
In the case of constants $\alpha $ and $\beta $ of a transistor:
$A)\text{ }\alpha =\beta $
$B)\text{ }\beta <1;\alpha >1$
$C)\text{ }\alpha \beta =1$
$D)\text{ }\beta >1;\alpha <1$
Answer
593.7k+ views
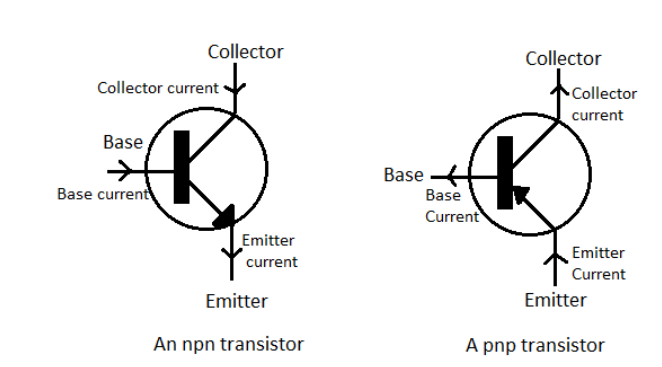
Hint: The constant $\alpha $ of a transistor is the ratio of the collector current to the emitter current while the constant $\beta $ of the transistor is the ratio of the collector current to the base current. The base current is lesser than the collector current which is lesser than the emitter current.
Formula used:
$\alpha =\dfrac{{{I}_{C}}}{{{I}_{E}}}$
$\beta =\dfrac{{{I}_{C}}}{{{I}_{B}}}$
Complete step by step answer:
The ratio of the collector current ${{I}_{C}}$ to the emitter current ${{I}_{E}}$ in a transistor is represented by the constant $\alpha $. Therefore, mathematically,
$\alpha =\dfrac{{{I}_{C}}}{{{I}_{E}}}$ -----(1)
In a transistor, the emitter current ${{I}_{E}}$ is the sum of the base current ${{I}_{B}}$ and the collector current ${{I}_{C}}$.
Therefore, obviously it can be said that ${{I}_{E}}>{{I}_{C}}$. Using this relation in (1), we can say that
$\alpha =\dfrac{{{I}_{C}}}{{{I}_{E}}}<1$
The ratio of the collector current ${{I}_{C}}$ to the base current ${{I}_{B}}$ in a transistor is represented by the constant $\beta $. Therefore, mathematically,
$\beta =\dfrac{{{I}_{C}}}{{{I}_{B}}}$ ------(2)
Also, the base current ${{I}_{B}}$ in a transistor is much smaller than both the emitter current ${{I}_{E}}$ and the collector current ${{I}_{C}}$. Therefore, mathematically, ${{I}_{B}}<{{I}_{C}}$.
Using this relation in (2), it can be concluded that
$\beta =\dfrac{{{I}_{C}}}{{{I}_{B}}}>1$
Therefore, we have found out that $\alpha <1$ and $\beta >1$ for a transistor.
Therefore, the correct option is $D)\text{ }\beta >1;\alpha <1$.
Note: Students should not get confused between the ratios $\alpha $ and $\beta $ of a semiconductor. In fact, the above-obtained result that $\alpha $ is less than one and $\beta $ is greater than one serves as a help to students in recalling the formulae in other problems if they keep in mind that the base current is smaller than the collector current which is in turn smaller than the emitter current in the transistor.
Formula used:
$\alpha =\dfrac{{{I}_{C}}}{{{I}_{E}}}$
$\beta =\dfrac{{{I}_{C}}}{{{I}_{B}}}$
Complete step by step answer:
The ratio of the collector current ${{I}_{C}}$ to the emitter current ${{I}_{E}}$ in a transistor is represented by the constant $\alpha $. Therefore, mathematically,
$\alpha =\dfrac{{{I}_{C}}}{{{I}_{E}}}$ -----(1)
In a transistor, the emitter current ${{I}_{E}}$ is the sum of the base current ${{I}_{B}}$ and the collector current ${{I}_{C}}$.
Therefore, obviously it can be said that ${{I}_{E}}>{{I}_{C}}$. Using this relation in (1), we can say that
$\alpha =\dfrac{{{I}_{C}}}{{{I}_{E}}}<1$
The ratio of the collector current ${{I}_{C}}$ to the base current ${{I}_{B}}$ in a transistor is represented by the constant $\beta $. Therefore, mathematically,
$\beta =\dfrac{{{I}_{C}}}{{{I}_{B}}}$ ------(2)
Also, the base current ${{I}_{B}}$ in a transistor is much smaller than both the emitter current ${{I}_{E}}$ and the collector current ${{I}_{C}}$. Therefore, mathematically, ${{I}_{B}}<{{I}_{C}}$.
Using this relation in (2), it can be concluded that
$\beta =\dfrac{{{I}_{C}}}{{{I}_{B}}}>1$
Therefore, we have found out that $\alpha <1$ and $\beta >1$ for a transistor.
Therefore, the correct option is $D)\text{ }\beta >1;\alpha <1$.

Note: Students should not get confused between the ratios $\alpha $ and $\beta $ of a semiconductor. In fact, the above-obtained result that $\alpha $ is less than one and $\beta $ is greater than one serves as a help to students in recalling the formulae in other problems if they keep in mind that the base current is smaller than the collector current which is in turn smaller than the emitter current in the transistor.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




