
In general in an alternating current circuit (one complete cycle) which of the following is possible:
A. the average value of current is zero.
B. The average value of the square of the current is zero.
C. Average power dissipation is zero.
D. The phase difference between voltage and current is zero.
Answer
577.2k+ views
Hint: Firstly you could recall what exactly defines one complete cycle of an AC circuit. Then consider the possibility of each of the given options being true for such a situation. Since the question shows a possibility of more than one correct answer, you should check the possibility of every option being correct.
Complete step by step answer:
In the question we are discussing one complete cycle of alternating current circuits. We are given four conditions and are asked to find which among those conditions are true for one complete cycle of alternating current circuit.
For that we should understand what all things happen during one complete cycle of an AC circuit.
We could call a one cycle of an AC complete only when it completes one full pattern from its positive half to its negative half and back to its zero baseline again. So one full cycle contains both positive half cycles as well as negative half cycle.
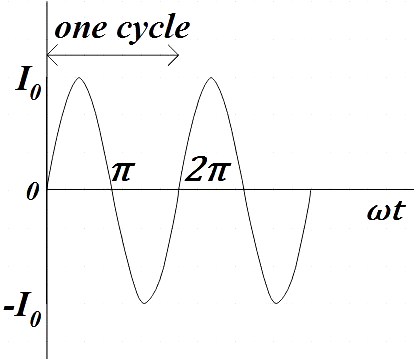
The waveform above clearly represents one full cycle for AC current and we see that one full cycle contains both negative and positive halves, so, the average value of current is obviously zero over one full cycle. That is for one full cycle of AC,
$\left\langle i \right\rangle =0$ …………………………….. (1)
But when the value of current is squared and then taken average over a full cycle, it cannot be zero because squaring makes the whole set of values positive.
$\left\langle {{i}^{2}} \right\rangle \ne 0$ ……………………………. (2)
We know that average power dissipated is given by,
$\left\langle p \right\rangle =\left\langle {{i}^{2}}R \right\rangle $
From (2), for a complete cycle of AC the average power dissipated $\left\langle p \right\rangle \ne 0$
Also, the phase difference between current and voltage remains the same throughout the cycle and is not zero after the completion of one full cycle.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: Since the question shows a possibility of more than one option being correct, we must consider all other options even if we find the very first option correct. That is why we have discussed options B, C and D even when we know that option A is correct. Periodic time defines the time taken by the waveform to complete one full cycle.
Complete step by step answer:
In the question we are discussing one complete cycle of alternating current circuits. We are given four conditions and are asked to find which among those conditions are true for one complete cycle of alternating current circuit.
For that we should understand what all things happen during one complete cycle of an AC circuit.
We could call a one cycle of an AC complete only when it completes one full pattern from its positive half to its negative half and back to its zero baseline again. So one full cycle contains both positive half cycles as well as negative half cycle.

The waveform above clearly represents one full cycle for AC current and we see that one full cycle contains both negative and positive halves, so, the average value of current is obviously zero over one full cycle. That is for one full cycle of AC,
$\left\langle i \right\rangle =0$ …………………………….. (1)
But when the value of current is squared and then taken average over a full cycle, it cannot be zero because squaring makes the whole set of values positive.
$\left\langle {{i}^{2}} \right\rangle \ne 0$ ……………………………. (2)
We know that average power dissipated is given by,
$\left\langle p \right\rangle =\left\langle {{i}^{2}}R \right\rangle $
From (2), for a complete cycle of AC the average power dissipated $\left\langle p \right\rangle \ne 0$
Also, the phase difference between current and voltage remains the same throughout the cycle and is not zero after the completion of one full cycle.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: Since the question shows a possibility of more than one option being correct, we must consider all other options even if we find the very first option correct. That is why we have discussed options B, C and D even when we know that option A is correct. Periodic time defines the time taken by the waveform to complete one full cycle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




