
In photoelectric effect, the number of photoelectrons emitted is proportional to
A. velocity of incident beam
B. frequency of incident beam
C. intensity of incident beam
D. work function of cathode material.
Answer
588k+ views
Hint: The photoelectric effect is the phenomenon in which some materials emit electrons in the presence of light.
Hallwach Lenard’s experiment on photoelectric effect successfully helped in confirming Einstein's theory of photoelectric effect.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Here is the experimental setup for the photoelectric experiment for the study of photoelectric effect:
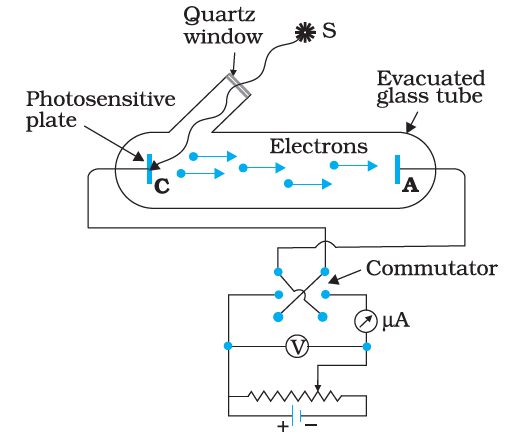
The experimental setup consists of an evacuated glass tube in which there are two electrodes. There is a quartz window which allows the light source through the glass tube. The electrodes are connected to a commutator which is used for changing the direction of the electric current.
One such experiment performed is the effect of intensity on photocurrent –
The collector anode is maintained at a constant positive potential with respect to cathode C which emits electrons. The light window is opened, and the ammeter reading is recorded. Now, keeping the frequency and potential fixed, the intensity of the incident radiation is increased slowly. We see that the current increases linearly with the increase in the intensity.
Thus, the number of photoelectrons emitted per second is directly proportional to the intensity of the light.
Hence, the correct option is Option C.
Note: The premise for classifying the light consists of particle is primarily, based on the Planck’s Law, which states that –
Energy, $E \propto \upsilon $
$E = h\upsilon $
A photon is defined as a particle whose energy is equal to $E = h\upsilon $. The photoelectric effect proves the theory of light as a particle.
Hallwach Lenard’s experiment on photoelectric effect successfully helped in confirming Einstein's theory of photoelectric effect.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Here is the experimental setup for the photoelectric experiment for the study of photoelectric effect:

The experimental setup consists of an evacuated glass tube in which there are two electrodes. There is a quartz window which allows the light source through the glass tube. The electrodes are connected to a commutator which is used for changing the direction of the electric current.
One such experiment performed is the effect of intensity on photocurrent –
The collector anode is maintained at a constant positive potential with respect to cathode C which emits electrons. The light window is opened, and the ammeter reading is recorded. Now, keeping the frequency and potential fixed, the intensity of the incident radiation is increased slowly. We see that the current increases linearly with the increase in the intensity.
Thus, the number of photoelectrons emitted per second is directly proportional to the intensity of the light.
Hence, the correct option is Option C.
Note: The premise for classifying the light consists of particle is primarily, based on the Planck’s Law, which states that –
Energy, $E \propto \upsilon $
$E = h\upsilon $
A photon is defined as a particle whose energy is equal to $E = h\upsilon $. The photoelectric effect proves the theory of light as a particle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




