
In ${\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{3}}}$, the B-F bond length is 1.30 A. When ${\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{3}}}$ is allowed to react with ${\text{M}}{{\text{e}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{N}}$, it forms an adduct, ${\text{M}}{{\text{e}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{N}} \to {\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{3}}}$. The bond length of B-F in the adduct is:
A. Greater than 1.30 A
B. Smaller than 1.30 A
C. Equal to 1.30 A
D. None of these
Answer
585.9k+ views
Hint: In this question, we will consider the concept of back bonding in the case of ${\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{3}}}$. Back bonding happens between the atom having lone pair of an electron, whereas the other atom has a vacant orbital, a pi bond will be formed. Back bonding affects the bond length, but when an adduct is formed there will be no back bonding.
Complete step by step answer:
-First, we will discuss the back bonding in the case of ${\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{3}}}$ molecule.
-In this molecule, boron and fluorine both contains an empty p-orbital, whereas the p-orbital of fluorine contains a lone pair of electrons as shown:
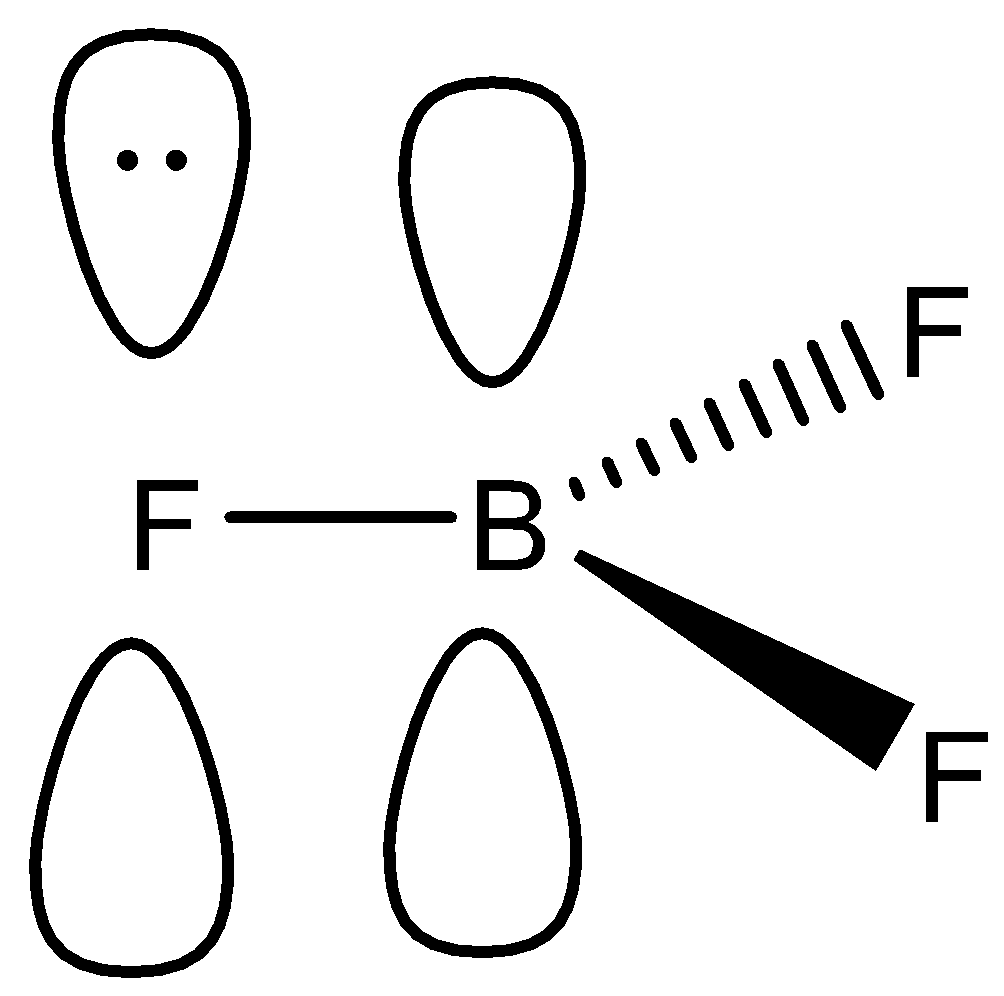
-Now, in this case, fluorine will donate its lone pair to the boron, and there will be the formation of a pi bond as mentioned. We know that this is also known as back bonding.
-If we talk about the bond length, then back bonding leads to the decrease in bond length, but the bond angle remains the same.
-We can say that double bond characteristics are being imparted with back bonding.
-As we know, when ${\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{3}}}$ reacts with the ${\text{M}}{{\text{e}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{N}}$, it forms an adduct.
-Thus, in the adduct, there will be no back bonding, and the double bond characteristics disappear.
-We can say that the no longer presence of back bonding in the molecule will lead to an increase in the bond length.
-So, in the end, we can conclude that the bond length of the B-F bond in the adduct will be greater than 1.30 due to the absence of back bonding.
Hence, the correct option is A.
Note: There could be confusion as to why fluorine donates its lone pair to the boron. Then, we have seen that the fluorine contains a lone pair in its orbital, and it will act as a Lewis base. The other important point is that when an adduct is formed, there will be no pi-bond, it will again form a sigma bond. That’s why the bond length is greater than 1.30 A.
Complete step by step answer:
-First, we will discuss the back bonding in the case of ${\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{3}}}$ molecule.
-In this molecule, boron and fluorine both contains an empty p-orbital, whereas the p-orbital of fluorine contains a lone pair of electrons as shown:

-Now, in this case, fluorine will donate its lone pair to the boron, and there will be the formation of a pi bond as mentioned. We know that this is also known as back bonding.
-If we talk about the bond length, then back bonding leads to the decrease in bond length, but the bond angle remains the same.
-We can say that double bond characteristics are being imparted with back bonding.
-As we know, when ${\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{3}}}$ reacts with the ${\text{M}}{{\text{e}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{N}}$, it forms an adduct.
-Thus, in the adduct, there will be no back bonding, and the double bond characteristics disappear.
-We can say that the no longer presence of back bonding in the molecule will lead to an increase in the bond length.
-So, in the end, we can conclude that the bond length of the B-F bond in the adduct will be greater than 1.30 due to the absence of back bonding.
Hence, the correct option is A.
Note: There could be confusion as to why fluorine donates its lone pair to the boron. Then, we have seen that the fluorine contains a lone pair in its orbital, and it will act as a Lewis base. The other important point is that when an adduct is formed, there will be no pi-bond, it will again form a sigma bond. That’s why the bond length is greater than 1.30 A.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




