
In a pure capacitive A.C circuit current and voltage differs in the phase by:
$A.{{0}^{0}}$
$B.{{45}^{0}}$
$C.{{90}^{0}}$
$D.{{180}^{0}}$
Answer
579k+ views
Hint: To find the phase in pure capacitors, first find the expressions for current flow through capacitor. Write an equation of potential difference across its plates i.e., capacitor plate at instant which is given as $e=\dfrac{q}{c}.q=ec,$ differentiate this with respect to t. You will get an expression which will give a relation between current, frequency, capacitance and phase as ($\omega t$). Convert it in standard form i.e., $e={{e}_{0}}\sin \omega t$ and calculate the value of the phase difference between current and voltage.
Complete answer:
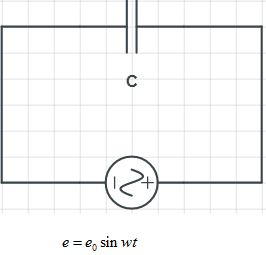
Consider an EMF (A.C) $e={{e}_{0}}\sin \omega t$ applied across a capacitor of capacitance ‘c’ as shown in the above figure. If q be the magnitude of the charge on any one plate of a capacitor at any instant, then the potential difference across its plates at that instant is given by,
$v=\dfrac{q}{c}$
Above equation is equal to the instantaneous value of the applied EMF (e).
$\begin{align}
& \therefore e=\dfrac{q}{c} \\
& \Rightarrow q=ce \\
\end{align}$
Put the value of $e={{e}_{0}}\sin \omega t$
$q = c ({{e}_{0}}\sin \omega t)$
Now differentiate on both side, we get
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{dq}{dt}=\dfrac{d}{dt}\left( \omega c{{e}_{0}}\sin \omega t \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dq}{dt}=\omega c{{e}_{0}}\cos \omega t \\
\end{align}$
We know that,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{dq}{dt}=I \\
&\Rightarrow I=\omega c{{e}_{0}}\cos \omega t \\
\end{align}$
This is the expression of the instantaneous current.
If $\omega c{{e}_{0}}={{i}_{0}}$ then
$I={{I}_{0}}\cos wt={{i}_{0}}\sin \left( \omega t+\dfrac{\pi }{2} \right).......(1)$
Now if you compare equation (1) with $e={{e}_{0}}\sin \omega t$
Then we conclude that EMF or voltage across the capacitor lags behind the current by $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ rad phase.
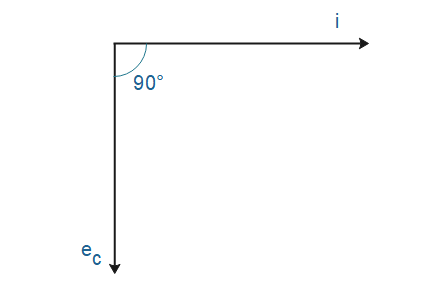
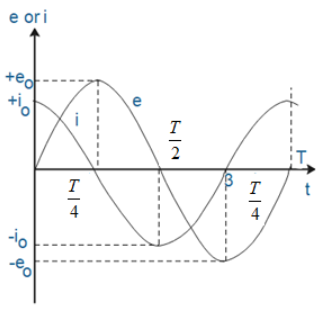
Hence in a pure capacitor AC circuit current and voltage differs in phase by ${{90}^{0}}$.
Therefore option (C) is correct.
Note:
In pure AC capacitors, voltage across the capacitor lags behind the current by ${{90}^{0}}$ or can be said as current leads the E.M.F or voltage by ${{90}^{0}}$, whereas in case of the pure inductors, voltage leads to the current by the phase $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ rad or can be said as current lags behind the E.M.F or voltage by $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ rad. In case of pure resistance, no phase has occurred since the resistor does not depend on AC frequency. In this case, current and voltage both are sinusoidal in the nature of the same frequency.
Complete answer:

Consider an EMF (A.C) $e={{e}_{0}}\sin \omega t$ applied across a capacitor of capacitance ‘c’ as shown in the above figure. If q be the magnitude of the charge on any one plate of a capacitor at any instant, then the potential difference across its plates at that instant is given by,
$v=\dfrac{q}{c}$
Above equation is equal to the instantaneous value of the applied EMF (e).
$\begin{align}
& \therefore e=\dfrac{q}{c} \\
& \Rightarrow q=ce \\
\end{align}$
Put the value of $e={{e}_{0}}\sin \omega t$
$q = c ({{e}_{0}}\sin \omega t)$
Now differentiate on both side, we get
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{dq}{dt}=\dfrac{d}{dt}\left( \omega c{{e}_{0}}\sin \omega t \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dq}{dt}=\omega c{{e}_{0}}\cos \omega t \\
\end{align}$
We know that,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{dq}{dt}=I \\
&\Rightarrow I=\omega c{{e}_{0}}\cos \omega t \\
\end{align}$
This is the expression of the instantaneous current.
If $\omega c{{e}_{0}}={{i}_{0}}$ then
$I={{I}_{0}}\cos wt={{i}_{0}}\sin \left( \omega t+\dfrac{\pi }{2} \right).......(1)$
Now if you compare equation (1) with $e={{e}_{0}}\sin \omega t$
Then we conclude that EMF or voltage across the capacitor lags behind the current by $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ rad phase.


Hence in a pure capacitor AC circuit current and voltage differs in phase by ${{90}^{0}}$.
Therefore option (C) is correct.
Note:
In pure AC capacitors, voltage across the capacitor lags behind the current by ${{90}^{0}}$ or can be said as current leads the E.M.F or voltage by ${{90}^{0}}$, whereas in case of the pure inductors, voltage leads to the current by the phase $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ rad or can be said as current lags behind the E.M.F or voltage by $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ rad. In case of pure resistance, no phase has occurred since the resistor does not depend on AC frequency. In this case, current and voltage both are sinusoidal in the nature of the same frequency.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




