
In $\Delta ABC$, let L, M, N be the feet of the altitudes. Then calculate $\sin \left( \angle MLN \right)+\sin \left( \angle LMN \right)+\sin \left( \angle MNL \right)$
(a) $4\sin A\sin B\sin C$
(b) $3\sin A\sin B\sin C$
(c) $2\sin A\sin B\sin C$
(d) $\sin A\sin B\sin C$
Answer
611.4k+ views
Hint:After drawing altitude we can join L, M, N to form a pedal triangle and use properties to change angles into A, B, C then use identities $\sin \left( \pi -\theta \right)=\sin \theta ,\cos \left( \pi -\theta \right)2\cos \theta $
$\sin A+\sin B=2\sin \dfrac{\left( A+B \right)}{2}\cos \dfrac{\left( A-B \right)}{2}$ and
$\cos A-\cos B=2\sin \dfrac{A+B}{2}\sin \theta \dfrac{-A}{2}$ and get results.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let’s draw a triangle ABC with altitude AL, BM and CN and then join L, M, N to form a triangle LMN, as shown below:
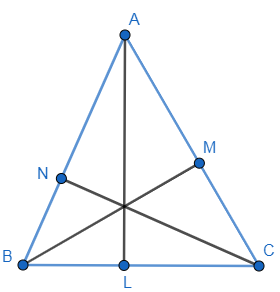
Now we will say triangle LMN is a pedal triangle of triangle ABC. Pedal triangle is a triangle that is obtained by joining points lying on the three sides of the triangle.
So, by using the property of pedal triangle we can write,
i)$\angle MLN={{180}^{\circ }}-2\times \angle A$
ii) $\angle NML={{180}^{\circ }}-2\times \angle B$
iii) $\angle MLN={{180}^{\circ }}-2\times \angle C$
Now we will find what is asked in the equation which is $\sin \left( \angle MNL \right)+\sin \left( \angle NML \right)+\sin \left( \angle MNL \right)$ which can also be written as $\sin \left( {{180}^{\circ }}-2\times \angle A \right)+\sin \left( {{180}^{\circ }}-2\times \angle B \right)+\sin \left( {{180}^{\circ }}-2\times \angle C \right)$
Now we will use the identity,
$\sin \left( {{180}^{\circ }}-\theta \right)=\sin \theta $
So instead of $\theta $ we will put values 2A, 2B, 2C so,
$\sin \left( \angle MNL \right)+\sin \left( \angle NML \right)+\sin \left( \angle MNL \right)=\sin \left( 2A \right)+\sin \left( 2B \right)+\sin \left( 2C \right)$
As we know that in triangle ABC we can say $A+B+C={{180}^{\circ }}$,
Then we can write,
$\sin \left( 2A \right)+\sin \left( 2B \right)+\sin \left( 2C \right)$ as $2\sin A\cos A+2\sin \left( B+C \right)\cos \left( B-C \right)$
Using formula $\sin 2\theta =2\sin \theta \cos \theta $ . Where $\theta $ can be replaced by A and by using another formula,
$\sin C+\sin D=2\sin \dfrac{\left( C+D \right)}{2}\cos \dfrac{\left( C-D \right)}{2}$where C can be taken as 2B and D can be taken as 2C.
So, $2\sin A\cos A+2\sin \left( B+C \right)\cos \left( B-C \right)$
Now as we know that $A+B+C=\pi $ then we can write $B+C=\pi -A$
So,$2\sin A\cos A+2\sin \left( \pi -A \right)\cos \left( B-C \right)$
Now we will use the identity $\sin \left( \pi -\theta \right)-\sin \theta $ so in place of $\theta $ we will use A.
Now we can write it as,
$2\sin A\cos A+2\operatorname{sinA}\cos \left( B-C \right)$ we take common $2\sin A$ from both the terms so we can write it as,
$2\sin A\left( \cos A+\cos \left( B-C \right) \right)$
Now we will substitute A as $\pi -\left( B+C \right)$ then $\cos \left( \pi -\left( B+C \right) \right)=-\cos \left( B+C \right)$
Using identity $\cos \left( \pi -\theta \right)=-\cos \theta $
$2\sin A\left( -\cos \left( B+C \right)+\cos \left( B-C \right) \right)$
So by rearranging and writing it as,
$2\sin A\left( \cos \left( B-C \right)-\cos \left( B+C \right) \right)$
Now we will use identity that,
$\cos \left( B-C \right)-\cos \left( B+C \right)=2\sin B\sin C$
Hence we can write it as,
$2\sin A\left( 2\sin B\sin C \right)=4\sin A\sin B\sin C$
Hence the correct option is ‘A’.
