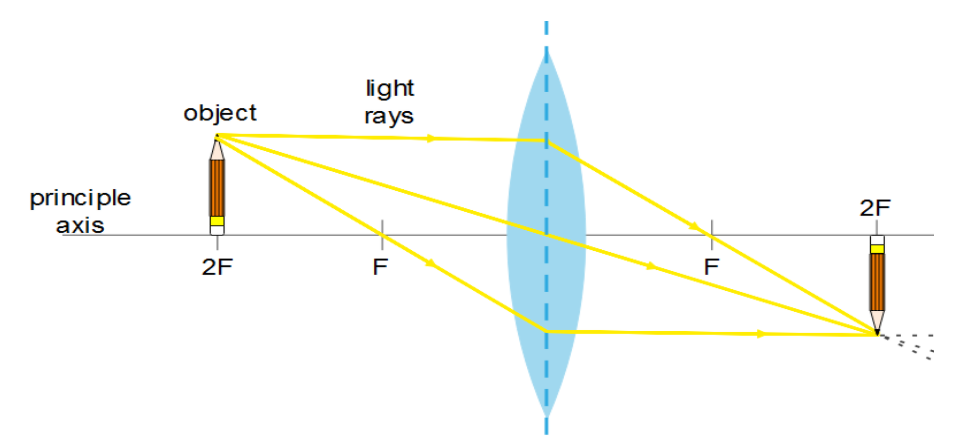
Thus it is true that in a convergent beam of light, all light meets at a point.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Additional Information: A concave mirror is also known as converging mirror. It has a reflecting surface that is bent away from the incoming light. Concave mirrors concentrate light inward to one focal point. They are used to focus light. Depending upon the distance between the object and the mirror, a concave mirror can provide different types of images.
Note: Concave mirrors are used in reflecting telescopes. They are also used to provide a magnified image when the object is placed between focus and the pole. So such mirrors can be used for make up or shaving. Concave mirrors are used to produce a beam of light by gathering light from a smaller source. Divergent beams of light are the light rays from a point source that travels in all directions. Optical instruments have the ability to bend the beam of light according to their requirement.
Complete step by step answer:
Convergent beams of light ray change their direction and meet at a point known as focus.
For a concave mirror, rays of light travelling parallel before reflection meet at the focus and the ray through the focus reflects as parallel to the principal axis. Also, the ray through the center of curvature of the mirror reflects back through the same path. Beam of light meets on the same side of the source.

For a convex lens, the parallel rays of light to the principal axis refract to meet at the focus and the ray through the pole goes through the lens without any deviation. Beam of light meets at the opposite side of the source.

Thus it is true that in a convergent beam of light, all light meets at a point.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Additional Information: A concave mirror is also known as converging mirror. It has a reflecting surface that is bent away from the incoming light. Concave mirrors concentrate light inward to one focal point. They are used to focus light. Depending upon the distance between the object and the mirror, a concave mirror can provide different types of images.
Note: Concave mirrors are used in reflecting telescopes. They are also used to provide a magnified image when the object is placed between focus and the pole. So such mirrors can be used for make up or shaving. Concave mirrors are used to produce a beam of light by gathering light from a smaller source. Divergent beams of light are the light rays from a point source that travels in all directions. Optical instruments have the ability to bend the beam of light according to their requirement.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




