
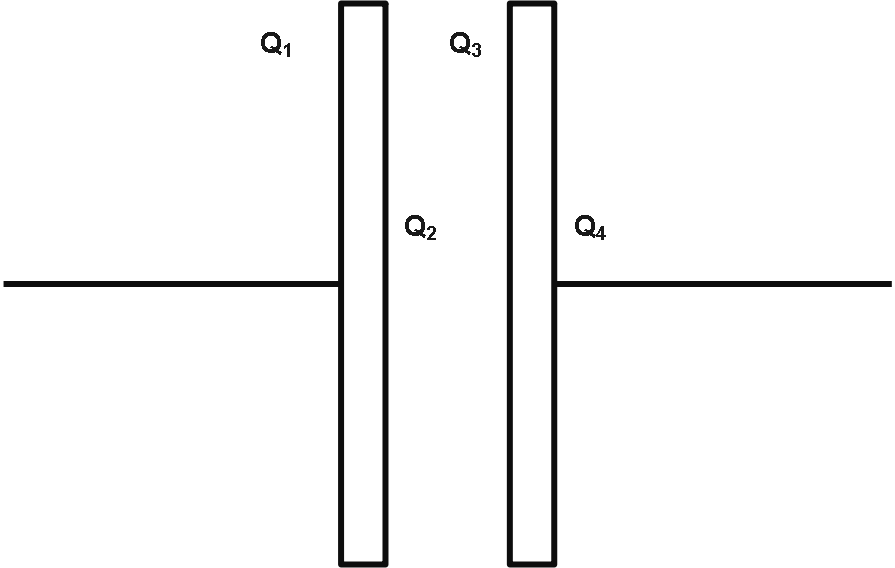
In an isolated parallel plate capacitor of capacitance $C$ , the four surfaces have charges ${Q_1},{Q_2},{Q_3}$ and ${Q_4}$ as shown. The potential difference between the plates is:
(a). $\dfrac{{{Q_1} + {Q_2} + {Q_3} + {Q_4}}}{{2C}}$
(b). $\dfrac{{{Q_2} + {Q_3}}}{{2C}}$
(c). $\dfrac{{{Q_2} - {Q_3}}}{{2C}}$
(d). $\dfrac{{{Q_1} + {Q_4}}}{{2C}}$

Answer
495k+ views
Hint: In order to solve this question, one must know about parallel plate capacitors. Here we have used the property that Facing surfaces have equal and opposite charges and then put the values in formula and then added both the equations to get the potential difference.
Formula used:
$Q = CV$
Where,
$Q$ is the charge,
$C$ is the capacitance and
$V$ is the voltage.
Complete answer:
As we know that the charge on a capacitor means the charge on the inner surface of the positive plate.
We also know that,
Facing surfaces have equal and opposite charges.
i.e., ${Q_3} = - {Q_2}$
And we know that the potential difference between the plates is equal to the charge on the capacitor divided by capacitance.
$\therefore V = \dfrac{{{Q_2}}}{C}$ -----(1)
Also, we can write
$\therefore V = \dfrac{{ - {Q_3}}}{C}$ -----(2) because ${Q_3} = - {Q_2}$ .
Now let’s add both the equation,
$
2V = \dfrac{{{Q_2} - {Q_3}}}{C} \\
\Rightarrow V = \dfrac{{{Q_2} - {Q_3}}}{{2C}} \\
$
So, the potential difference between the plates is $V = \dfrac{{{Q_2} - {Q_3}}}{{2C}}$ .
Hence, the correct option is (c).
Note:
Here we have to take care that if the charge is negative, we will not put the negative sign while calculating the potential difference. Also, there would be two electric fields for the two plates of the capacitor.
Formula used:
$Q = CV$
Where,
$Q$ is the charge,
$C$ is the capacitance and
$V$ is the voltage.
Complete answer:
As we know that the charge on a capacitor means the charge on the inner surface of the positive plate.
We also know that,
Facing surfaces have equal and opposite charges.
i.e., ${Q_3} = - {Q_2}$
And we know that the potential difference between the plates is equal to the charge on the capacitor divided by capacitance.
$\therefore V = \dfrac{{{Q_2}}}{C}$ -----(1)
Also, we can write
$\therefore V = \dfrac{{ - {Q_3}}}{C}$ -----(2) because ${Q_3} = - {Q_2}$ .
Now let’s add both the equation,
$
2V = \dfrac{{{Q_2} - {Q_3}}}{C} \\
\Rightarrow V = \dfrac{{{Q_2} - {Q_3}}}{{2C}} \\
$
So, the potential difference between the plates is $V = \dfrac{{{Q_2} - {Q_3}}}{{2C}}$ .
Hence, the correct option is (c).
Note:
Here we have to take care that if the charge is negative, we will not put the negative sign while calculating the potential difference. Also, there would be two electric fields for the two plates of the capacitor.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




