
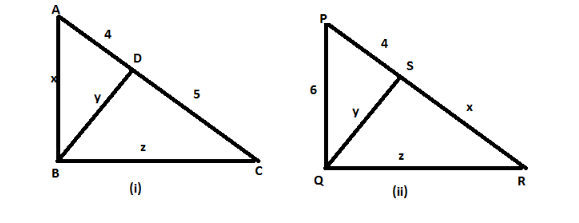
In each figure given below, altitude is drawn on hypotenuse by a right angled triangle. The length of different segments is marked in each figure. Determine x, y, z in each case.

Answer
598.5k+ views
Hint: In both cases there is a right angled triangle (Third side is an altitude) in a right angled triangle.
We can use Pythagora's theorem to establish a relation between inner triangle and outer triangle. Then by using substitution we can find x, y, z.
Complete step-by-step answer:
i.In the given figure,
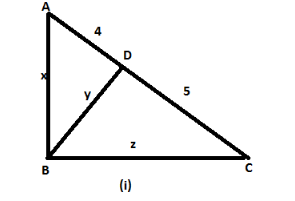
In triangle DBE by Pythagoras theorem,
(In a right triangle square of hypotenuse is equal to the sum of square of height and square of base.)
$ \begin{align}
& {{z}^{2}}={{y}^{2}}+{{5}^{2}} \\
& {{z}^{2}}={{y}^{2}}+25 \\
\end{align} $
………………….(1)
Now use Pythagoras theorem in triangle ABC
$ \begin{align}
& {{(4+5)}^{2}}={{x}^{2}}+{{z}^{2}} \\
& 81={{x}^{2}}+{{z}^{2}} \\
& {{z}^{2}}=81-{{x}^{2}} \\
\end{align} $ ………………………….(2)
From equation 1 and 2 we can conclude that,
$ \begin{align}
& {{y}^{2}}+25=81-{{x}^{2}} \\
& {{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}=81-25 \\
& {{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}=56 \\
\end{align} $ …………………..(3)
Now, in triangle ADB use Pythagoras theorem,
$ \begin{align}
& {{x}^{2}}={{y}^{2}}+16 \\
& {{x}^{2}}-{{y}^{2}}=16 \\
\end{align} $ …………………….. (4)
Now add equation 3 and 4,
$ \begin{align}
& {{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+{{x}^{2}}-{{y}^{2}}=56+16 \\
& 2{{x}^{2}}=72 \\
& {{x}^{2}}=36 \\
& x=6 \\
\end{align} $
We will ignore -6 because the side of a triangle cannot be negative.
Now, put the value of x in equation 3,
$ \begin{align}
& {{6}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}=56 \\
& {{y}^{2}}=56-36 \\
& {{y}^{2}}=20 \\
& y=2\sqrt{5} \\
\end{align} $
Ignore negative values for the same reason.
Again put the value of x in equation 2,
$ \begin{align}
& {{z}^{2}}=81-{{6}^{2}} \\
& {{z}^{2}}=81-36 \\
& {{z}^{2}}=45 \\
& z=3\sqrt{5} \\
\end{align} $
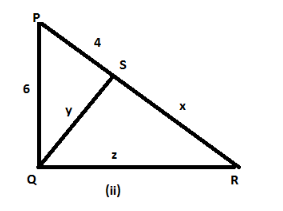
In triangle PSQ, use Pythagoras theorem,
$ \begin{align}
& {{6}^{2}}={{4}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}} \\
& 36-16={{y}^{2}} \\
& {{y}^{2}}=20 \\
& y=4\sqrt{5} \\
\end{align} $ ………………….(1)
Use Pythagoras theorem in triangle QSR,
$ \begin{align}
& {{z}^{2}}={{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}} \\
& {{z}^{2}}-{{x}^{2}}=20 \\
\end{align} $ (from equation 1) …………………….. (2)
Now, take triangle PQR and apply Pythagoras theorem in it.
$ {{6}^{2}}+{{z}^{2}}={{(x+4)}^{2}} $
From equation 2 put the value of z in it.
$ \begin{align}
& {{6}^{2}}+{{x}^{2}}+20={{x}^{2}}+16+8x \\
& 56=16+8x \\
& 8x=40 \\
& x=5 \\
& \\
\end{align} $
Put the value of x in equation 2.
$ \begin{align}
& {{z}^{2}}-{{5}^{2}}=20 \\
& {{z}^{2}}=45 \\
& z=3\sqrt{5} \\
\end{align} $
Note:In figure (i) angle D is a right angle that’s why AB and BC is hypotenuse for triangle ADB and BDC respectively. Same for figure (ii) angle S is a right angle that’s why PQ and QR are hypotenuse for triangle PSQ and triangle QSR respectively. Always ignore negative values for a side of the triangle.
We can use Pythagora's theorem to establish a relation between inner triangle and outer triangle. Then by using substitution we can find x, y, z.
Complete step-by-step answer:
i.In the given figure,

