
In an experiment to determine the resistance of a galvanometer by half deflection method, the circuit shown is used. In one set of readings, if $R=10\Omega $ and $S=4\Omega $, then the resistance of the galvanometer is
$\begin{align}
& \text{A}\text{. }\dfrac{20}{3}\Omega \\
& \text{B}\text{. }\dfrac{40}{3}\Omega \\
& \text{C}\text{. }\dfrac{50}{3}\Omega \\
& \text{D}\text{. }\dfrac{10}{3}\Omega \\
\end{align}$
Answer
583.5k+ views
Hint: A galvanometer is an electronic device used to detect feeble electric current flowing in a circuit. It consists of a magnetic coil suspended between the poles of a powerful magnet. As current passes through the coil, it deflects. Its motion can be detected from the deflection in the galvanometer needle. The deflection is proportional to the current passed through the galvanometer.
Complete step by step answer:
A galvanometer is a type of an electromechanical device which is used for detecting and indicating an electric current through a circuit. A galvanometer basically works like an actuator, by producing a rotatory deflection of the pointer, in response to the electric current flowing through a coil placed in a uniform and constant magnetic field. It is a sensitive device which can measure low currents even of the order of a few microamperes.
Principle of working of galvanometer – A current carrying coil when placed in an external magnetic field experiences magnetic torque. The angle by which the coil is deflected due to the effect of the magnetic torque is proportional to the magnitude of current in the coil.
Half-deflection method for measuring the current through the galvanometer:
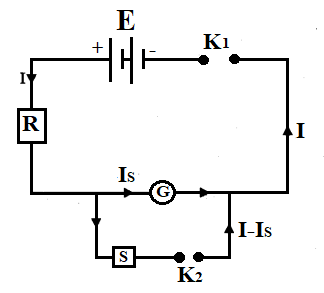
When key ${{K}_{1}}$ is closed, the current through the galvanometer is,
${{I}_{G}}=\dfrac{E}{R+G}$
(Let’s say equation 1)
If $\theta $ is the deflection shown in the galvanometer due to the flow of current ${{I}_{G}}$ , then,
${{I}_{G}}\propto \theta $
Or,
${{I}_{G}}=k\theta $
(Let’s say equation 2)
Where,
$k$ is known as the figure of merit
Using equation 1 and equation 2,
$\dfrac{E}{R+G}=k\theta $
(Let’s say equation 3)
When key ${{K}_{2}}$ is closed, the current through the galvanometer is,
$\left( {{I}_{G}} \right)'=\dfrac{S}{G+S}\times I$
Where,
$I$ is the current flowing in the main circuit
Now,
The value of $S$ is adjusted in a way that the deflection $\theta $ will be half, that is, $\dfrac{\theta }{2}$
Thus,
$\left( {{I}_{G}} \right)'=k\left( \dfrac{\theta }{2} \right)$
Put $\left( {{I}_{G}} \right)'=\dfrac{S}{G+S}\times I$
We get,
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{S}{G+S}\times I=k\left( \dfrac{\theta }{2} \right)$
(Let’s say equation 4)
Total resistance of the circuit is given as,
${{R}_{t}}=R+\dfrac{SG}{S+G}$
Thus,
$I=\dfrac{E}{{{R}_{t}}}$
Put ${{R}_{t}}=R+\dfrac{SG}{S+G}$
We get,
$\Rightarrow I=\dfrac{E}{R+\dfrac{SG}{S+G}}$
(Let’s say equation 5)
Diving equation 4 by equation 3,
$\dfrac{\dfrac{S}{G+S}\times I}{\dfrac{E}{R+G}}=\dfrac{k\left( \dfrac{\theta }{2} \right)}{k\theta }$
Or,
$\dfrac{SI\left( R+G \right)}{\left( G+S \right)E}=\dfrac{1}{2}$
(Let’s say equation 6)
Now,
Substituting the value of $I$ in equation 6 using the equation 5,
$I=\dfrac{E}{R+\dfrac{SG}{S+G}}$
Solving above,
$ S\left( \dfrac{E}{R+\dfrac{SG}{S+G}} \right)\dfrac{\left( R+G \right)}{\left( G+S \right)E}=\dfrac{1}{2} $
$\Rightarrow S\left( \dfrac{E}{\dfrac{R\left( S+G \right)+SG}{S+G}} \right)\dfrac{\left( R+G \right)}{\left( G+S \right)E}=\dfrac{1}{2} $
$ \dfrac{S\left( R+G \right)}{R\left( S+G \right)+SG}=\dfrac{1}{2} $
$\Rightarrow 2S\left( R+G \right)=R\left( S+G \right)+SG $
$\Rightarrow 2S\left( R+G \right)=S\left( R+G \right)+RG $
$\Rightarrow S\left( R+G \right)=RG $
$\Rightarrow RS=G\left( R-S \right)$
$\Rightarrow G=\dfrac{RS}{R-S} $
We get,
$\Rightarrow I=\dfrac{E}{R+\dfrac{SG}{S+G}}$
We get,
$\Rightarrow G=\dfrac{RS}{R-S}$
Putting the given values,
$\begin{align}
& R=10\Omega \\
& S=4\Omega \\
\end{align}$
We get,
$\Rightarrow G=\dfrac{10\times 4}{10-4}=\dfrac{40}{6} $
$\Rightarrow G=\dfrac{20}{3}\Omega $
The resistance of the galvanometer is $\dfrac{20}{3}\Omega $
Hence, the correct option is A.
