
In ECG deflection waves, ventricular systole occurs during
(a) PQ
(b) PQR
(c) QRS
(d) T
Answer
588k+ views
Hint: ECG stands for Electrocardiography. The letters P, Q, R, S, and T reflect the depolarization and repolarization of the heart. The cardiac cycle of the heart is made of two stages – the diastole and the systole. In the diastole, the heart muscle relaxes and fills itself with blood, while in systole, the heart contracts and pumps blood.
Complete step by step answer:
During a ventricular systole, the ventricles contract and pump blood in two paths, one to the lungs and other to the rest of the body. During this stage, the atria are relaxed and are in atrial diastole.
A healthy human heart shows a defined graph in ECG. The graph consists of mainly 3 parts, the P wave, the QRS complex, and the T wave. Let us understand what each wave in an electrocardiogram means.
- The P wave represents atrial depolarization (atrial diastole) or activation of the ventricles.
- The QRS complex represents ventricular depolarization or the ventricular systole.
- The T wave represents repolarization of ventricles, or the ventricular diastole.
Additional Information:
- The human heart has four chambers, two atria and two ventricles.
- An ECG traces a heartbeat which is defined by the following mechanism - depolarization occurs in the sinoatrial (SA) node, which spreads all over the atrium, passes to the atrioventricular (AV) node down into the bundle of His and Purkinje fibres, spreading downwards and throughout the ventricles.
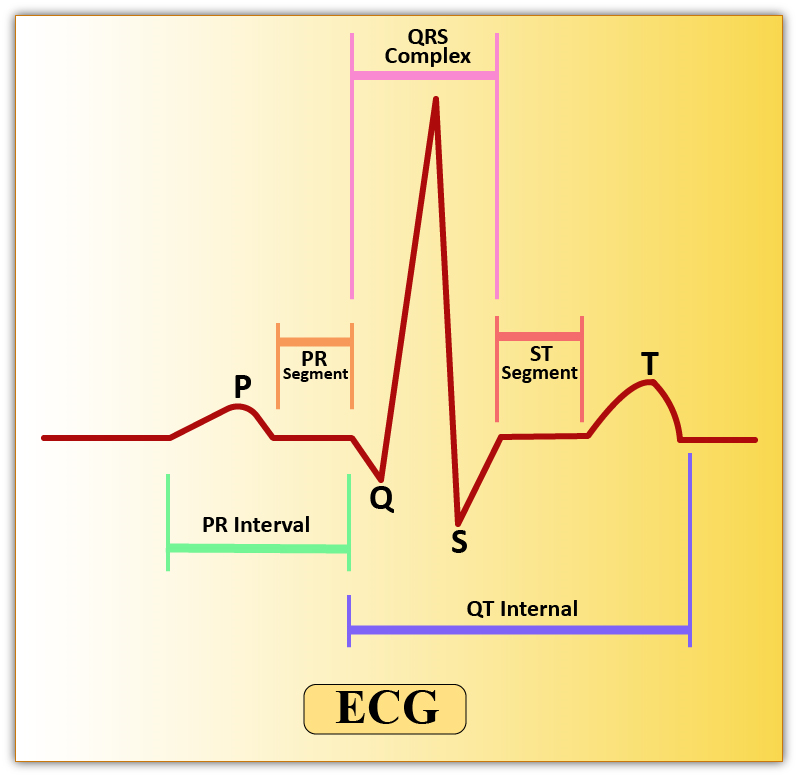
So, the correct answer is QRS complex.
Note: .
- Contractile cells make up most of the cells in the heart and are responsible for the contractions that pump blood. Keep a note of this if the term is mentioned in any question.
- Electrocardiography measures the electrical activity of the heart in the form of a graph of voltage versus time – known as an electrocardiogram.
- The abbreviation ECG and EKG are used interchangeably and mean the same.
Complete step by step answer:
During a ventricular systole, the ventricles contract and pump blood in two paths, one to the lungs and other to the rest of the body. During this stage, the atria are relaxed and are in atrial diastole.
A healthy human heart shows a defined graph in ECG. The graph consists of mainly 3 parts, the P wave, the QRS complex, and the T wave. Let us understand what each wave in an electrocardiogram means.
- The P wave represents atrial depolarization (atrial diastole) or activation of the ventricles.
- The QRS complex represents ventricular depolarization or the ventricular systole.
- The T wave represents repolarization of ventricles, or the ventricular diastole.
Additional Information:
- The human heart has four chambers, two atria and two ventricles.
- An ECG traces a heartbeat which is defined by the following mechanism - depolarization occurs in the sinoatrial (SA) node, which spreads all over the atrium, passes to the atrioventricular (AV) node down into the bundle of His and Purkinje fibres, spreading downwards and throughout the ventricles.

So, the correct answer is QRS complex.
Note: .
- Contractile cells make up most of the cells in the heart and are responsible for the contractions that pump blood. Keep a note of this if the term is mentioned in any question.
- Electrocardiography measures the electrical activity of the heart in the form of a graph of voltage versus time – known as an electrocardiogram.
- The abbreviation ECG and EKG are used interchangeably and mean the same.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




