
In $P{{O}_{4}}^{3-}$ ion, the formal charge on the oxygen atom of P-O bond is:
Answer
573.6k+ views
Hint: The answer for this question is based upon the formula to calculate the formal charge that is, Formal charge = [Number of valence electrons on an atom] – [ non-bonded electrons + number of bonds].
Complete answer:
The concepts of inorganic chemistry that includes calculation of bond order based on the various orbital theories and also about the calculation of formal charge are well known to us.
Now, let us try to understand the base of what is meant by formal charge and how can that be calculated.
Formal charge is basically defined as the charge assigned to a particular atom in a molecule by assuming that the electrons in all chemical bonds are shared equally between atoms regardless of the electronegativity present.
Now, to know the formal charge we must first know the structure of the given molecule so that we can understand the number of bonds between each atom.
For the given molecule$P{{O}_{4}}^{3-}$ion, the structure is as shown below,
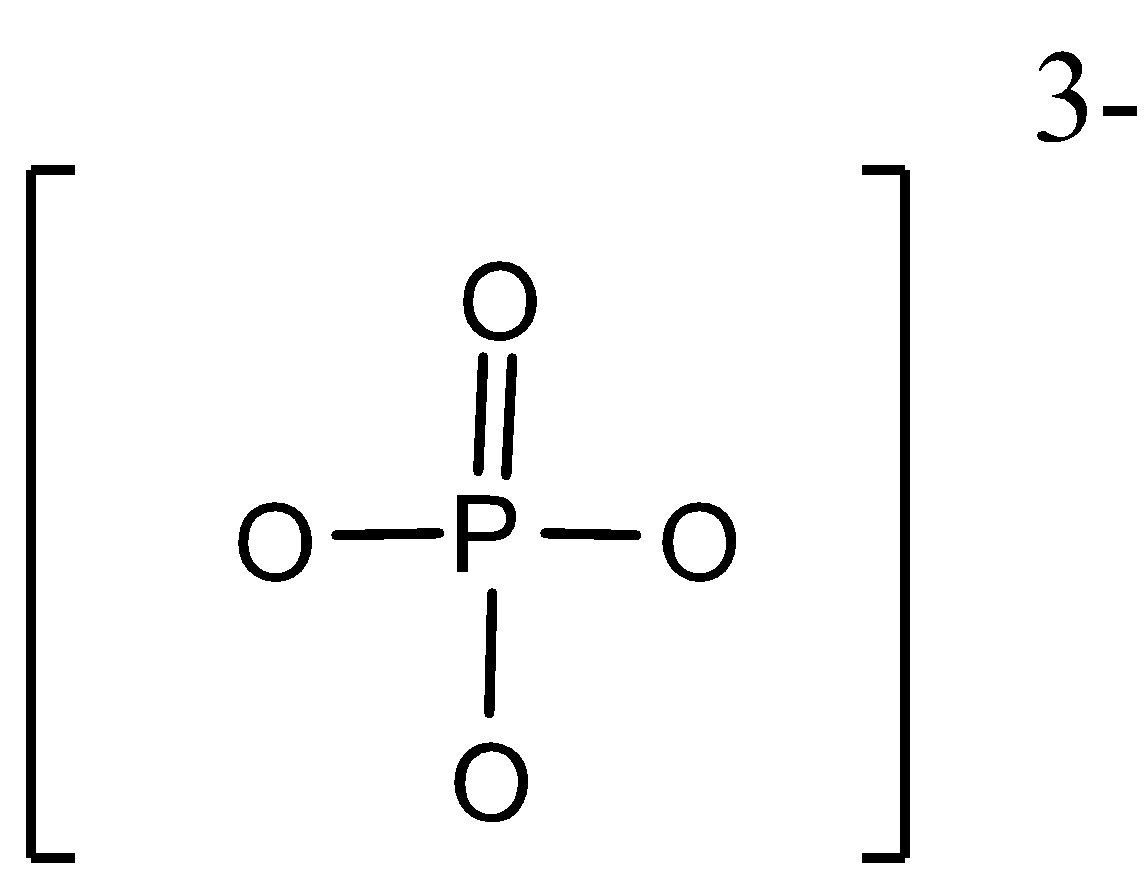
Here, the phosphorus atom is linked to four oxygen atoms with the ionic charge as -3. Among these oxygen atoms, one atom is the double bond and the rest of the three atoms are bonded with single bonds each.
Now, to calculate the formal charge according to the formula, Formal charge = [Number of valence electrons on an atom] – [non-bonded electrons + number of bonds] can be given as,
For oxygen atom with double bond formation with phosphorus,
FC= 6-[4+2] = 0
Thus, there is no formal charge for double bonded oxygen atoms.
Now, for the oxygen atoms that is bonded to phosphorus with single bond, the formal charge is,
FC = 6-[6+1] = -1
Since there are three oxygen atom bonded with single bonds, the formal charge will be -3
Now, as there are four oxygen atoms and a total of -3 charge is distributed among them.
Therefore, total formal charge on each oxygen atom will be-3/4 = -0.75.
Thus, the correct answer is -0.75
Note: While calculating the formal charge, the structure of the given molecules plays an important role and make sure that you are thorough with some basic structures of the molecules and also now many bonds each atom can bear.
Complete answer:
The concepts of inorganic chemistry that includes calculation of bond order based on the various orbital theories and also about the calculation of formal charge are well known to us.
Now, let us try to understand the base of what is meant by formal charge and how can that be calculated.
Formal charge is basically defined as the charge assigned to a particular atom in a molecule by assuming that the electrons in all chemical bonds are shared equally between atoms regardless of the electronegativity present.
Now, to know the formal charge we must first know the structure of the given molecule so that we can understand the number of bonds between each atom.
For the given molecule$P{{O}_{4}}^{3-}$ion, the structure is as shown below,

Here, the phosphorus atom is linked to four oxygen atoms with the ionic charge as -3. Among these oxygen atoms, one atom is the double bond and the rest of the three atoms are bonded with single bonds each.
Now, to calculate the formal charge according to the formula, Formal charge = [Number of valence electrons on an atom] – [non-bonded electrons + number of bonds] can be given as,
For oxygen atom with double bond formation with phosphorus,
FC= 6-[4+2] = 0
Thus, there is no formal charge for double bonded oxygen atoms.
Now, for the oxygen atoms that is bonded to phosphorus with single bond, the formal charge is,
FC = 6-[6+1] = -1
Since there are three oxygen atom bonded with single bonds, the formal charge will be -3
Now, as there are four oxygen atoms and a total of -3 charge is distributed among them.
Therefore, total formal charge on each oxygen atom will be-3/4 = -0.75.
Thus, the correct answer is -0.75
Note: While calculating the formal charge, the structure of the given molecules plays an important role and make sure that you are thorough with some basic structures of the molecules and also now many bonds each atom can bear.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




