
In graphite, electrons are:
(A) Localized on each carbon atom
(B) Spread out between the sheets
(C) localized on every third carbon atom
(D) present in antibonding orbital
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Graphite is an allotrope of carbon element. When the same element is present in more than one form they are called allotropes.
Carbon is present in three forms in nature i.e. Diamond, Graphite and fullerene.
Complete step by step answer:
Carbon atom in graphite present in$s{p^2}$ hybridized state.
Electronic configuration of C is$ - 1{s^2}2{s^2}2p{x^1}2p{y^1}$
At ground state =
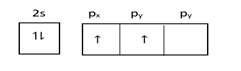
At excited state =
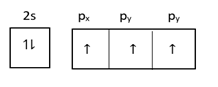
In graphite $1s$ and $2p$ orbital hybridize and form $s{p^2}$ hybridized orbital and one orbital remains hybridized.
Hybridized state=
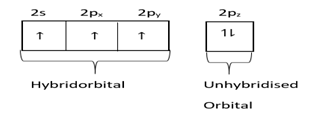
Three hybrid orbits contain one electron each.
These electrons form a covalent bond with the hybrid orbital of other C-atoms.
Each carbon atom forms a covalent bond with another carbon atom. They form interlinked six membered rings of carbon atoms. The remaining half filled unhybridized $2{p^2}$orbital is used for$\pi $bonding. So that layers of carbon atoms i.e. graphite is formed.
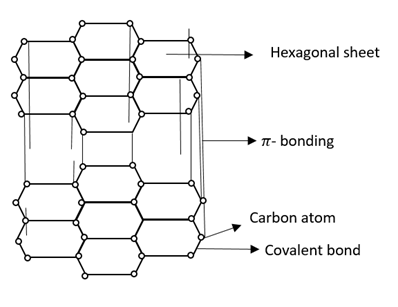
Graphite has delocalized molecular orbital and delocalized electrons and is free to move in delocalized molecular orbital.
Therefore, electrons get spread between the sheets.
Therefore, from the above explanation, the correct option is B
Additional information:
Graphite is a good conductor of heat and electricity. The layer of carbon atoms in graphite can slide over another layer. So it is used in lubricants for reducing friction.
Note: Graphite forms hexagonal layers and these layers of carbon atom are held together by weak Van der Waals forces of attraction.
Carbon atoms have a unique property to link with itself called catenation. Due to this property allotropes of carbon form giant molecules.
Carbon is present in three forms in nature i.e. Diamond, Graphite and fullerene.
Complete step by step answer:
Carbon atom in graphite present in$s{p^2}$ hybridized state.
Electronic configuration of C is$ - 1{s^2}2{s^2}2p{x^1}2p{y^1}$
At ground state =

At excited state =

In graphite $1s$ and $2p$ orbital hybridize and form $s{p^2}$ hybridized orbital and one orbital remains hybridized.
Hybridized state=

Three hybrid orbits contain one electron each.
These electrons form a covalent bond with the hybrid orbital of other C-atoms.
Each carbon atom forms a covalent bond with another carbon atom. They form interlinked six membered rings of carbon atoms. The remaining half filled unhybridized $2{p^2}$orbital is used for$\pi $bonding. So that layers of carbon atoms i.e. graphite is formed.

Graphite has delocalized molecular orbital and delocalized electrons and is free to move in delocalized molecular orbital.
Therefore, electrons get spread between the sheets.
Therefore, from the above explanation, the correct option is B
Additional information:
Graphite is a good conductor of heat and electricity. The layer of carbon atoms in graphite can slide over another layer. So it is used in lubricants for reducing friction.
Note: Graphite forms hexagonal layers and these layers of carbon atom are held together by weak Van der Waals forces of attraction.
Carbon atoms have a unique property to link with itself called catenation. Due to this property allotropes of carbon form giant molecules.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




