
In pentagonal bipyramidal structure, the coordination number
(a). 7
(b). 6
(c). 8
(d). 10
Answer
576.6k+ views
Hint: The coordination number is the same as that of the number of B atoms in the pentagonal bipyramidal geometry. ($\text{A}{{\text{B}}_{\text{n}}}$)
Complete answer:
Before knowing the coordination number, we need to understand what the unit cell is. The simplest repeating unit in a crystal is called a unit cell. Each unit cell is defined in terms of lattice points-the point in space about which the particles are free to vibrate in a crystal. There are 14 different types of crystal unit cell structures or lattices that are found in nature. They are called Bravais lattices. However, most metals and many other solids have unit cell structures described as body centered cubic (bcc), face centered cubic (fcc) or Hexagonal Close Packed (hcp), since these structures are most common in nature.
The coordination number is the number of atoms or atomic groups directly bonded to a given atom in complex compounds. The concept of coordination numbers is also used in descriptions of fluids and amorphous bodies. In this case, the coordination number is the average number of the nearest neighbors of the atom; it may be fractional. The coordination number is a measure of short-range order in liquids and amorphous bodies
In covalent bonded molecules and polyatomic ions, the coordination number is determined by just counting the number of bonded atoms. Each sodium ion in sodium chloride, NaCl, is surrounded by six chlorine ions, and each chlorine ion is surrounded by six sodium ions, meaning that the coordination numbers are 6 for both types of ions and the corresponding polyhedron is an octahedron. The highest possible coordination number is 12, which is typical of metals with cubic or hexagonal-close packed structure.
In chemistry, a pentagonal bipyramidal is a molecular geometry with one atom at the centre with seven ligands at the corners of the pentagonal pyramid.
Example of such geometry is: $\text{I}{{\text{F}}_{7}}$
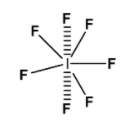
Hence, the correct option is (a).7
Note:
The bond angle in the pentagonal bi-pyramidal structure is ${{90}^{\text{o}}}$, formed by each axial F atom and ${{72}^{\text{o}}}$, on the equatorial F atom. Also, the point group of $\text{I}{{\text{F}}_{7}}$ is ${{\text{D}}_{5\text{h}}}$.
Complete answer:
Before knowing the coordination number, we need to understand what the unit cell is. The simplest repeating unit in a crystal is called a unit cell. Each unit cell is defined in terms of lattice points-the point in space about which the particles are free to vibrate in a crystal. There are 14 different types of crystal unit cell structures or lattices that are found in nature. They are called Bravais lattices. However, most metals and many other solids have unit cell structures described as body centered cubic (bcc), face centered cubic (fcc) or Hexagonal Close Packed (hcp), since these structures are most common in nature.
The coordination number is the number of atoms or atomic groups directly bonded to a given atom in complex compounds. The concept of coordination numbers is also used in descriptions of fluids and amorphous bodies. In this case, the coordination number is the average number of the nearest neighbors of the atom; it may be fractional. The coordination number is a measure of short-range order in liquids and amorphous bodies
In covalent bonded molecules and polyatomic ions, the coordination number is determined by just counting the number of bonded atoms. Each sodium ion in sodium chloride, NaCl, is surrounded by six chlorine ions, and each chlorine ion is surrounded by six sodium ions, meaning that the coordination numbers are 6 for both types of ions and the corresponding polyhedron is an octahedron. The highest possible coordination number is 12, which is typical of metals with cubic or hexagonal-close packed structure.
In chemistry, a pentagonal bipyramidal is a molecular geometry with one atom at the centre with seven ligands at the corners of the pentagonal pyramid.
Example of such geometry is: $\text{I}{{\text{F}}_{7}}$

Hence, the correct option is (a).7
Note:
The bond angle in the pentagonal bi-pyramidal structure is ${{90}^{\text{o}}}$, formed by each axial F atom and ${{72}^{\text{o}}}$, on the equatorial F atom. Also, the point group of $\text{I}{{\text{F}}_{7}}$ is ${{\text{D}}_{5\text{h}}}$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




