
In human beings’ blue eye colour is recessive to brown eye colour. A brown-eyed man has a blue-eyed mother.
(a) What is the genotype of the man and his mother?
(b) What are the possible genotypes of his father?
(c) If the man marries a blue-eyed woman, what are the possible genotypes of their offspring?
Answer
564.6k+ views
Hint: Genes are available in different forms, called alleles. Somatic cells produced two alleles for each gene, with one allele per organism parent. It is difficult to grasp on a daily basis there are two alleles of the gene inside the chromosomes of an organism purely based on the external appearance of the organism.
Complete answer: In different ways, genetic traits can be transferred from parent to infant. As you can see, individuals can transfer a gene, but they themselves do not specifically affect it. Our genes are divided into chromosome sets. There are 46 chromosomes in most individuals, in 23 pairs. Each of the pairs on the sex chromosomes is X and Y. Our sex chromosomes comprise the genes that characterize you male or female. Men have chromosomes X and Y, and females have two X chromosomes. The majority of your chromosomes are called autosomal chromosomes, so '50 percent' is the right response. The brown eye colour dominates the blue eye colour according to the given condition
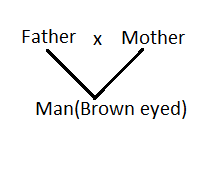
(a)The genotype of the mother has to be 'bb' because she is a recessive blue eye (dominant). Getting one of his mother's recessive genes, he wants to be "Bb" his potential genotype. Because the mother is blue-eyed, bb would be her genotype (recessive trait). Therefore, though the son is brown-eyed, his genotype will be Bb (heterozygous).
(b) As the man's genotype is 'BB,' his father could be BB or Bb, as a potential genotype. Because the son is brown, the father also has brown eyes. So, BB or Bb would be the potential genotypes.
(c) The organism has brown skin, genotype Bb. The blue-eyed woman would have the bb genotype. The probable genotypes of their descendants would therefore be as follows:
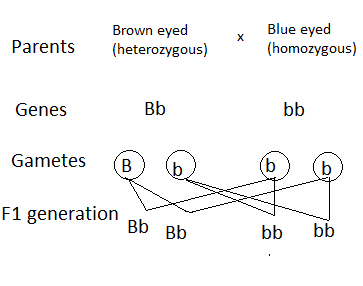
Note: There is a 1 in 2 risks (50 percent) that a daughter would be affected if the mother is a carrier and the father has the disease. She will consistently get the gene from her father that doesn't work properly, yet she could get the functioning gene from her mother.
Complete answer: In different ways, genetic traits can be transferred from parent to infant. As you can see, individuals can transfer a gene, but they themselves do not specifically affect it. Our genes are divided into chromosome sets. There are 46 chromosomes in most individuals, in 23 pairs. Each of the pairs on the sex chromosomes is X and Y. Our sex chromosomes comprise the genes that characterize you male or female. Men have chromosomes X and Y, and females have two X chromosomes. The majority of your chromosomes are called autosomal chromosomes, so '50 percent' is the right response. The brown eye colour dominates the blue eye colour according to the given condition

(a)The genotype of the mother has to be 'bb' because she is a recessive blue eye (dominant). Getting one of his mother's recessive genes, he wants to be "Bb" his potential genotype. Because the mother is blue-eyed, bb would be her genotype (recessive trait). Therefore, though the son is brown-eyed, his genotype will be Bb (heterozygous).
(b) As the man's genotype is 'BB,' his father could be BB or Bb, as a potential genotype. Because the son is brown, the father also has brown eyes. So, BB or Bb would be the potential genotypes.
(c) The organism has brown skin, genotype Bb. The blue-eyed woman would have the bb genotype. The probable genotypes of their descendants would therefore be as follows:

Note: There is a 1 in 2 risks (50 percent) that a daughter would be affected if the mother is a carrier and the father has the disease. She will consistently get the gene from her father that doesn't work properly, yet she could get the functioning gene from her mother.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




