
In mating between two people of intermediate skin color, each heterozygous at all three gene loci for skin color, what is the chance that their child will have a very light skin color.
(a)1/64
(b)1/4
(c)5/8
(d)9/64
Answer
566.7k+ views
Hint: Inheritance of skin color of human beings is an example of polygenic inheritance. Polygenic inheritance is defined as the inheritance in which there are multiple genes responsible for the expression of one phenotype.
Complete answer:
The phenotype of skin color is controlled by three genes whose dominant allele is denoted by capital letters A, B, and C, and recessive alleles are represented by small letters a, b, and c. The dominant alleles cause more pigmentation which means more melanin production in the body whereas the recessive alleles induce low melanin production.
The genotype which has all dominant alleles AABBCC, the phenotype will be very dark skin due to the highest amount of melanin. Whereas the genotype with all recessive alleles aabbcc will have the lightest skin color due to the lowest amount of melanin.
Each dominant allele increases the pigmentation by one unit, thus there are a number of intermediate phenotypes with a range of skin shades.
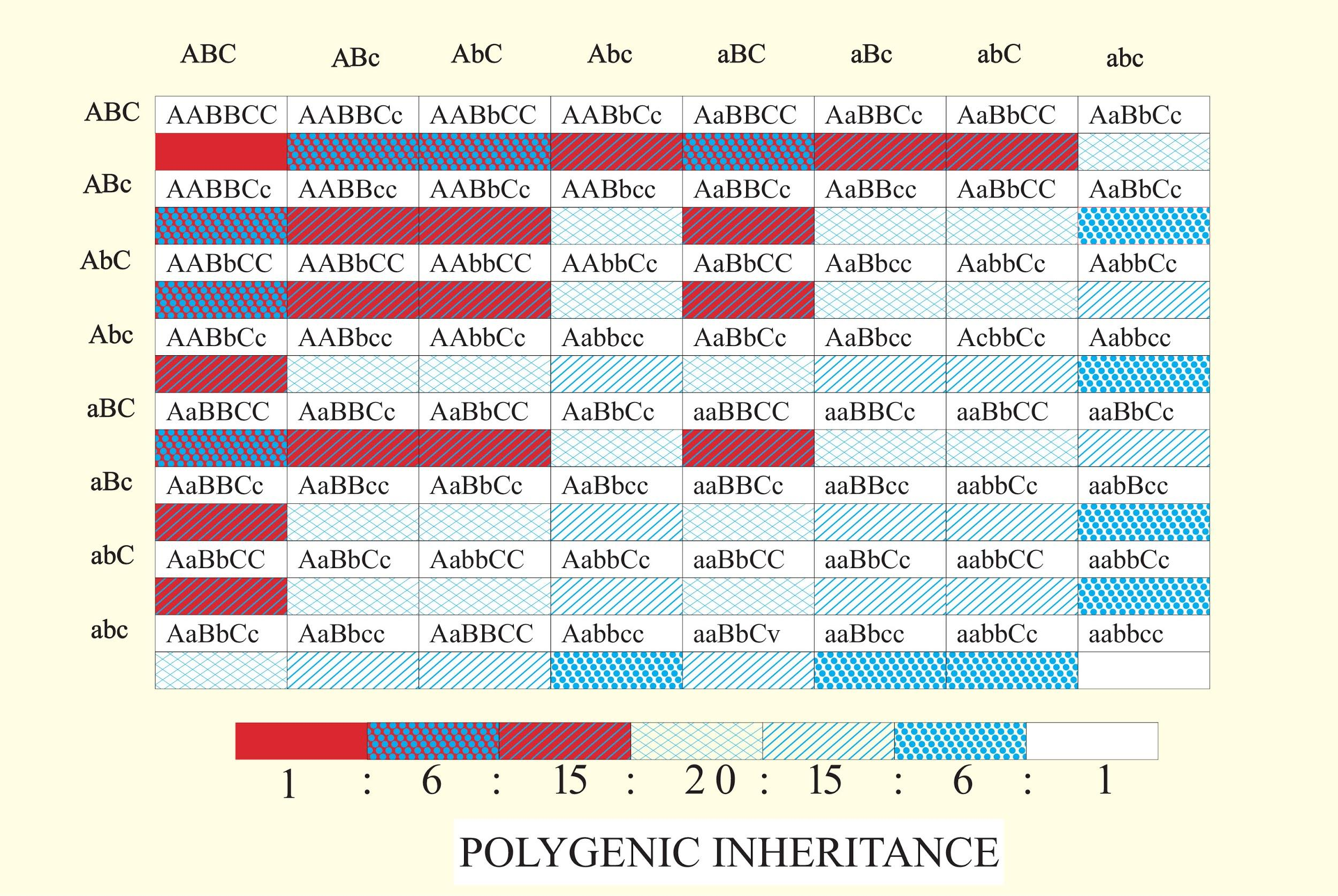
-A person with half dominant alleles and half recessive alleles will have a medium amount of melanin and intermediate skin color. Such a genotype is known as mulatto. When such a person is crossed with another similar person we obtain the following Punnett square.
Here we can see that a total number of 64 outcomes are available which give 7 different skin colors. Out of which only 1 outcome has the genotype of aabbcc (completely recessive). Thus, the ratio would be 1/64.
So, the correct option is ‘1/64’.
Note: -Polygenic inheritance is an exception to Mendel’s laws.
-More examples of polygenic inheritance include human eye color, height, weight, and intelligence in people.
-The terms dominant and recessive used in cases of polygenic inheritance are not truly dominant and recessive as was seen in the garden pea traits that Mendel studied.
Complete answer:
The phenotype of skin color is controlled by three genes whose dominant allele is denoted by capital letters A, B, and C, and recessive alleles are represented by small letters a, b, and c. The dominant alleles cause more pigmentation which means more melanin production in the body whereas the recessive alleles induce low melanin production.
The genotype which has all dominant alleles AABBCC, the phenotype will be very dark skin due to the highest amount of melanin. Whereas the genotype with all recessive alleles aabbcc will have the lightest skin color due to the lowest amount of melanin.
Each dominant allele increases the pigmentation by one unit, thus there are a number of intermediate phenotypes with a range of skin shades.
-A person with half dominant alleles and half recessive alleles will have a medium amount of melanin and intermediate skin color. Such a genotype is known as mulatto. When such a person is crossed with another similar person we obtain the following Punnett square.
Here we can see that a total number of 64 outcomes are available which give 7 different skin colors. Out of which only 1 outcome has the genotype of aabbcc (completely recessive). Thus, the ratio would be 1/64.
So, the correct option is ‘1/64’.

Note: -Polygenic inheritance is an exception to Mendel’s laws.
-More examples of polygenic inheritance include human eye color, height, weight, and intelligence in people.
-The terms dominant and recessive used in cases of polygenic inheritance are not truly dominant and recessive as was seen in the garden pea traits that Mendel studied.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