Note:
A resistor having a very small value of resistance is called a Shunt resistance and it is always connected in parallel in a circuit. Shunt resistance is used for converting a galvanometer into ammeter as most of the current will flow through it and only a small fraction of current will flow through the galvanometer, which is sufficient to make a deflection. Figure of merit is a numerical that represents the degree of efficiency or effectiveness of an instrument approximated by the different estimation techniques.
Complete step by step answer:
A galvanometer is a type of an electromechanical device which is used for detecting and indicating an electric current through a circuit. A galvanometer basically works like an actuator, by producing a rotatory deflection of the pointer, in response to the electric current flowing through a coil placed in a uniform and constant magnetic field. It is a sensitive device which can measure low currents even of the order of a few microamperes.
Principle of working of galvanometer – A current carrying coil when placed in an external magnetic field experiences magnetic torque. The angle by which the coil is deflected due to the effect of the magnetic torque is proportional to the magnitude of current in the coil.
Half-deflection method for measuring the current through the galvanometer:

When key ${{K}_{1}}$ is closed, the current through the galvanometer is,
${{I}_{G}}=\dfrac{E}{R+G}$
(Let’s say equation 1)
If $\theta $ is the deflection shown in the galvanometer due to the flow of current ${{I}_{G}}$ , then,
${{I}_{G}}\propto \theta $
Or,
${{I}_{G}}=k\theta $
(Let’s say equation 2)
Where,
$k$ is known as the figure of merit
Using equation 1 and equation 2,
$\dfrac{E}{R+G}=k\theta $
(Let’s say equation 3)
When key ${{K}_{2}}$ is closed, the current through the galvanometer is,
$\left( {{I}_{G}} \right)'=\dfrac{S}{G+S}\times I$
Where,
$I$ is the current flowing in the main circuit
Now,
The value of $S$ is adjusted in a way that the deflection $\theta $ will be half, that is, $\dfrac{\theta }{2}$
Thus,
$\left( {{I}_{G}} \right)'=k\left( \dfrac{\theta }{2} \right)$
Put $\left( {{I}_{G}} \right)'=\dfrac{S}{G+S}\times I$
We get,
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{S}{G+S}\times I=k\left( \dfrac{\theta }{2} \right)$
(Let’s say equation 4)
Total resistance of the circuit is given as,
${{R}_{t}}=R+\dfrac{SG}{S+G}$
Thus,
$I=\dfrac{E}{{{R}_{t}}}$
Put ${{R}_{t}}=R+\dfrac{SG}{S+G}$
We get,
$\Rightarrow I=\dfrac{E}{R+\dfrac{SG}{S+G}}$
(Let’s say equation 5)
Diving equation 4 by equation 3,
$\dfrac{\dfrac{S}{G+S}\times I}{\dfrac{E}{R+G}}=\dfrac{k\left( \dfrac{\theta }{2} \right)}{k\theta }$
Or,
$\dfrac{SI\left( R+G \right)}{\left( G+S \right)E}=\dfrac{1}{2}$
(Let’s say equation 6)
Now,
Substituting the value of $I$ in equation 6 using the equation 5,
$I=\dfrac{E}{R+\dfrac{SG}{S+G}}$
Solving above,
$ S\left( \dfrac{E}{R+\dfrac{SG}{S+G}} \right)\dfrac{\left( R+G \right)}{\left( G+S \right)E}=\dfrac{1}{2} $
$\Rightarrow S\left( \dfrac{E}{\dfrac{R\left( S+G \right)+SG}{S+G}} \right)\dfrac{\left( R+G \right)}{\left( G+S \right)E}=\dfrac{1}{2} $
$ \dfrac{S\left( R+G \right)}{R\left( S+G \right)+SG}=\dfrac{1}{2} $
$\Rightarrow 2S\left( R+G \right)=R\left( S+G \right)+SG $
$\Rightarrow 2S\left( R+G \right)=S\left( R+G \right)+RG $
$\Rightarrow S\left( R+G \right)=RG $
$\Rightarrow RS=G\left( R-S \right)$
$\Rightarrow G=\dfrac{RS}{R-S} $
We get,
$\Rightarrow I=\dfrac{E}{R+\dfrac{SG}{S+G}}$
We get,
$\Rightarrow G=\dfrac{RS}{R-S}$
Putting the given values,
$\begin{align}
& R=10\Omega \\
& S=4\Omega \\
\end{align}$
We get,
$\Rightarrow G=\dfrac{10\times 4}{10-4}=\dfrac{40}{6} $
$\Rightarrow G=\dfrac{20}{3}\Omega $
The resistance of the galvanometer is $\dfrac{20}{3}\Omega $
Hence, the correct option is A.
Note:
A resistor having a very small value of resistance is called a Shunt resistance and it is always connected in parallel in a circuit. Shunt resistance is used for converting a galvanometer into ammeter as most of the current will flow through it and only a small fraction of current will flow through the galvanometer, which is sufficient to make a deflection. Figure of merit is a numerical that represents the degree of efficiency or effectiveness of an instrument approximated by the different estimation techniques.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




