
In birds, 6-10 caudal vertebrae are usually fused to form
(A) Sesamoid bone
(B) Odontoid process
(C) Plow-share bone
(D) Synsacrum
Answer
579.6k+ views
Hint: It is a skeletal structure of birds and dinosaurs. This structures a more broad rigid structure than the pelvis of a vertebrate, satisfying necessity for flight, locomotion, and respiration. For accommodating the glycogen body, the central section of this skeletal structure is swollen and an organ whose function is as yet unclear but which may be associated with balance.
Complete step by step answer:
The birds have a pair of kidneys recessed into renal fossa, hard sorrows in the fused vertebrae of the synsacrum. They stretch out from the posterior edges of the lungs to the furthest limit of the synsacrum. The urinary bladder is missing in all birds. The body of the bird is adjusted for flight. One of the important adaptations for this is the fusing of bones into single ossification. The compound structure present in the bird’s vertebral column is called the synsacrum and it is formed by the fusion of 14 to 16 vertebrae.
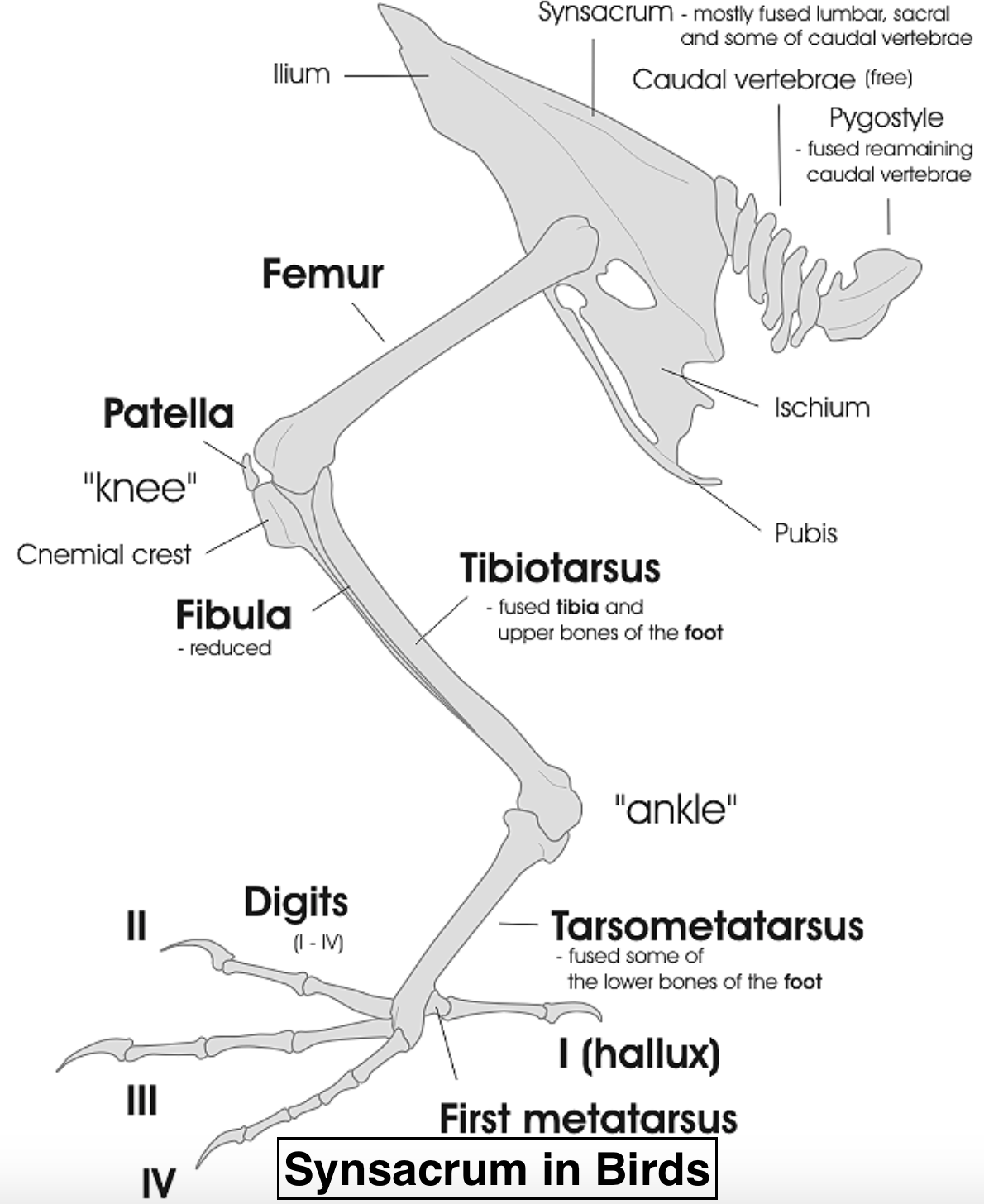
So, the correct answer is ‘ Synsacrum’.
Additional information: The association between the synsacrum and the ilium bone, which ventures far into the thoracic area, is highly significant for the shape of the trunk in the birds. With the help of spines the bony connection is achieved cranially and transverse processes and caudally by the transverse process of the synsacrum, which is fused into a continuous bony plate that allows the passage of nerves and blood vessels. Going from cranial to caudal the accompanying vertebrae in the synsacrum are separated: synsacrum thoracic, synsacrolumbar, primary sacral, and syn sacrocaudal.
Note: Acute or chronic trauma that affects the synsacrum/caudal segments can lead to urinary, intestinal, and/or cloacal autonomic dysfunction with coprostasis and marked intestinal/cloacal distension. Acute axonal injury with Wallerian degeneration is a typical result of nerve and spinal rope injury.
Complete step by step answer:
The birds have a pair of kidneys recessed into renal fossa, hard sorrows in the fused vertebrae of the synsacrum. They stretch out from the posterior edges of the lungs to the furthest limit of the synsacrum. The urinary bladder is missing in all birds. The body of the bird is adjusted for flight. One of the important adaptations for this is the fusing of bones into single ossification. The compound structure present in the bird’s vertebral column is called the synsacrum and it is formed by the fusion of 14 to 16 vertebrae.

So, the correct answer is ‘ Synsacrum’.
Additional information: The association between the synsacrum and the ilium bone, which ventures far into the thoracic area, is highly significant for the shape of the trunk in the birds. With the help of spines the bony connection is achieved cranially and transverse processes and caudally by the transverse process of the synsacrum, which is fused into a continuous bony plate that allows the passage of nerves and blood vessels. Going from cranial to caudal the accompanying vertebrae in the synsacrum are separated: synsacrum thoracic, synsacrolumbar, primary sacral, and syn sacrocaudal.
Note: Acute or chronic trauma that affects the synsacrum/caudal segments can lead to urinary, intestinal, and/or cloacal autonomic dysfunction with coprostasis and marked intestinal/cloacal distension. Acute axonal injury with Wallerian degeneration is a typical result of nerve and spinal rope injury.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




