
In Reimer-Tiemann reaction, reactants are,
A.Phenol, $CHC{l_3}$ and alkali
B.Phenol, $CC{l_4}$ and alkali
C.Aniline, $CHC{l_3}$ and alkali
D.Both Phenol, $CHC{l_3}$ and alkali and Phenol, $CC{l_4}$ and alkali
Answer
561k+ views
Hint: Reimer-Tiemann reaction involves ortho formylation of phenols. An aldehyde group will be introduced at the ortho position of phenol. A simple example is the conversion of phenol to salicylaldehyde.
Complete step by step answer:
Reimer-Tiemann reaction involves reaction of phenol with chloroform ($CHC{l_3}$) in the presence of an alkali, mainly NaOH. Then an aldehyde group (-CHO) will be introduced at the ortho position of the benzene ring giving the product o-hydroxybenzaldehyde or salicylaldehyde. The reaction can be represented as,
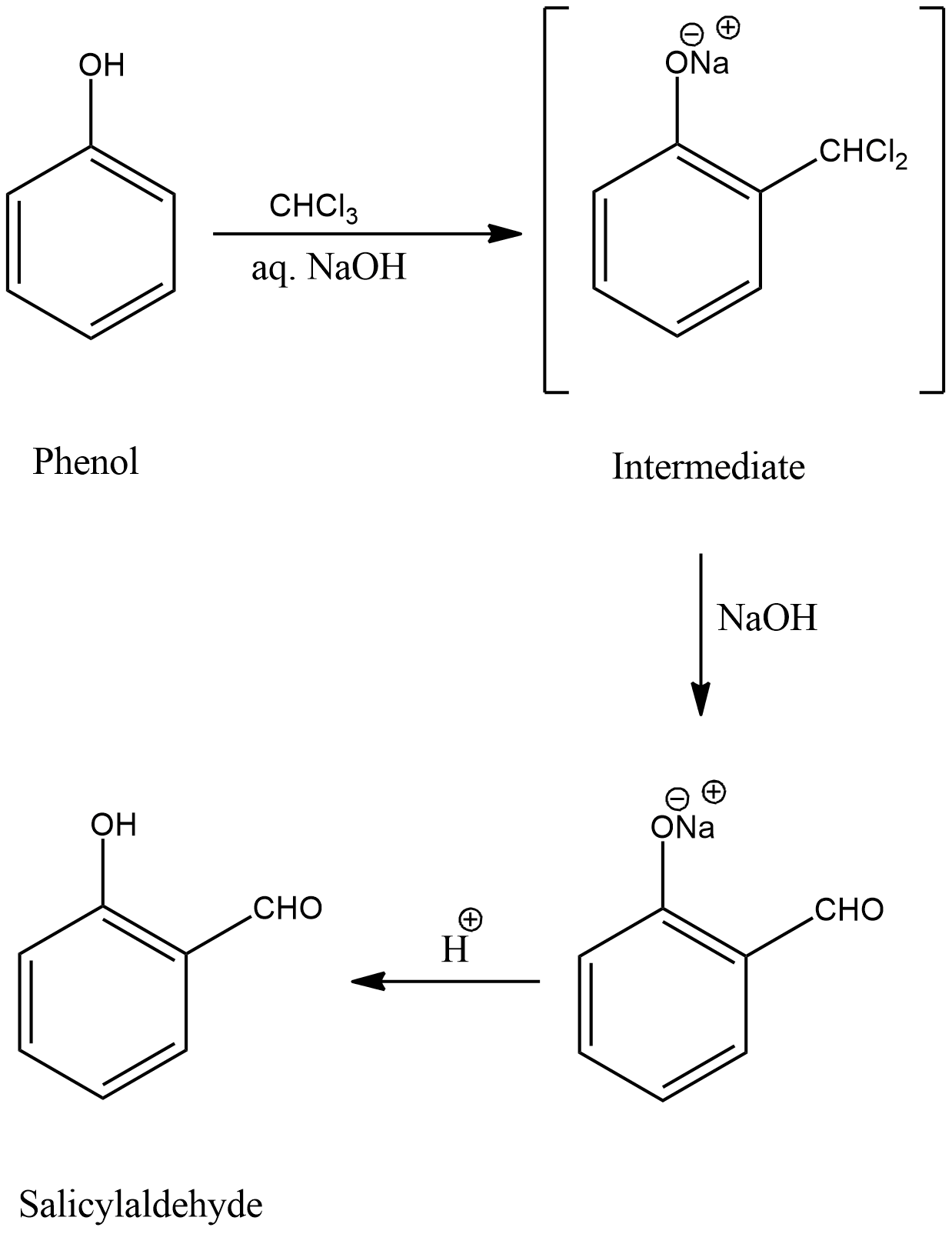
The reaction involves formation of an intermediate as shown.
We can also use $CC{l_4}$ and alkali instead of $CHC{l_3}$ and alkali as reagents. When $CC{l_4}$ and alkali is used with phenol, the product will be salicylic acid. This reaction is also a Reimer-Tiemann reaction. The corresponding reaction is shown below.
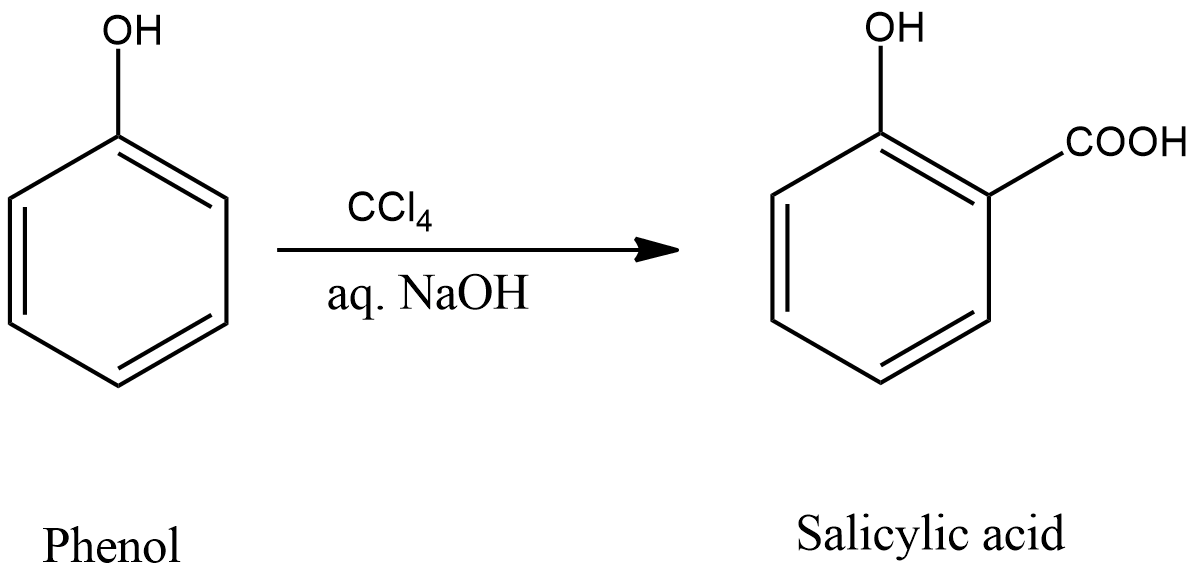
Hence both Phenol, $CHC{l_3}$ and alkali and Phenol, $CC{l_4}$ and alkali can be used in the Reimer-Tiemann reaction.
Therefore Option D is correct.
Additional information-
Hydroxides are not much soluble in chloroform. Hence in order to carry out the reaction, a biphasic solvent system should be used. The biphasic solvent system contains an aqueous hydroxide solution with an organic phase containing chloroform. During the reaction, the reagents are brought together using methods like rapid mixing, using emulsifying agents or phase transfer catalysts.
Note:
The Reimer-Tiemann reaction is more effective when other hydroxyl aromatic compounds such as naphthol are used. Heterocyclic compounds such as pyrrole and indole can also give Reimer-Tiemann reactions as they are electron rich.
Complete step by step answer:
Reimer-Tiemann reaction involves reaction of phenol with chloroform ($CHC{l_3}$) in the presence of an alkali, mainly NaOH. Then an aldehyde group (-CHO) will be introduced at the ortho position of the benzene ring giving the product o-hydroxybenzaldehyde or salicylaldehyde. The reaction can be represented as,

The reaction involves formation of an intermediate as shown.
We can also use $CC{l_4}$ and alkali instead of $CHC{l_3}$ and alkali as reagents. When $CC{l_4}$ and alkali is used with phenol, the product will be salicylic acid. This reaction is also a Reimer-Tiemann reaction. The corresponding reaction is shown below.

Hence both Phenol, $CHC{l_3}$ and alkali and Phenol, $CC{l_4}$ and alkali can be used in the Reimer-Tiemann reaction.
Therefore Option D is correct.
Additional information-
Hydroxides are not much soluble in chloroform. Hence in order to carry out the reaction, a biphasic solvent system should be used. The biphasic solvent system contains an aqueous hydroxide solution with an organic phase containing chloroform. During the reaction, the reagents are brought together using methods like rapid mixing, using emulsifying agents or phase transfer catalysts.
Note:
The Reimer-Tiemann reaction is more effective when other hydroxyl aromatic compounds such as naphthol are used. Heterocyclic compounds such as pyrrole and indole can also give Reimer-Tiemann reactions as they are electron rich.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




