
In a meter bridge experiment the resistance of the resistance box is $16\,\Omega $, which is inserted in the right gap. The null point is obtained at $36\,cm$from the left end. The least count of meter scale is $1\,mm.$ The value of unknown resistance is?
Answer
492.9k+ views
Hint:A metre bridge, also known as a sliding wire bridge, is a device that works on the Wheatstone bridge idea. It's used to figure out a conductor's unknown resistance. The experiment below shows how to use a metre bridge to estimate the resistance of a specific wire and the resistivity of its substance.
Complete step by step answer:
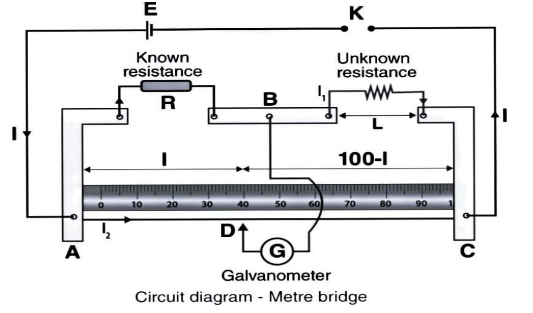
A slide wire bridge is another name for a metre bridge equipment. It is made out of a long wire with a uniform cross-sectional area that is fastened to the wooden block. The Wheatstone's bridge is made up of two gaps formed by thick metal strips.
Then, applying Wheatstone's principle, we have:
$\dfrac{X}{R} = \dfrac{l}{{(100 - l)}}$
We can calculate unknown resistance:
$X = R \times \dfrac{l}{{(100 - l)}}$
By using above formula:
$R = $Value of known resistance $ = 16\Omega $
$\Rightarrow l = length = 36\,cm$
For calculating unknown resistance formula:
$X = R \times \dfrac{l}{{(100 - l)}}$
$\Rightarrow X = 16 \times \dfrac{{36}}{{(100 - 36)}}$
$\Rightarrow X = 16 \times \dfrac{{36}}{{64}}$
$\therefore X = 9\Omega $
The accuracy with which a metre bridge can measure the value of current is known as its sensitivity. When all resistances are of the same order, the bridge is most responsive.
Note:Because of its high specific resistance or resistivity, manganin or eureka wire is utilised in metre bridges. Because copper is a good conductor of electricity, thick copper strips are utilised in metre bridges.
Complete step by step answer:
A slide wire bridge is another name for a metre bridge equipment. It is made out of a long wire with a uniform cross-sectional area that is fastened to the wooden block. The Wheatstone's bridge is made up of two gaps formed by thick metal strips.
Then, applying Wheatstone's principle, we have:
$\dfrac{X}{R} = \dfrac{l}{{(100 - l)}}$
We can calculate unknown resistance:
$X = R \times \dfrac{l}{{(100 - l)}}$

By using above formula:
$R = $Value of known resistance $ = 16\Omega $
$\Rightarrow l = length = 36\,cm$
For calculating unknown resistance formula:
$X = R \times \dfrac{l}{{(100 - l)}}$
$\Rightarrow X = 16 \times \dfrac{{36}}{{(100 - 36)}}$
$\Rightarrow X = 16 \times \dfrac{{36}}{{64}}$
$\therefore X = 9\Omega $
The accuracy with which a metre bridge can measure the value of current is known as its sensitivity. When all resistances are of the same order, the bridge is most responsive.
Note:Because of its high specific resistance or resistivity, manganin or eureka wire is utilised in metre bridges. Because copper is a good conductor of electricity, thick copper strips are utilised in metre bridges.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




