
In orbital motion, the angular momentum vector is
A. along the radius vector
B. parallel to the linear momentum
C. in the orbital plane
D. perpendicular to the orbital plane
Answer
585k+ views
Hint: Orbital motion is a form of rotational motion of a body around another body which after a certain amount of time, called orbital period, traces back its path again. Angular momentum is known to be the cross product of radial vector and linear momentum vector.
Complete step by step answer:
In rotational motion angular momentum of a body is known to be the moment of linear momentum of the body around its axis. It is measured to be the product of Linear Momentum and perpendicular distance from the axis of rotation. Another way of saying this is that it is the cross product of the radius vector and linear momentum vector:
$\vec{L} = \vec{r} \times \vec{p} $
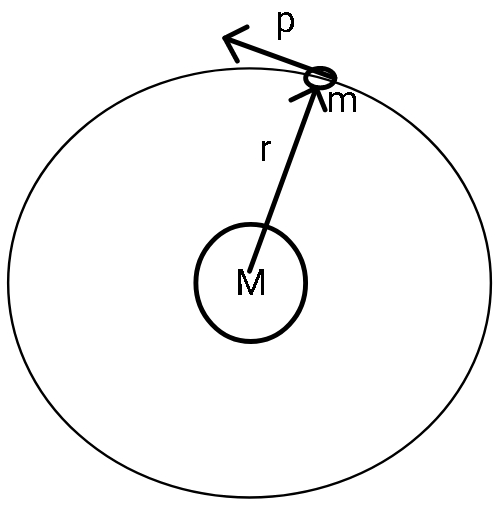
If we consider a massive body like the sun (or nucleus) at the origin and consider the orbital motion of a light body like earth around it, we can say that the direction of the radius vector is along the line joining the sun and the earth. The linear momentum has a direction which is tangential to the earth's motion i.e., linear momentum will be in the direction of linear velocity.
We know that when we take a cross product of two vectors, we always get the resultant in a direction that is perpendicular to both the vectors. In our case the radius vector and linear momentum vector both lie in the orbital plane. Therefore, the direction of the angular momentum vector in orbital motion is perpendicular to the orbital plane.
So, the correct answer is option (D).
Note:
The direction of orbital angular momentum plays a very important role when dealing with the motion of electrons in the nucleus. In planetary motion too, Kepler's law gives special focus on the conservation of angular momentum which helps us in concluding the fact that the planet sweeps equal areas in equal intervals of time.
Complete step by step answer:
In rotational motion angular momentum of a body is known to be the moment of linear momentum of the body around its axis. It is measured to be the product of Linear Momentum and perpendicular distance from the axis of rotation. Another way of saying this is that it is the cross product of the radius vector and linear momentum vector:
$\vec{L} = \vec{r} \times \vec{p} $

If we consider a massive body like the sun (or nucleus) at the origin and consider the orbital motion of a light body like earth around it, we can say that the direction of the radius vector is along the line joining the sun and the earth. The linear momentum has a direction which is tangential to the earth's motion i.e., linear momentum will be in the direction of linear velocity.
We know that when we take a cross product of two vectors, we always get the resultant in a direction that is perpendicular to both the vectors. In our case the radius vector and linear momentum vector both lie in the orbital plane. Therefore, the direction of the angular momentum vector in orbital motion is perpendicular to the orbital plane.
So, the correct answer is option (D).
Note:
The direction of orbital angular momentum plays a very important role when dealing with the motion of electrons in the nucleus. In planetary motion too, Kepler's law gives special focus on the conservation of angular momentum which helps us in concluding the fact that the planet sweeps equal areas in equal intervals of time.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




