
In a metre bridge, the balancing length from the left end (standard resistance of one ohm is in the right gap) is found to be \[20{\rm{ cm}}\]. The value of the unknown resistance is
A. \[4{\rm{ }}\Omega \]
B. \[0.5{\rm{ }}\Omega \]
C. \[0.4{\rm{ }}\Omega \]
D. \[0.25{\rm{ }}\Omega \]
Answer
586.5k+ views
Hint: The ratio of resistances on the left end and right end of the given meter bridge will be equal to the ratio of the distance between the left end and right end and jockey. We will use this expression for the metre bridge to calculate the value of unknown resistance.
Complete step by step answer:
Given:
The balancing length from the left end is \[l = 20{\rm{ cm}}\].
The value of resistance in the right gap is \[{R_2} = 1{\rm{ }}\Omega \].
We have to find the value of unknown resistance \[{R_2}\].
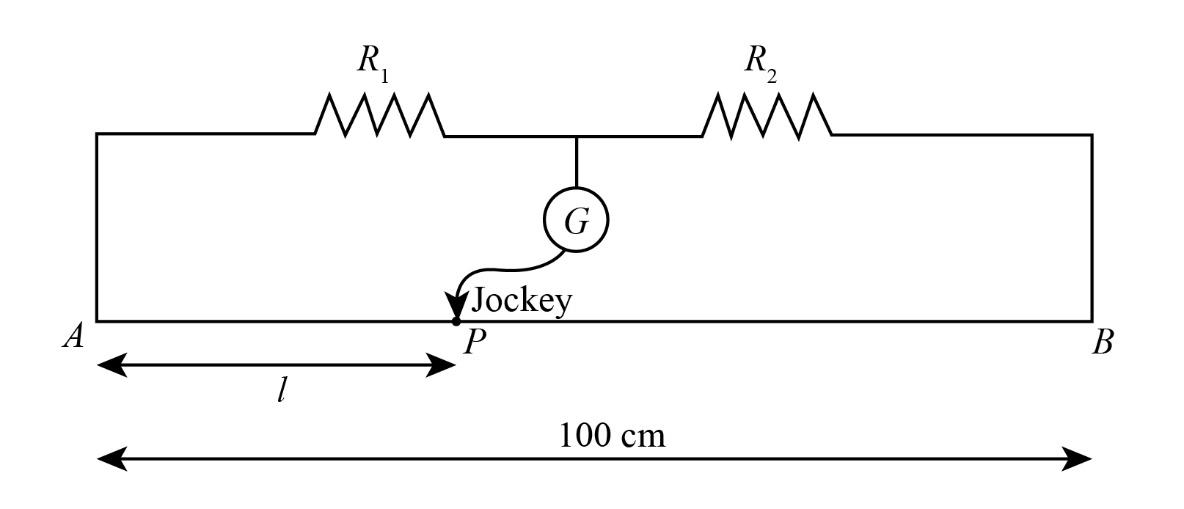
It is given that the metre bridge is in a balanced condition, so the value of the current through the jockey will be zero.
We can write the expression for balanced metre bridge as below:
\[\dfrac{{{R_1}}}{{{R_2}}} = \dfrac{{{\rm{AP}}}}{{{\rm{BP}}}}\]……(1)
We know that the length of the metre bridge is \[100{\rm{ cm}}\].
\[{\rm{AB}} = 100{\rm{ cm}}\]
Therefore from the above diagram, we can say that the distance between point B and point P is \[\left( {100 - l} \right){\rm{ cm}}\].
\[{\rm{BP}} = \left( {100{\rm{ cm}} - l} \right)\]
Substitute \[l\] for AP and \[\left( {100{\rm{ cm}} - l} \right)\] for BP in equation (1).
\[\dfrac{{{R_1}}}{{{R_2}}} = \dfrac{l}{{\left( {100{\rm{ cm}} - l} \right)}}\]
Substitute \[20{\rm{ cm}}\] for l and \[1{\rm{ }}\Omega \] for \[{R_2}\] in the above expression.
\[\begin{array}{l}
\dfrac{{{R_1}}}{{1{\rm{ }}\Omega }} = \dfrac{{20{\rm{ cm}}}}{{100{\rm{ cm}} - 20{\rm{ cm}}}}\\
{R_1} = 0.25{\rm{ }}\Omega
\end{array}\]
Therefore, the value of unknown resistance is \[0.25{\rm{ }}\Omega \]
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note:
In metre bridge, a wire of length one-metre having uniform cross-sectional area is mounted between two clips of metals which are bent at right angles in such a way that the provision for the introduction of two resistors is provided. A battery is connected to the endpoints of the wire. Also, there is a galvanometer whose one end is connected to the strip and another to a jockey. This jockey is moved across the length of the wire, and unknown resistance is calculated.
Complete step by step answer:
Given:
The balancing length from the left end is \[l = 20{\rm{ cm}}\].
The value of resistance in the right gap is \[{R_2} = 1{\rm{ }}\Omega \].
We have to find the value of unknown resistance \[{R_2}\].

It is given that the metre bridge is in a balanced condition, so the value of the current through the jockey will be zero.
We can write the expression for balanced metre bridge as below:
\[\dfrac{{{R_1}}}{{{R_2}}} = \dfrac{{{\rm{AP}}}}{{{\rm{BP}}}}\]……(1)
We know that the length of the metre bridge is \[100{\rm{ cm}}\].
\[{\rm{AB}} = 100{\rm{ cm}}\]
Therefore from the above diagram, we can say that the distance between point B and point P is \[\left( {100 - l} \right){\rm{ cm}}\].
\[{\rm{BP}} = \left( {100{\rm{ cm}} - l} \right)\]
Substitute \[l\] for AP and \[\left( {100{\rm{ cm}} - l} \right)\] for BP in equation (1).
\[\dfrac{{{R_1}}}{{{R_2}}} = \dfrac{l}{{\left( {100{\rm{ cm}} - l} \right)}}\]
Substitute \[20{\rm{ cm}}\] for l and \[1{\rm{ }}\Omega \] for \[{R_2}\] in the above expression.
\[\begin{array}{l}
\dfrac{{{R_1}}}{{1{\rm{ }}\Omega }} = \dfrac{{20{\rm{ cm}}}}{{100{\rm{ cm}} - 20{\rm{ cm}}}}\\
{R_1} = 0.25{\rm{ }}\Omega
\end{array}\]
Therefore, the value of unknown resistance is \[0.25{\rm{ }}\Omega \]
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note:
In metre bridge, a wire of length one-metre having uniform cross-sectional area is mounted between two clips of metals which are bent at right angles in such a way that the provision for the introduction of two resistors is provided. A battery is connected to the endpoints of the wire. Also, there is a galvanometer whose one end is connected to the strip and another to a jockey. This jockey is moved across the length of the wire, and unknown resistance is calculated.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




