
In a plant species, the height is controlled by four pairs of dominant polygenes in an additive way. If the tallest one is 20 feet and the shortest one is 4 feet, then how much height is contributed by each dominant allele.
Answer
569.7k+ views
Hint: The dominant genes control the trait for a particular organism. The recessive genes only show their trait when they are present in the homozygous condition. In heterozygous dominant the trait expressed is that of the dominant gene.
Complete answer:
In the above question we are given that the height of a plant is controlled by the four pairs of dominant genes or eight dominant alleles. The short height of the plant is controlled only by the recessive genes. So, we need to subtract the height given which is 20 and 4 feet. That would give us 16 feet. These 16 feet of the height needs to be divided into the 8 dominant alleles present. Then each allele present has a contribution of 2 feet in height.
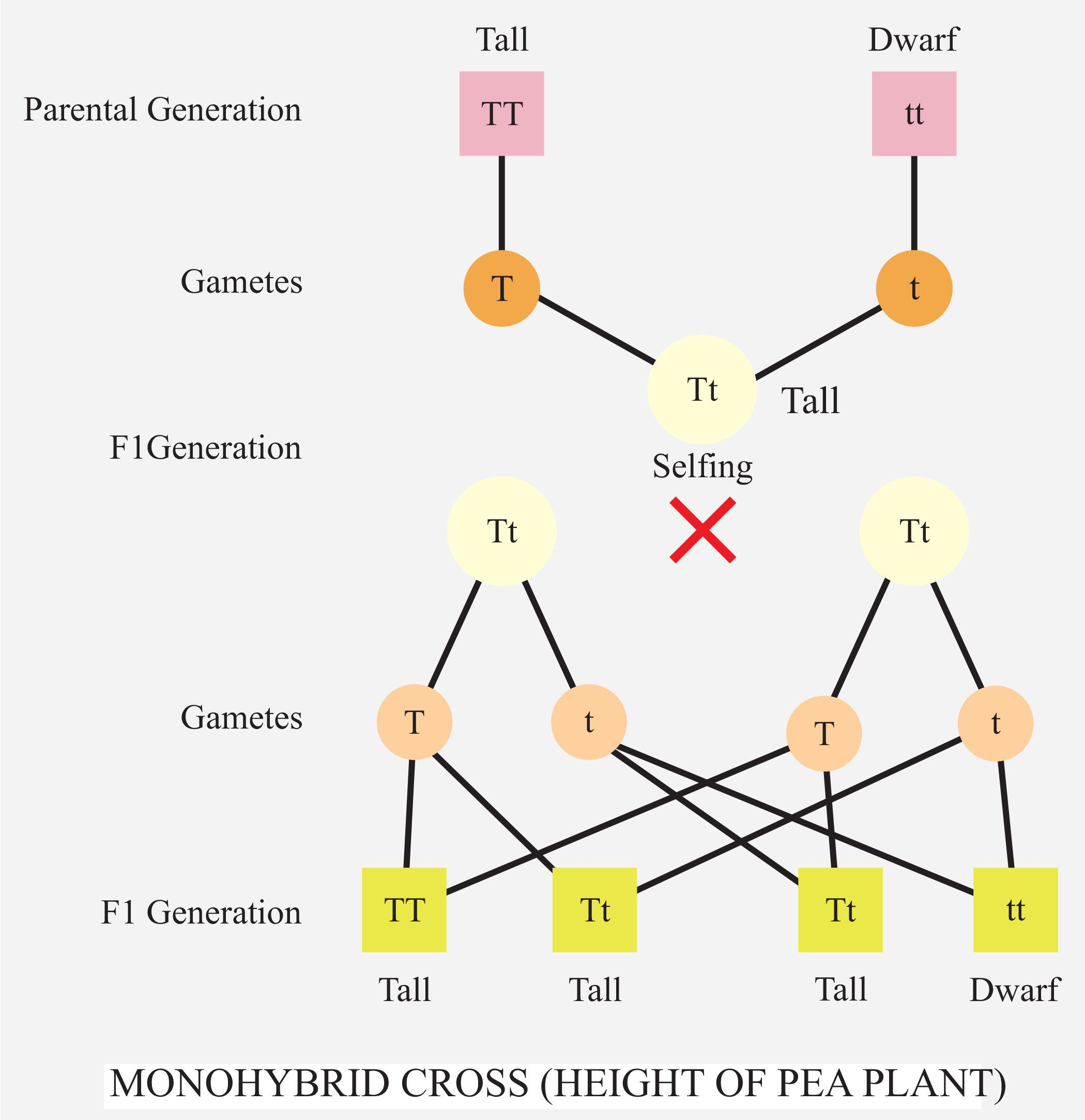
Mendel in his experiment used the pea plants and he had noticed seven characters in the pea plant regarding his experiment. Using this experiment, he provided laws of inheritance. Punnett square is used to find the probability of the genes that would be present in the offspring. The law of equal segregation states that every organism has two alleles present in them and out of them one was passed onto the offspring. The law of independent assortment states that the two genes each of opposite character separate independently during the gamete formation and lead to the recombination in the offspring.
Note: The Mendel’s laws were very useful in studying the genes and characters present in the organism but it also had some exceptions. The rules of Mendel’s do not apply to the polygenic traits, intermediate expression, codominance, multiple alleles, incomplete penetrance, pleiotropy environmental influence, and regulator genes.
Complete answer:
In the above question we are given that the height of a plant is controlled by the four pairs of dominant genes or eight dominant alleles. The short height of the plant is controlled only by the recessive genes. So, we need to subtract the height given which is 20 and 4 feet. That would give us 16 feet. These 16 feet of the height needs to be divided into the 8 dominant alleles present. Then each allele present has a contribution of 2 feet in height.

Mendel in his experiment used the pea plants and he had noticed seven characters in the pea plant regarding his experiment. Using this experiment, he provided laws of inheritance. Punnett square is used to find the probability of the genes that would be present in the offspring. The law of equal segregation states that every organism has two alleles present in them and out of them one was passed onto the offspring. The law of independent assortment states that the two genes each of opposite character separate independently during the gamete formation and lead to the recombination in the offspring.
Note: The Mendel’s laws were very useful in studying the genes and characters present in the organism but it also had some exceptions. The rules of Mendel’s do not apply to the polygenic traits, intermediate expression, codominance, multiple alleles, incomplete penetrance, pleiotropy environmental influence, and regulator genes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




