
In a graphical solution, the redundant constraint is
( a ) which form the boundary of the feasible region
( b ) which do not optimize the objective function
( c ) which does not form the boundary of the feasible region.
( d ) which optimize the objective function
Answer
591.6k+ views
Hint: To solve this question, we will first see the meaning of redundant constraint and then with an example, we will show that if there are two constraints differ by an integer then one of the constraints can be ignored and that ignored constraint is the redundant constraint.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Before we start the solution, let us see what is LPP, what is the objective function, what is the feasible region, and what is a redundant constraint.
Linear Programming Problem ( LPP ) is a mathematical method that is used to determine the best possible outcome or solution from a given set of parameters or lists of requirements, which is represented in the form of linear relationships.
The objective function of LPP is that function which is desired to be maximized or minimized.
A feasible solution is a set of values for the decision variables that satisfies all the constraint in a linear programming problem.
Now, redundant constraints are constraints that can be omitted from a system of linear constraints without hanging the feasible region.
Let, get all definitions with an example.
Let , we have LPP problem to solve $x+2y\ge 20$ and $2x+4y\ge 40$. So, these two are constraints.
Now, let see second constraint $2x+4y\ge 40$,
We can write $2x+4y\ge 40$ as $2(x+2y)\ge 40$,
On solving we get, $x+2y\ge 20$ which is the same as the first constraint.
Therefore, $2x+4y\ge 40$ can be removed. By removing this constraint the feasible region does not change that is both constraints will show the same feasible region.
Feasible region of $x+2y\ge 20$ is,
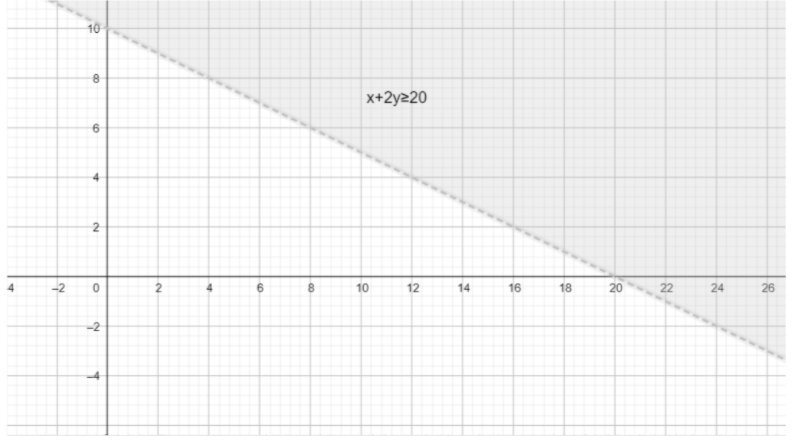
So, the redundant constraints cannot be the boundary of the feasible region.
Hence, option ( c ) is correct.
Note: This question was not numerically based but was theoretical so, for these types of questions concept of linear programming problem ( LPP ) must be remembered and must have a better understanding of definitions of the term related to LPP.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Before we start the solution, let us see what is LPP, what is the objective function, what is the feasible region, and what is a redundant constraint.
Linear Programming Problem ( LPP ) is a mathematical method that is used to determine the best possible outcome or solution from a given set of parameters or lists of requirements, which is represented in the form of linear relationships.
The objective function of LPP is that function which is desired to be maximized or minimized.
A feasible solution is a set of values for the decision variables that satisfies all the constraint in a linear programming problem.
Now, redundant constraints are constraints that can be omitted from a system of linear constraints without hanging the feasible region.
Let, get all definitions with an example.
Let , we have LPP problem to solve $x+2y\ge 20$ and $2x+4y\ge 40$. So, these two are constraints.
Now, let see second constraint $2x+4y\ge 40$,
We can write $2x+4y\ge 40$ as $2(x+2y)\ge 40$,
On solving we get, $x+2y\ge 20$ which is the same as the first constraint.
Therefore, $2x+4y\ge 40$ can be removed. By removing this constraint the feasible region does not change that is both constraints will show the same feasible region.
Feasible region of $x+2y\ge 20$ is,

So, the redundant constraints cannot be the boundary of the feasible region.
Hence, option ( c ) is correct.
Note: This question was not numerically based but was theoretical so, for these types of questions concept of linear programming problem ( LPP ) must be remembered and must have a better understanding of definitions of the term related to LPP.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