Note: Students should know all the trigonometric formulas and identities before solving the problem related like this. They should know the facts about pedal triangles too.
Students often make mistakes when considering the pedal triangle property.
$\sin A+\sin B=2\sin \dfrac{\left( A+B \right)}{2}\cos \dfrac{\left( A-B \right)}{2}$ and
$\cos A-\cos B=2\sin \dfrac{A+B}{2}\sin \theta \dfrac{-A}{2}$ and get results.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let’s draw a triangle ABC with altitude AL, BM and CN and then join L, M, N to form a triangle LMN, as shown below:

Now we will say triangle LMN is a pedal triangle of triangle ABC. Pedal triangle is a triangle that is obtained by joining points lying on the three sides of the triangle.
So, by using the property of pedal triangle we can write,
i)$\angle MLN={{180}^{\circ }}-2\times \angle A$
ii) $\angle NML={{180}^{\circ }}-2\times \angle B$
iii) $\angle MLN={{180}^{\circ }}-2\times \angle C$
Now we will find what is asked in the equation which is $\sin \left( \angle MNL \right)+\sin \left( \angle NML \right)+\sin \left( \angle MNL \right)$ which can also be written as $\sin \left( {{180}^{\circ }}-2\times \angle A \right)+\sin \left( {{180}^{\circ }}-2\times \angle B \right)+\sin \left( {{180}^{\circ }}-2\times \angle C \right)$
Now we will use the identity,
$\sin \left( {{180}^{\circ }}-\theta \right)=\sin \theta $
So instead of $\theta $ we will put values 2A, 2B, 2C so,
$\sin \left( \angle MNL \right)+\sin \left( \angle NML \right)+\sin \left( \angle MNL \right)=\sin \left( 2A \right)+\sin \left( 2B \right)+\sin \left( 2C \right)$
As we know that in triangle ABC we can say $A+B+C={{180}^{\circ }}$,
Then we can write,
$\sin \left( 2A \right)+\sin \left( 2B \right)+\sin \left( 2C \right)$ as $2\sin A\cos A+2\sin \left( B+C \right)\cos \left( B-C \right)$
Using formula $\sin 2\theta =2\sin \theta \cos \theta $ . Where $\theta $ can be replaced by A and by using another formula,
$\sin C+\sin D=2\sin \dfrac{\left( C+D \right)}{2}\cos \dfrac{\left( C-D \right)}{2}$where C can be taken as 2B and D can be taken as 2C.
So, $2\sin A\cos A+2\sin \left( B+C \right)\cos \left( B-C \right)$
Now as we know that $A+B+C=\pi $ then we can write $B+C=\pi -A$
So,$2\sin A\cos A+2\sin \left( \pi -A \right)\cos \left( B-C \right)$
Now we will use the identity $\sin \left( \pi -\theta \right)-\sin \theta $ so in place of $\theta $ we will use A.
Now we can write it as,
$2\sin A\cos A+2\operatorname{sinA}\cos \left( B-C \right)$ we take common $2\sin A$ from both the terms so we can write it as,
$2\sin A\left( \cos A+\cos \left( B-C \right) \right)$
Now we will substitute A as $\pi -\left( B+C \right)$ then $\cos \left( \pi -\left( B+C \right) \right)=-\cos \left( B+C \right)$
Using identity $\cos \left( \pi -\theta \right)=-\cos \theta $
$2\sin A\left( -\cos \left( B+C \right)+\cos \left( B-C \right) \right)$
So by rearranging and writing it as,
$2\sin A\left( \cos \left( B-C \right)-\cos \left( B+C \right) \right)$
Now we will use identity that,
$\cos \left( B-C \right)-\cos \left( B+C \right)=2\sin B\sin C$
Hence we can write it as,
$2\sin A\left( 2\sin B\sin C \right)=4\sin A\sin B\sin C$
Hence the correct option is ‘A’.
Note: Students should know all the trigonometric formulas and identities before solving the problem related like this. They should know the facts about pedal triangles too.
Students often make mistakes when considering the pedal triangle property.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