In triangle DBE by Pythagoras theorem,
(In a right triangle square of hypotenuse is equal to the sum of square of height and square of base.)
$ \begin{align}
& {{z}^{2}}={{y}^{2}}+{{5}^{2}} \\
& {{z}^{2}}={{y}^{2}}+25 \\
\end{align} $
………………….(1)
Now use Pythagoras theorem in triangle ABC
$ \begin{align}
& {{(4+5)}^{2}}={{x}^{2}}+{{z}^{2}} \\
& 81={{x}^{2}}+{{z}^{2}} \\
& {{z}^{2}}=81-{{x}^{2}} \\
\end{align} $ ………………………….(2)
From equation 1 and 2 we can conclude that,
$ \begin{align}
& {{y}^{2}}+25=81-{{x}^{2}} \\
& {{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}=81-25 \\
& {{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}=56 \\
\end{align} $ …………………..(3)
Now, in triangle ADB use Pythagoras theorem,
$ \begin{align}
& {{x}^{2}}={{y}^{2}}+16 \\
& {{x}^{2}}-{{y}^{2}}=16 \\
\end{align} $ …………………….. (4)
Now add equation 3 and 4,
$ \begin{align}
& {{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+{{x}^{2}}-{{y}^{2}}=56+16 \\
& 2{{x}^{2}}=72 \\
& {{x}^{2}}=36 \\
& x=6 \\
\end{align} $
We will ignore -6 because the side of a triangle cannot be negative.
Now, put the value of x in equation 3,
$ \begin{align}
& {{6}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}=56 \\
& {{y}^{2}}=56-36 \\
& {{y}^{2}}=20 \\
& y=2\sqrt{5} \\
\end{align} $
Ignore negative values for the same reason.
Again put the value of x in equation 2,
$ \begin{align}
& {{z}^{2}}=81-{{6}^{2}} \\
& {{z}^{2}}=81-36 \\
& {{z}^{2}}=45 \\
& z=3\sqrt{5} \\
\end{align} $

In triangle PSQ, use Pythagoras theorem,
$ \begin{align}
& {{6}^{2}}={{4}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}} \\
& 36-16={{y}^{2}} \\
& {{y}^{2}}=20 \\
& y=4\sqrt{5} \\
\end{align} $ ………………….(1)
Use Pythagoras theorem in triangle QSR,
$ \begin{align}
& {{z}^{2}}={{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}} \\
& {{z}^{2}}-{{x}^{2}}=20 \\
\end{align} $ (from equation 1) …………………….. (2)
Now, take triangle PQR and apply Pythagoras theorem in it.
$ {{6}^{2}}+{{z}^{2}}={{(x+4)}^{2}} $
From equation 2 put the value of z in it.
$ \begin{align}
& {{6}^{2}}+{{x}^{2}}+20={{x}^{2}}+16+8x \\
& 56=16+8x \\
& 8x=40 \\
& x=5 \\
& \\
\end{align} $
Put the value of x in equation 2.
$ \begin{align}
& {{z}^{2}}-{{5}^{2}}=20 \\
& {{z}^{2}}=45 \\
& z=3\sqrt{5} \\
\end{align} $
Note:In figure (i) angle D is a right angle that’s why AB and BC is hypotenuse for triangle ADB and BDC respectively. Same for figure (ii) angle S is a right angle that’s why PQ and QR are hypotenuse for triangle PSQ and triangle QSR respectively. Always ignore negative values for a side of the triangle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE





