
In the above general formula for an amino acid, the letter R stands for
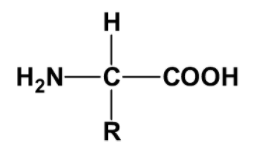
a. Amino group
b. A carboxyl group
c. A variable group
d. A hydroxyl group

Answer
573.3k+ views
Hint: Amino acids have four substituent groups occupying four valency positions namely hydrogen, carboxyl group, amino group, and a variable group. Amino acids are organic compounds. They are called $\alpha $ -amino acids because they contain an amino group and an acidic group as substituents on the same carbon which is called the $\alpha $ -carbon.
Complete answer:
The variable group is designated as R. The R group in these amino groups could be hydrogen (then the amino acid is called Glycine), a methyl group (alanine), a hydroxymethyl group (serine), etc. The amino, carboxyl, and the R group determine the physical and chemical properties of amino acids.
Amino acids can be classified into seven types:
• Neutral amino acids have one amino group and one carboxylic group with a noncyclic hydrocarbon chain. For example Glycine
• Acidic amino acids have a carboxyl group as their functional group. For example Glutamic acid
• Basic amino acids have an extra amino group. For example Lysine.
• Sulphur containing amino acids contain sulphur. For example Cysteine
• Alcoholic amino acids have a hydroxyl group. For example Serine
• Aromatic amino acids have cyclic structures with a straight side chain. For example: Tryptophan
• Heterocyclic amino acids have nitrogen in the ring structure. For example: Histidine
Hence, the correct answer is option (C).
Additional information:
• Proline is the only $\beta $ - amino acid.
• There are many non-protein amino acids like $\gamma $ -amino butyric acid, ornithine.
Note: Peptides are formed by the condensation of amino acids. There are $20$ amino acids of which $10$ are essential amino acids and $10$ are non-essential amino acids. Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins and enzymes. Amino acids are left behind when proteins are digested or left behind.
Complete answer:
The variable group is designated as R. The R group in these amino groups could be hydrogen (then the amino acid is called Glycine), a methyl group (alanine), a hydroxymethyl group (serine), etc. The amino, carboxyl, and the R group determine the physical and chemical properties of amino acids.
Amino acids can be classified into seven types:
• Neutral amino acids have one amino group and one carboxylic group with a noncyclic hydrocarbon chain. For example Glycine
• Acidic amino acids have a carboxyl group as their functional group. For example Glutamic acid
• Basic amino acids have an extra amino group. For example Lysine.
• Sulphur containing amino acids contain sulphur. For example Cysteine
• Alcoholic amino acids have a hydroxyl group. For example Serine
• Aromatic amino acids have cyclic structures with a straight side chain. For example: Tryptophan
• Heterocyclic amino acids have nitrogen in the ring structure. For example: Histidine
Hence, the correct answer is option (C).
Additional information:
• Proline is the only $\beta $ - amino acid.
• There are many non-protein amino acids like $\gamma $ -amino butyric acid, ornithine.
Note: Peptides are formed by the condensation of amino acids. There are $20$ amino acids of which $10$ are essential amino acids and $10$ are non-essential amino acids. Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins and enzymes. Amino acids are left behind when proteins are digested or left behind.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




